Economic Equality
Across the globe there are huge disparities in access to basic services such as healthcare, education, and economic resources, with the UN estimating over 98 million people live on less than $1.90 a day. It is vital for microbial research to identify those areas which actively maintain cycles of poverty and disparity. In recognising the interconnected nature of human financial systems and environmental health, microbial research can be a leader in working toward Economic Equality.
News
From palm oil to designer enzymes: researchers reprogram yeast cells
Many everyday products contain fatty acids from palm oil or coconut oil, but the extraction of these raw materials is associated with massive environmental issues. Researchers have now developed a biotechnological approach that could enable a more environmentally friendly production method.
Read story- News
Commercially viable biomanufacturing: designer yeast turns sugar into lucrative chemical 3-HP
Using a tiny, acid-tolerant yeast, scientists have demonstrated a cost-effective way to produce industial chemical 3-Hydroxypropanoic acid, making disposable diapers, microplastics, and acrylic paint more sustainable through biomanufacturing.
- News
Beyond gene scissors: New CRISPR mechanism discovered
Two studies describe how researchers found a novel CRISPR mechanism, Cas12a2, in a family of nucleases that exclusively cleave DNA. In contrast, Cas12a2 was able to broadly cleave both RNA and DNA.
- News
CRISPR discovery could lead to single diagnostic test for COVID, flu, RSV
Researchers report newly discovered details about the Cas12a3 immune system that precisely targets transfer RNA in invading pathogens, without destroying host cells.
More Economic Equality
News
Researchers eye goal of turning garden and crop waste into plastics
A research team will combine eco-friendly and application-oriented approaches to develop a cost-effective, energy-efficient technology for making innovative plastics based on polybutylene succinate (PBS) which are made entirely out of organic waste.
New database to target chronic UTIs – a long-overlooked condition that may begin in childhood
A new database targeting chronic urinary tract infections (UTIs) – a long-overlooked condition that may begin in childhood – is set to help researchers uncover why millions of women and girls worldwide suffer from infections that defy treatment and stump microbiologists.
A practical guide for characterization of novel CRISPR-Cas systems with Pro-CRISPR factors
In this protocol, the authors provide a method encompassing protein purification, biochemical characterization, validation of protein-protein interactions, and preliminary in vivo functional assays in bacteria for Cas nuclease and its associated Pro-CRISPR factor.
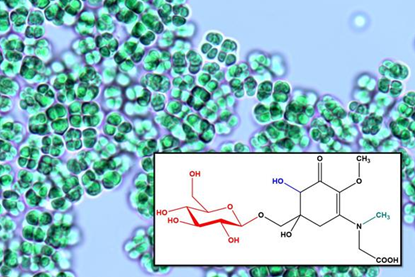
A new natural sunscreen: novel compound discovered from thermophilic cyanobacteria
Natural sunscreens shield the skin from harmful radiation, without triggering allergic reactions. Researchers have discovered a novel compound, β-glucose-bound hydroxy mycosporine-sarcosine, which is produced in thermal cyanobacteria under UV-A/UV-B and salt stress.
Scientists reveal how excess hydrogen triggers metabolic shifts and viral defense in syngas microbiomes
Syngas biomethanation—converting CO/CO₂/H₂ into renewable methane—relies on coordinated microbial interactions. A study reveals that excess hydrogen disrupts this balance, reducing methanogenesis efficiency and triggering major shifts in microbial metabolism and viral dynamics.
Rare earth elements: of peptides and the origins of life
Elements from the group of rare earth metals are of great importance today, also in technical applications. Researchers have published two new studies - one examining peptides, which can bind these elements, while the other highlights the potential role of the elements in the origins of life.
Mutated baker’s yeast at the forefront of petroleum substitute tech
Researchers engineering Saccharomyces cerevisiae to produce 2,3-butanediol (2,3-BDO) introduced mutations into the genomic DNA. The researchers engineered four altered strains and subjected them to ethanol, heat, and low pH stressors.
Bacteria double as Trojan horse for artificial amino acids
Researchers have hijacked a natural transport system of the bacterium E. coli to develop a solution that allows artificial amino acids to be introduced into bacteria efficiently. This means the “amino acid toolbox” can be expanded for widespread use in medicine and the biotech industry.
AFYREN and ESSE Skincare begin partnership to offer 100% natural cosmetic solutions with enhanced skincare performance
AFYREN, a greentech company offering manufacturers biobased, low-carbon ingredients through a unique fermentation technology, and South Africa-based Esse Skincare, a leader in microbiome skincare science, are partnering to introduce the world’s first bio-based propionic acid for the skincare industry.
Algae show how to make two proteins from one messenger RNA
Scientists have uncovered a hidden feature of protein translation in green algae, offering a new perspective on the basic rules of gene expression.
Study links childhood vaccination to lower risk of drug-resistant bacteria
Children in Guatemala who received a common vaccine that helps prevent pneumonia were less likely to carry antibiotic-resistant bacteria, according to a new study examining whether rotavirus (RV) and pneumococcal (PCV13) vaccines reduce gut colonization by a group of bacteria.
‘Creeping catastrophe’: Climate change is driving global rise in infectious diseases, leading health experts warn
Infectious diseases such as malaria, dengue, and tuberculosis are considered to pose as great a challenge to global health as new or emerging pathogens, according to a study. Participants reported that climate change, poverty, and drug resistance are combining to create an escalating health crisis.
Horizon Awards 2025: Max Fisher named as individual winner of Dorothy Jones Award
Max Fisher, a leading Disability & LGBTQIA+ Advocate, and Senior Research Associate at ViaNautis Bio, has been named as individual winner of the Dorothy Jones Diversity & Inclusion Achievement Award 2025.
Point-of-care rapid tests can improve screening for latent tuberculosis
A new test shows promising results for detecting latent tuberculosis infection in resource-limited settings. Latent tuberculosis is often diagnosed using a laboratory test called QuantiFERON-TB Gold Plus - this was compared with another test, TB-Feron.
New prevention tools and investment in services essential in the fight against AIDS
On World AIDS Day, the World Health Organization (WHO) calls on governments and partners to rapidly expand access to new WHO-approved tools including lenacapavir (LEN) to drive down infections and counter disruption to essential health services caused by cuts to foreign aid.
New guideline on pre-exposure and postexposure HIV prevention
Multiple pre-exposure (PrEP) and postexposure (PEP) treatments are now available to prevent HIV infection. An updated Canadian guideline contains 31 recommendations and 10 good practice statements to help clinicians and other health care professionals offer these options to patients.
Fractional-dose vaccines can save millions during shortages
New research shows that using smaller, fractional doses of vaccines can significantly reduce infections during epidemics, especially when vaccine supply, delivery, or administration capacity is limited.
Research into zoonotic disease risks requires a One Health approach
A new evidence brief, based on a study by the Juno Evidence Alliance conducted in collaboration with CABI’s One Health Hub, has highlighted that a One Health approach is needed in research into zoonotic disease risks around the world.
We couldn’t get people interested in science - until we started speaking their language
In 2020, Puerto Rico faced a misinformation crisis. Melanie Ortiz Alvarez De La Campa reveals how five STEM undergraduates created a sci-comm organization that helped pass legislation, educated thousands, and created an inclusive database of Caribbean scientists.