Food security
Millions of people are undernourished globally and with the population growing, food security is a major concern. Food security is multifaceted, requiring advancements in food safety, ensuring products have a good shelf life, reducing spoilage and providing dietary additions to improve the nutrient intake of the population. The application of microbiology is far reaching, and new approaches are required to maintain food security. Through an improved understanding of plant-microbe interactions, it is possible to forecast and mitigate food shortages.
News
Everyday foods could hide fungal risks for mothers and children
A collaborative, multi-institutional project will examine how exposure to zearalenone – a mycoestrogen produced by mold with estrogen-like activity – may affect pregnancy outcomes and children’s growth.
Read story- News
Scientists trace crop viruses back to the last Ice Age
Long before humans cultivated crops or sailed between continents, a group of plant viruses was already evolving among wild plants in Eurasia. Tthe ancestors of modern tymoviruses likely emerged before the last Ice Age, a new study reveals.
- News
Soybeans recruit beneficial soil microbes to defend against major pest
Researchers report that resistant soybean varieties actively recruit beneficial soil microorganisms that help suppress soybean cyst nematode. Even more striking, those protective microbes can be transferred to soil to help defend susceptible soybean plants.
- News
Scientists successfully harvest chickpeas from ‘moon dirt’
Scientists have successfully grown and harvested chickpeas using simulated “moon dirt,” the first instance of this crop produced in this medium. They added vermicompost and coated the chickpeas with the fungi arbuscular mycorrhizae before planting.
More food security
News
New study reveals how hygienic honey bees show unique advantages in fighting infectious pathogens in adult bees
For the first time, research shows that a key social trait in honey bees is linked to measurable physiological advantages that can improve colony survival. The study uncovers how hygienic honey bee colonies mount stronger individual immune defenses against Nosema ceranae.
- News
Pig farm ammonia pollution may indirectly accelerate climate warming, new study finds
A new study shows that ammonia released from intensive livestock farms can significantly increase nearby soil emissions of nitrous oxide, a powerful greenhouse gas that contributes to climate change and ozone depletion.
- News
Nitrous oxide, a product of fertilizer use, may harm some soil bacteria
While some nitrous oxide is produced naturally at the plant root, agricultural practices can increase its levels. While it has long been believed that nitrous oxide doesn’t meaningfully interact with living organisms, a new paper shows that it may in fact shape microbial communities.
- News
Editing for timing, not overdrive: A new genetic route to fire blight resistance in apple
Fire blight remains one of the most destructive bacterial diseases threatening global apple production. A new study identifies a family of inducible lectin genes, MdAGGs, as critical components of apple immune defense and demonstrates that their precise activation timing is key to effective resistance.
- News
Periphyton closes the nitrogen budget gap in rice paddies
Scientists identify a previously overlooked microbial N sink in rice paddies. Periphyton, a thin microbial community that develops at the soil–water interface, is composed of algae, bacteria, and extracellular polymeric substances, forming a dense microhabitat with strong capacities for nutrient uptake, transformation, and temporary storage.
- News
Epigenetic rewiring fuels potato susceptibility to late blight
Scientists performed whole-genome bisulfite sequencing and RNA sequencing on the widely cultivated potato cultivar Qingshu No.9 following Phytophthora infestans infection, uncovering dynamic DNA methylation shifts that correlate with large-scale transcriptional reprogramming and immune suppression.
- News
World’s first rum brewed with high ginjo-aroma–producing fission yeast Schizosaccharomyces japonicusponicus
Researchers at Kumamoto University have announced the world’s first rum produced using the fission yeast Schizosaccharomyces japonicus, marking a breakthrough in fermentation science and craft spirits innovation. The new product, “JAPONICUS RHUM AGRICOLE,” goes on sale February 27, 2026.
- News
Fungi could transform leftovers into lifelines
A new paper outlines an ’emerging circular fungal biorefinery’ – a system in which low-value agricultural byproducts are converted through fungal fermentation into high-protein, nutrient-rich foods.
- News
Nanoplastics can interact with Salmonella to affect food safety, study shows
Researchers investigating what happens when nanoplastics (polystyrene) interact with Salmonella discovered an increased expression of virulence-related genes. The bacteria also formed thicker biofilms, which indicates they are becoming more virulent.
- News
Under the Lens: Nicola Holden and Gil Domingue weigh in on the raw milk debate
The latest episode of Applied Microbiology International’s ‘Under The Lens’ video series turns the spotlight on the contentious issue of raw milk, with AMI Trustee Professor Emmanuel Adukwu interviewing Professor Nicola Holden and Dr Gil Domingue.
- News
The new ‘forever’ contaminant? Study raises alarm on marine fiberglass pollution
Researchers investigating fibreglass contamination of an estuary looked at the biofilm and the deeper sediment layer where sediment‑dwelling invertebrates live and feed. They found fibreglass particles at several of the surface biofilm testing sites and 96 per cent of the sediment testing sites.
- News
Applied Microbiology International launches new report on improving soil health in the UK
Scientists have warned that the world’s tiniest organisms need to be taken into account in efforts to improve soil health. AMI has launched a new policy report setting out key recommendations to support the long-term protection, restoration and sustainable management of soils across the UK’s four nations.
- News
Novel structural insights into Phytophthora effectors challenge long-held assumptions in plant pathology
How do evolutionarily conserved pathogen effectors maintain structural stability while engaging diverse host targets? In a new study, researchers define a conserved subset of Phytophthora RxLR effectors in which short linear motifs (SLiMs) are embedded within folded WY domain cores.
- News
How citrus rewires its vascular system to fight Huanglongbing
By profiling thousands of individual cells, researchers mapped how different vascular cell types in citrus roots respond during early stages of infection with Candidatus Liberibacter asiaticus, revealing profound changes in cell fate, gene expression, and tissue differentiation.
- News
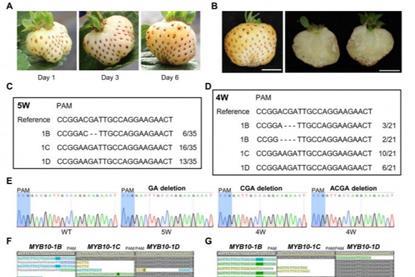
A single gene, a dramatic change: CRISPR unlocks white strawberries
Researchers used CRISPR/Cas9 to selectively edit a single dominant gene copy controlling fruit color in the commercial octoploid strawberry cultivar ‘Florida Brilliance’. By targeting the MYB10-1B gene, they successfully converted red strawberries into stable white-fruited plants.
- News
Breadcrumbs lead to fossil free production of everyday goods
The humble breadcrumb could hold the key to cutting out fossil fuels from one of the chemical industry’s most widely used reactions. Scientists have found a one-pot microbial formula that uses waste bread to replace fossil fuel-derived hydrogen in hydrogenation.
- News
Research teams will develop automated compost monitoring system
Composting turns organic waste into nutrient-rich material, but improper temperature and moisture control can allow pathogens to survive and increase safety risks. Researchers have received a $362,000 grant to develop an automated sensor network to improve monitoring of compost piles.
- News
Healthier, tastier kelp: food scientists boost nutrition and flavour of kombu
A team of food scientists has found a way to unlock the trapped nutrients in the edible seaweed, kombu, and replace the strong odours with more appealing scents, directly overcoming the two major challenges – limited nutrient bioaccessibility and poor sensory experience.
- News
Hope for global banana farming in genetic discovery
Scientists have pinpointed crucial genetic resistance to fight a fungal disease which threatens the global banana supply in a wild subspecies of the fruit. The team have identified the genomic region that controls resistance to Fusarium wilt Sub Tropical Race 4 (STR4).