This study is led by Dr. Changjun Huang (Key Laboratory of Tobacco Biotechnological Breeding, Yunnan Academy of Tobacco Agricultural Sciences, Kunming, China).
The authors report that field disease surveys conducted from 2016 to 2019 across 13 major tobacco-producing counties in Yunnan revealed that resistant varieties carrying the va locus (lacking the eIF4E1-S susceptibility gene) significantly reduced Potato virus Y (PVY) incidence and yield loss. However, prolonged cultivation of va-resistant varieties has led to the emergence of resistance-breaking (RB) PVY isolates.
READ MORE: Chiral phytovirucide targets viral Nia protein to inhibit proliferation
READ MORE: Researchers find new defense against hard-to-treat plant diseases
Additionally, the surveys highlighted Tobacco vein banding mosaic virus (TVBMV) and Chilli veinal mottle virus (ChiVMV) as major emerging pathogens in Yunnan, with co-infections observed in some samples, raising concerns about potential viral recombination and resistance breaking of va mediated resistance . These findings underscore the urgent need to develop crops with durable and broad-spectrum resistance.
Single mutation
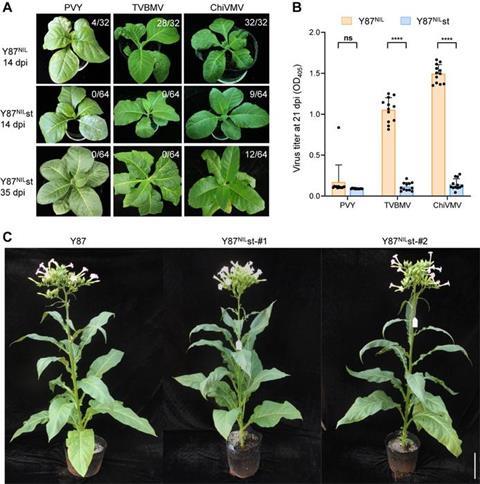
Sequence analysis and infectious clone validation identified a single amino acid mutation (K105Q) in the VPg protein of PVY RB strains. Yeast two-hybrid and bimolecular fluorescence complementation (BiFC) assays confirmed that eIFiso4E-T serves as a second essential host factor for PVY RB infection. Using CRISPR-Cas9, the team designed sgRNAs targeting conserved regions of eIFiso4E-T and eIFiso4E-S to generate gene-edited mutants in both wild-type and va tobacco backgrounds. Infection assays with PVY, PVY RB, TVBMV, and ChiVMV demonstrated that eIFiso4E-T is critical for PVY RB to overcome va resistance. Introducing eifiso4e-t mutations into the va background established durable PVY resistance. Furthermore, plants with dual eifiso4e-s and va mutations exhibited broad-spectrum resistance to TVBMV and reduced susceptibility to ChiVMV.
Finally, stacking eifiso4e-t and eifiso4e-s mutations in the va background produced triple mutants with robust, broad-spectrum resistance to PVY and TVBMV, while maintaining resistance to ChiVMV. Importantly, these triple mutants displayed no adverse effects on plant development under greenhouse conditions, highlighting their potential for engineering crops with durable, multi-virus resistance.





No comments yet