Young Innovators & Early Career Research
Early career research is crucial for science, and in delivering applied microbiology to the world. This page is focused on showcasing innovations and research from early career researchers across the globe and provides a hub for the latest news, opinions, careers advice and research for early career scientists. Discover how interdisciplinary colleagues from around the world are making advancements in, and through, applied microbiology.
News
Herpes virus fluidizes cell nuclei to multiply faster
A new study finds that herpes simplex virus uses a protein called infected cell protein 4 (ICP4) to make the human nucleus more fluid-like, which in turn makes it easier for the virus to replicate itself. Blocking the ability of ICP4 to fluidize the nuclear compartment caused a drop in viral copy production.
Read story- News
How viruses mess with our brains
What impact does a viral infection have on our memory, attention, and concentration? A new review has identified several biological markers associated with cognitive decline in the context of infection. It also provides a solid foundation for future research.
- News
Bacteria found in mouth and gut may help protect against severe peanut allergic reactions
One of the big mysteries in food allergy is why two people with similar levels of peanut specific antibodies can react so differently. A new study shows for the first time how gut bacteria break down parts of an allergenic food and influence how a person reacts to peanuts.
- News
Fecal transplants from older mice significantly improve ovarian function and fertility in younger mice
A new study details how fecal transplants from older female mice significantly improve ovarian function and fertility in young mice. The surprising results reveal a direct link between the microbiome of the gut and ovarian health and function.
More Early Career Research
News
Ultrasound-activated ‘nanoagents’ kill superbugs hiding in biofilms
Scientists have designed nanoagents that act like smart drug‑delivery capsules – carrying an antibiotic deep into bacterial infection sites and releasing it only when activated by gentle ultrasound.
- News
Fungi could transform leftovers into lifelines
A new paper outlines an ’emerging circular fungal biorefinery’ – a system in which low-value agricultural byproducts are converted through fungal fermentation into high-protein, nutrient-rich foods.
- News
Nanoplastics can interact with Salmonella to affect food safety, study shows
Researchers investigating what happens when nanoplastics (polystyrene) interact with Salmonella discovered an increased expression of virulence-related genes. The bacteria also formed thicker biofilms, which indicates they are becoming more virulent.
- News
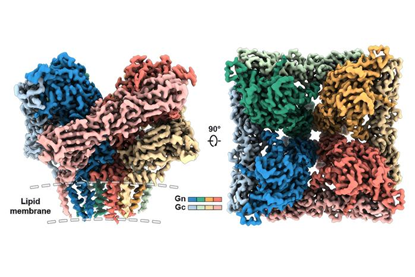
Imaging technique is step towards needed treatments for hantaviruses in new molecular ma
Researchers have produced a detailed blueprint, the highest resolution yet, for a protein complex the Andes virus uses to infect host cells. The new detailed structural information enabled the researchers to produce a vaccine candidate that caused mice to produce neutralizing antibodies against the Andes virus.
- News
Source or sink? Trees with heart rot disease emit more methane, upending forest carbon models
New research suggests that upland forests harboring trees with a common and incurable fungal disease known as heart rot could actually be emitting more methane than they take in, therefore releasing more greenhouse gases than previously thought.
- News
Scientists uncover mechanism used by three bacteria-killing viruses to target transporter
Biochemists have homed in on an underexplored small transporter called MurJ that is a vital part of the pathway bacteria use to build their chain-mail-like cell wall. Using advanced tools, the scientists have determined the common mechanism used by three different bacteria-killing viruses to block MurJ from doing its job.
- News
COVID-19 infection predicts higher risk of kidney disease, study finds
Researchers have found that previous COVID-19 infection is a significant risk factor for kidney disease. Compared to influenza, those with a history of COVID-19 infection have a 2.3-times higher risk of acute kidney injury and a 1.4-times higher risk of chronic kidney disease, according to an analysis of over three million patients.
- News
Emerging class of antibiotics to tackle global tuberculosis crisis
Researchers investigated how three naturally occurring antibiotic compounds – ecumicin, ilamycin and cyclomarin – act on a vital protein degradation machine inside Mycobacterium tuberculosis, the bacterium that causes TB.
- News
Study finds no evidence of persistent tick-borne infection in people who link chronic illness to ticks
When researchers studied Norwegians who thought tick bites caused their chronic health problems, they found no objective evidence linking the symptoms to ticks. The same study finds that health problems reported by participants were associated with little physical activity and low labour force participation.
- News
Studying yeast in the gut could lead to new, better drugs
A new study sheds light on the behavior of yeast cells in the gut, paving the way for new lines of yeast that more efficiently produce therapeutic drugs tailored to address specific diseases.
- News
Three women named Britain’s Brightest Young Scientists, each winning ‘unrestricted’ £100,000 Blavatnik Awards prize
The Blavatnik Family Foundation and The New York Academy of Sciences has announced the three 2026 Laureates of the Blavatnik Awards for Young Scientists in the United Kingdom, who each receive £100,000 – the nation’s largest unrestricted prize for science.
- News
New strategies aim at HIV’s last strongholds
A new study has overcome a long-standing challenge—how to isolate and study elusive HIV-infected cells called authentic reservoir clones (ARCs) that evade the immune system, making the disease difficult to cure.
- News
Scientists unlock magnetic secrets of bacteria with built-in compass
Some bacteria are miniature masters of navigation: A built-in “compass” made of magnetic nanoparticles helps them to reliably find the optimal habitat. Researchers have now unlocked the magnetic properties of individual bacteria — an important step toward harnessing the potential for technology.
- News
Healthier, tastier kelp: food scientists boost nutrition and flavour of kombu
A team of food scientists has found a way to unlock the trapped nutrients in the edible seaweed, kombu, and replace the strong odours with more appealing scents, directly overcoming the two major challenges – limited nutrient bioaccessibility and poor sensory experience.
- News
First evidence of fungal pathogen becoming more deadly when co-infected with tuberculosis
Co-infection of Mycobacterium tuberculosis, together with Cryptococcus neoformans, is a grave public health concern, increasing the risk of death significantly. Researchers have found that in the presence of Mycobacteria, the fungus changed its cell density, cell diversity, and capsule size.
- News
Biocodex Microbiota Foundation announces open call for projects for $50,000 2026 USA Microbiome Research Grant
The Biocodex Microbiota Foundation, an independent organization founded by Biocodex, has opened applications for its 2026 USA research grant. The $50,000 grant will be awarded to a U.S.-based investigator studying the gut microbiota and its relationship to human health and disease.
- News
Holy Grail: One vaccine may provide broad protection against many respiratory infections and allergens
In a new study in mice, researchers have developed a universal vaccine formula that protects against a wide range of respiratory viruses, bacteria and even allergens.
- News
New review points to faster, safer vaccine development
A new review examines viral mimic systems that reproduce key features of dangerous pathogens such as SARS-CoV-2, the virus that causes Covid-19, without the ability to replicate or cause disease. These systems allow researchers to study infection safely, quickly, and in a wider range of laboratories.
- News
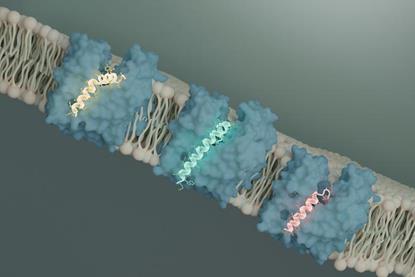
Researchers discover how tuberculosis bacteria use a “stealth” mechanism to evade the immune system
New research reveals that mycobacteria release tiny packages called extracellular vesicles that fuse with the membranes of immune cells. These vesicles contain specialized lipids—fatty molecules—that make the cell membrane more rigid.