Latest news
Corpses leave microbial fingerprints behind in the soil long after they’re gone
Researchers have found that trace elements of a cadaver linger at an original dump site even after an extensive amount of time. These elements can provide insights into postmortem processes, helping forensic investigators uncover clandestine burials and relocate the remains of murder victims.
Trial finds vitamin D supplements don’t reduce Covid severity but could reduce long COVID risk
In a large, randomized trial, researchers have found that high-dose vitamin D3 did not reduce COVID-19 infection severity, but may impact long COVID outcomes.
Mothers' exposure to microbes protect their newborn babies against infection
A study dives into new depths to explore why only some babies develop severe infection to common bacteria. The research revealed that the babies that became most severely ill from E. coli infections also had markedly lower levels of germ-fighting antibodies transferred from their mothers.
Still standing but mostly dead: Recovery of dying coral reef in Moorea stalls
In 2019, a marine heat wave struck a coral reef on the island of Moorea in French Polynesia, killing much of the coral and the beneficial algae that colonized it. A long-term study of the area is challenging scientists’ understanding of the cycles of destruction and repair that can occur on a coral reef.
Medicinal plants with anti-entamoeba histolytica activity: phytochemistry, efficacy, and clinical potential
Reported adverse effects associated with the current first-line treatment for amoebiasis, coupled with the evolution of resistance to it, call for the need to search for plant-based alternatives. This study systematically reviews medicinal plants with activity against Entamoeba histolytica.
Scientists reveal how deadly Marburg virus enters human cells, identify therapeutic vulnerability
Researchers found that the Marburg virus, one of the world’s deadliest pathogens, is unusually efficient at getting inside human cells. They also showed that the virus’s entry protein contains structural features that explain this efficiency and point to a strategy for blocking infection.
Corpses leave microbial fingerprints behind in the soil long after they’re gone
Researchers have found that trace elements of a cadaver linger at an original dump site even after an extensive amount of time. These elements can provide insights into postmortem processes, helping forensic investigators uncover clandestine burials and relocate the remains of murder victims.
Trial finds vitamin D supplements don’t reduce Covid severity but could reduce long COVID risk
In a large, randomized trial, researchers have found that high-dose vitamin D3 did not reduce COVID-19 infection severity, but may impact long COVID outcomes.
Mothers' exposure to microbes protect their newborn babies against infection
A study dives into new depths to explore why only some babies develop severe infection to common bacteria. The research revealed that the babies that became most severely ill from E. coli infections also had markedly lower levels of germ-fighting antibodies transferred from their mothers.
EnteroBiotix announces completion of enrolment in Phase 2a Trial evaluating EBX-102-02 prior to allogeneic stem cell transplantation
EnteroBiotix announced that the investigator-initiated Phase 2a MAST trial has completed its enrolment of 50 adult patients undergoing allogeneic haematopoietic stem cell transplantation (allo-HSCT) for defined haematological malignancies.
Thermo Fisher Scientific launches new color-based culture media to help detect Candida infections faster
Thermo Fisher Scientific today announced the launch of Thermo Scientific™ Brilliance™ Candida 2 Agar and Spectra™ Candida Agar, new color-based (chromogenic) culture media to help laboratories quickly detect and differentiate clinically important Candida species.
Acoziborole Winthrop receives European Medicines Agency positive opinion as three-tablet, single-dose treatment for most common form of sleeping sickness
The European Medicines Agency has granted a positive opinion to Acoziborole Winthrop (acoziborole) as a single-dose oral treatment for both early- and advanced-stage gambiense sleeping sickness in adults as well as in adolescents 12 years and older weighing at least 40 kilograms.
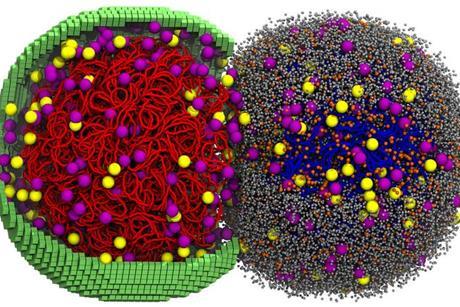
Team simulates a living cell that grows and divides
By simulating the life cycle of a minimal bacterial cell — from DNA replication to protein translation to metabolism and cell division — scientists have opened a new frontier of computer vision into the essential processes of life.
‘Bugs delivering drugs’ – new approach to colorectal cancer treatment using common food-borne bacteria
Researchers have published a novel approach to fight colorectal cancer, using modified bacteria as a courier to deliver potent cancer-killing proteins into tumor cells.
Mpox immune test validated during Rwandan outbreak
An antibody test for the infectious disease Mpox was successfully developed during the new clade 1b outbreak in Rwanda, the first time that an assay of its kind has been validated within this setting.
Everyday foods could hide fungal risks for mothers and children
A collaborative, multi-institutional project will examine how exposure to zearalenone – a mycoestrogen produced by mold with estrogen-like activity – may affect pregnancy outcomes and children’s growth.
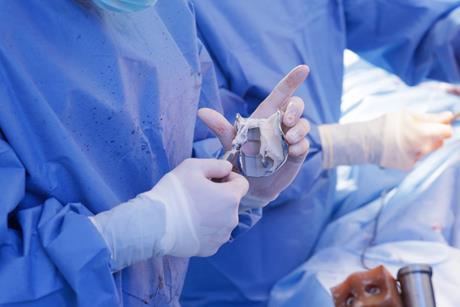
Webinar: Unraveling periprosthetic joint infection
The free ‘Unraveling Periprosthetic Joint Infection’ webinar on March 25 explores one of the most challenging complications in modern orthopedic medicine, sitting at the intersection of microbiology, surgery, and patient care.
Webinar: How to communicate your science to UK policymakers
Sign up for our free webinar - part of the Sustainable Microbiology Policy Spotlight journal webinar series - that will explore how microbiologists can most effectively influence policy in the UK, with insights that apply to the international policymaking context.