All Duke University articles
-
 News
News'Know-do gap' drives inappropriate antibiotic overprescribing for child diarrhea in India
Researchers report that the persistent “know-do gap” — where clinicians know guidelines but practice differently — is the primary driver of antibiotic overprescribing for pediatric diarrhea in India’s private sector.
-
 News
NewsTwo-dose therapy for S. aureus bloodstream infections on par with standard treatment
A clinical trial has found that the outcome of treating complicated Staphylococcus aureus bloodstream infections with two intravenous (IV) doses of the antibiotic dalbavancin seven days apart is just as good as daily IV doses of conventional antibiotics over four to six weeks.
-
 News
NewsGut microbiome may predict “invisible” chronic fatigue syndrome and long COVID
Millions suffering from myalgic encephalomyelitis/chronic fatigue syndrome (ME/CFS) may be closer to personalized care, according to new research that shows how the disease disrupts interactions between the microbiome, immune system, and metabolism.
-
 News
NewsNewly discovered ‘sixth sense’ links gut microbes to the brain in real time
Researchers have uncovered what they call a “neurobiotic sense,” a newly identified system that lets the brain respond in real time to signals from microbes in our gut. Tiny sensor cells lining the colon’s epithelium detect a microbial protein and send rapid messages to the brain.
-
 News
NewsNew study reveals how corals teach their offspring to beat the heat
A new study shows that rice coral, an important reef-building species, passes on thermal resistance to their offspring and avoids coral bleaching. Understanding this is important to building healthier coral reefs and protecting their future.
-
 News
NewsNew AI reimagines infectious disease forecasting
A new AI tool to predict the spread of infectious disease outperforms existing state-of-the-art forecasting methods. The tool could revolutionize how public health officials predict, track and manage outbreaks of infectious diseases including flu and COVID-19.
-
 News
NewsHantavirus in Madagascar linked to black rats in agricultural areas
A new study reveals that the black rat is likely responsible for transmitting deadly hantaviruses in rural Madagascar, where forested landscapes have been converted to agriculture and settlements.
-
 News
NewsNew CRISPRs expand upon the original’s abilities
By scouring through a massive bacterial metagenomic databases, researchers have discovered new CRISPR-Cas systems as efficient as the conventional one. One of the candidate system has found with the technological potential to expand its impact in research, biotechnology and medicine.
-
 News
NewsResearchers engineer biological reaction crucibles to rapidly produce proteins
Biomedical engineers have demonstrated a new synthetic approach that turbocharges bacteria into producing more of a specific protein, even proteins that would normally destroy them, such as antibiotics.
-
 News
NewsFirst-of-its-kind national trial exploring potential of antibiotics for lowering c-section rates in women with obesity
A multicenter national clinical trial will study whether antibiotics given at the beginning of labor induction result in a decrease in C-sections. The trial is thought to be the first large-scale study of its kind in the United States.
-
 News
NewsSelfishness mechanism points way to optimizing inhibitors that fight antibiotic resistance
Resistance can be fought by targeting bacteria that are ’selfish’ with their antibiotic resistance tools, according to a new study.
-
 News
NewsPlant prebiotics offer new ally in the fight against pathogens
Disruptions to the community of microbes that live inside the leaves of a spindly plant called <i>Arabidopsis</i> can compromise a plant’s ability to tell harmless invaders from harmful ones – effectively turning the plant’s defensive arsenal against itself.
-
 News
NewsIncreased ventilation not effective in reducing influenza virus spread in play-based model
Increasing ventilation in child-care settings may not always be effective at preventing flu virus spread, according to a new study.
-
 News
NewsKeto diet boosts lifesaving antifungal drug in mice
In animal tests, researchers have found that taking fluconazole in combination with a low-carb, high-fat keto diet worked significantly better at killing the fungus behind fungal meningitis than taking the medication alone.
-
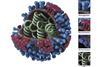 News
NewsNew strategy could lead to universal, long-lasting flu shot
Researchers have opened a new avenue in the attack against influenza viruses by creating a vaccine that encourages the immune system to target a portion of the virus surface that is less variable.
-
 News
NewsClimate change alters the hidden microbial food web in peatlands
A study of protists shows that a neglected part of the peatlands’ microbial food web is sensitive to climate change, and in ways that are currently not accounted for in models that predict future warming.
-
 News
NewsIndustrious communities can create cheaters, even in bacteria
These colorful patterns are proof that bacteria and humans aren’t all that different — both harbor individuals that will take the easy way out when given the chance. And that lifestyle can quickly spread to the detriment of all.
-
 News
NewsRefrigerate lettuce to reduce risk of E. coli contamination, researchers say
Leafy green vegetables are important sources of dietary fiber and nutrients, but they can harbor harmful pathogens. In particular, lettuce has often been involved in outbreaks of foodborne illness across the U.S. A new study from the University of Illinois Urbana-Champaign examines factors that affect E. coli ...
-
 News
NewsCopies of antibiotic resistance genes greatly elevated in humans and livestock
Biomedical engineers at Duke University have uncovered a key link between the spread of antibiotic resistance genes and the evolution of resistance to new drugs in certain pathogens. The research shows bacteria exposed to higher levels of antibiotics often harbor multiple identical copies of protective antibiotic resistance ...
-
 News
NewsFungi that live in healthy plants are sensitive to climate change
Findings more than a decade in the making reveal a rich diversity of beneficial fungi living in boreal forest trees, with implications for the health of forests.
