More Climate Action – Page 19
-
 News
NewsNew report outlines microbial solutions to mediate methane emissions
A new report highlights recommendations to further the scientific community’s understanding of microbial processes of methane production and consumption to mitigate methane emissions and address climate change.
-
 News
NewsFungi drive ice formation by excreting small proteins
An international team of researchers explored the characteristics and properties of fungal ice nucleators, revealing that they are made up of small protein subunits and play a role in both promoting and inhibiting ice growth.
-
 News
NewsNew way to count microbes speeds research and cuts waste
Researchers have developed a new way of counting microorganisms that works as much as 36 times faster than conventional methods, cuts plastic use and decreases the cost and carbon footprint of biomedical research.
-
 News
NewsiBridge programme proposes alternatives to chemical factories
A computer simulation program “iBridge” has been developed that can put together microbial cell factories quickly and efficiently to produce cosmetics and food additives, and raw materials for nylons.
-
 News
NewsBacteria use organic phosphorus and release methane in the process
Researchers have investigated how bacteria inadvertently release methane in order to obtain phosphorus – with significant effects on atmospheric greenhouse gases.
-
 News
NewsNew algae species rewrites understanding of reef systems
Scientists have identified and officially named four species of algae new to science, challenging previous taxonomical assumptions within the Porolithon genus.
-
 News
NewsNew calcifying phytoplankton species discovered off Bermuda
Researchers’ discovery bolsters the scientific record, indicating the global distribution of a coccolithophore species now formally described as Calciopappus curvus.
-
 News
NewsClimate change is increasing risk of high toxin concentrations in Northern US lakes
As climate change warms the Earth, higher-latitude regions will be at greater risk for toxins produced by algal blooms, with water temperatures of 20 to 25 degrees Celsius at greatest risk for developing dangerous levels of a common algae-produced toxin.
-
 News
NewsDesert bacterium paves way for paint that produces oxygen whilst capturing carbon
‘Green Living Paint’ features Chroococcidiopsis cubana, a bacterium that undergoes photosynthesis to produce oxygen while capturing CO2. This species is usually found in the desert and requires little water for survival.
-
 News
NewsUnique marimo threatened by rising lake temperatures
Rising lake water temperatures threaten the survival of marimo, unique algal balls found only in cold lakes - the warmer it gets, the more the inward decomposition outpaces the outward growth of these life forms, making them increasingly fragile.
-
 News
NewsSunlight-activated biohybrids transform wastewater into valuable chemicals
Researchers have proposed a novel method to transform wastewater contaminants into valuable chemicals using sunlight, thus paving the way for sustainable and eco-friendly chemical manufacturing.
-
 News
NewsResearchers awarded $2m to create carbon-negative ‘living’ construction materials
Researchers are working towards a future when homes and other buildings can be constructed using low-cost, sustainable materials that also can repair themselves and capture carbon dioxide from the atmosphere.
-
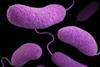 News
NewsFlesh-eating bacteria found in Florida’s coastal waters following Hurricane Ian
When Hurricane Ian struck southwest Florida in September 2022, it unleashed a variety of Vibrio bacteria that can cause illness and death in humans, according to a new study.
-
 News
NewsClimate change coping mechanism discovered in humble algae
One of the building blocks of ocean life can adapt to cope with the effects of climate change, according to new research.
-
 News
NewsEmerging diseases threatening trees around the world are accelerating
A study analyzing more than 900 new disease reports on 284 tree species in 88 countries found that the number of new disease emergences globally is doubling every ~11 years, with pines accumulating the most new diseases.
-
 News
NewsAcid-tolerant yeast engineered to produce valuable organic acid from plants
Researchers have engineered an acid-tolerant yeast to economically produce succinic acid, a key chemical in food, agricultural and pharmaceutical products, savings on money and emissions.
-
 News
NewsSoil bacteria prevail despite drought conditions
Recent research has uncovered the resilience of certain soil microorganisms in the face of increasing drought conditions. While many bacteria become inactive during dry spells, specific groups persist and even thrive.
-
 News
NewsCows and microbes put to work to reduce greenhouse gases
An international team of scientists is recruiting a surprising ally to make a powerful dent in greenhouse gas emissions: the cow. Animal sciences researchers from the University of Illinois Urbana-Champaign are driving a new project to reduce methane production resulting from rumen fermentation in beef and dairy cattle. The 3-year, ...
-
 News
NewsMicrobial enzyme captures CO2 with electricity
Scientists isolate a microbial enzyme and branch it on an electrode to efficiently and unidirectionally convert CO2 to formate.
-
 News
NewsBiological particles play crucial role in Arctic cloud ice formation
A new study reveals a crucial role of biological particles, including pollen, spores, and bacteria, in the formation of ice within Arctic clouds.
