All Pseudomonas aeruginosa articles – Page 2
-
 News
NewsTwo-step method to prevent biofilm regrowth is a SLAM dunk
A new study reports a novel, two-step method to effectively dismantle bacterial biofilms and prevent regrowth.
-
 News
NewsBlood eosinophil count is associated with Pseudomonas aeruginosa infection but not the efficacy of inhaled tobramycin
A study has demonstrated that blood eosinophil counts (BECs) correlate with the disease severity, lung function, exacerbations in bronchiectasis, a chronic airway suppurative disease.
-
 News
NewsStudy probes why patients with mitochondrial disease are more susceptible to infections
A new study shows that damaged mitochondria put the immune system in a constant state of alert, leading to dangerous overreactions when patients with rare mitochondrial diseases encounter bacteria.
-
 News
NewsScientists evaluate in-vitro activity of ceftazidime-avibactam against carbapenem-resistant gram-negative bacteria
Scientists explored the in-vitro activity of ceftazidime-avibactam (CAZ-AVI) in clinical isolates of carbapenem-resistant gram-negative bacteria collected at the outpatient, emergency, and inpatient departments of the Indus Hospital, Karachi.
-
 News
NewsThe first case of phage therapy for biliary tract infection caused by superbugs
A new study reports the first clinical application case of personalized phage therapy for biliary tract infection.
-
 News
NewsHidden virus harboured by fruit flies may influence experimental accuracy
A new study suggests the presence of Nora virus in laboratory strains of Drosophila fruit flies influences their resilience to stress and bacterial infection and can confound experimental studies of ageing.
-
 News
NewsA high-fat diet may impair response to infection
A new study in The Journal of Immunology reveals how a high-fat diet may impair the immune system’s ability to respond to infection by impacting the function of neutrophils, one of the first immune cells to respond to bacteria or viruses. The study demonstrated that male mice fed a high-fat ...
-
 News
NewsDamaged but not defeated: Bacteria use nano-spearguns to retaliate against attacks
Scientists used state-of-the-art microscopy technology to mimic a nano-speargun, the type VII secretion system, used as a bacterial pinpoint counterattack tactic in response to cell envelope damage against rival bacteria.
-
 News
NewsStudy uncovers the core principles of low-resistance antibiotics
Researchers have demonstrated that a dual-target approach, combining membrane disruption with an additional critical cellular pathway, significantly prevents the development of resistance in bacteria.
-
 News
NewsSuperbugs in our food: a new hope for tackling drug resistance
Researchers highlight the potential of quorum sensing inhibitors (QSIs) as a novel approach to tackle Pseudomonas aeruginosa. The study explores the mechanisms of action of various QSIs and potential applications in food safety and healthcare.
-
 News
NewsDangerous bacteria lurk in hospital sink drains, despite rigorous cleaning
Even in modern hospitals, drains can serve as reservoirs for known and novel pathogens, according to a new study.
-
 News
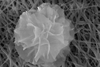
NewsDelicate nanoflower is deadly to bacteria
A carnation-like nanostructure could someday be used in bandages to promote wound healing. Researchers report that laboratory tests of their nanoflower-coated dressings demonstrate antibiotic, anti-inflammatory and biocompatible properties.
-
 News
NewsPapers outline 4 advances for inactivating infectious viruses and bacteria
Four papers provide insights into novel antiviral compounds and methods to inactivate infectious viral particles and bacteria.
-
 News
NewsResearchers identify genetic ‘fingerprint’ to predict drug resistance in bacteria
To avoid antibiotic overuse and allow precise bacterial infection treatment, particularly against bacteria with multidrug resistance, a diagnostic tool was developed that identifies the pattern of DNA repair deficiencies acting as the bacterial antibiotic resistance ‘fingerprint’.
-
 News
NewsCARB-X funds Rhode Island Hospital to assess feasibility of direct from blood detection of bacterial pneumonia
Combating Antibiotic-Resistant Bacteria Biopharmaceutical Accelerator (CARB-X) will award Rhode Island Hospital at Brown University Health US$1M to demonstrate proof-of-concept of a polymerase chain reaction (PCR) approach informed by RNA sequencing to detect bacterial pneumonia directly from whole blood.
-
 News
NewsSophisticated early warning system: How bacteria respond to threats
Recent research has found that exogenous petidoglycan fragments of Vibrio cholerae and other multidrug-resistant pathogens are able to trigger 3D biofilm formation as an universial danger response.
-
 News
NewsOvercoming resistance: McMaster researchers find new utility for old antibiotics
In a recent study, researchers found that zinc plays a vital role in how some of the world’s most dangerous bacteria resist antibiotics.
-
 News
NewsDiverse phage populations coexist on single strains of gut bacteria
A new study shows that a single bacterial species, the host of a phage, can maintain a diverse community of competing phage species. Several phage species coexist stably on a population of a genetically uniform strain of E. coli.
-
 News
NewsHistones show promise against bacterial infections
Scientists have outlined that human histones have antimicrobial activity against different bacteria, including biofilms of Pseudomonas aeruginosa, one of the six most resistant bacteria in the world.
-
 News
NewsA lung pathogen’s dilemma: infect or resist antibiotics?
Research has uncovered how Pseudomonas aeruginosa manages the trade-off between colonizing and surviving during infection by switching between biofilm formation for antibiotic protection and a more mobile, “planktonic” state to spread and access nutrients.
