All University of Cambridge articles
-
 News
NewsNew genomic study reveals key drivers of strangles transmission in UK horses
A novel study has revealed new insights into how the highly contagious disease strangles spreads amongst horses in the UK. It marks a significant step forward in understanding how to more effectively manage and prevent outbreaks of this devastating equine disease.
-
 News
NewsTiny soil microbes turn detective to uncover the timeline of oil spill contamination
Scientists in Belfast and Nigeria have developed a diagnostic tool that deploys microbes to uncover the timeline of crude oil contamination in soils.
-
 News
NewsModel can calculate the often hidden costs of fungicide resistance
An international research team has developed a mathematical model that can be used to calculate the economic and often hidden costs of fungicide resistance. They used a model that can be used to calculate the spread of fungal diseases in several fields.
-
 News
NewsLarge-scale DNA study maps 37,000 years of disease history
A new study maps infectious diseases across millennia and offers new insight into how human-animal interactions permanently transformed our health landscape.
-
 News
NewsStudies probe how novel inhibitors can switch efflux pumps off in TB bacteria
Two new studies aim to both identify and understand how novel inhibitors can switch efflux pumps off in the bacteria Mycobacterium tuberculosis.
-
 News
NewsStrongest hints yet of biological activity outside the solar system
Astronomers have detected the chemical fingerprints of dimethyl sulfide (DMS) and/or dimethyl disulfide (DMDS), in the atmosphere of the exoplanet K2-18b. On Earth, these are only produced by life, primarily microbial life such as marine phytoplankton.
-
 News
NewsCyanobacterium study reveals how circadian clocks maintain robustness in changing environments
New research has uncovered how a simple circadian clock network demonstrates advanced noise-filtering capabilities, enhancing our understanding of how biological circuits maintain accuracy in dynamic natural environments.
-
 News
NewsMulti-virus wastewater surveillance shows promise at smaller, site-specific scales
In a new study, wastewater surveillance for multiple pathogens at five different sites identified local trends that were not captured in larger surveillance programs, and some sites used the data to inform efforts to prevent disease spread.
-
 News
NewsCambridge initiative to address risks of future engineered pandemics
Management strategies are initiated by University of Cambridge to address the challenges and preventive measures required in response to a potential engineered pandemic threat in the future.
-
 News
NewsNew 3D imaging approach reveals intricate steps of virus assembly
A new integrated 3D imaging approach combines cryo-light microscopy and cryo-soft X-ray tomography to reveal the intricate ultrastructure of herpes simplex virus-1 (HSV-1) assembly.
-
 News
NewsFeeding your good gut bacteria through fibre in diet may boost body against infections
Researchers who used computational approaches to analyse the gut microbiome composition of over 12,000 peoplefrom their stool samples found that a person’s microbiome ‘signature’ can predict whether their gut is likely to be colonised by Enterobacteriaceae.
-
 News
NewsSystem to auto-detect new variants will inform better response to future infectious disease outbreaks
Researchers have come up with a new way to identify more infectious variants of viruses or bacteria that start spreading in humans - including those causing flu, COVID, whooping cough and tuberculosis.
-
![pastedGraphic_1[88]](https://d3rmrttq0bsnxi.cloudfront.net/Pictures/100x67/8/0/5/10805_pastedgraphic_188_47193_crop.jpg) News
NewsA team of scientists join forces for the fight against deadly childhood disease
A global consortium of scientists has been tasked with better understanding the scale of Shigella infections and the role of antibiotic resistance in seven countries.
-
 News
NewsBetter together: Gut microbiome communities’ resilience to drugs
Many human medications can directly inhibit the growth and alter the function of the bacteria that constitute our gut microbiome. EMBL Heidelberg researchers have now discovered that this effect is reduced when bacteria form communities.
-
 News
NewsMonoclonal antibodies offer hope for tackling antimicrobial resistance
Monoclonal antibodies – treatments developed by cloning a cell that makes an antibody – could help provide an answer to the growing problem of antimicrobial resistance, say scientists.
-
 News
NewsReport recommends ‘highly ambitious enterprise’ to create world-leading UK Microbiome Biobank
A new report calls for a ’highly ambitious enterprise’ to create a microbiome biobank that will contribute significantly to the advancement of science and its application to human health.
-
 News
NewsIncidence of heart attacks and strokes found to be lower after COVID-19 vaccination
A new study involving nearly the whole adult population of England has found that the incidence of heart attacks and strokes was lower after COVID-19 vaccination than before or without vaccination.
-
 News
NewsNext generation biosensor reveals gibberellin’s critical role in legume nitrogen-fixation
Researchers have identified the specific times and location where gibberellin (GA governs) the initiation, growth and function of nitrogen-fixing root nodules.
-
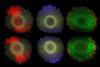 News
NewsScientists ID bacterial genes that yield iridescent colors
Scientists sequenced the DNA of 87 structurally colored bacteria and 30 colorless strains and identified genes that are responsible for iridescent bacterial colonies.
-
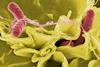 News
NewsAI able to identify drug-resistant typhoid-like infection from microscopy images in matter of hours
Artificial intelligence (AI) could be used to identify drug resistant infections, significantly reducing the time taken for a correct diagnosis, researchers have shown. An algorithm can be trained to identify drug-resistant bacteria correctly from microscopy images alone.
