All Early Career Research Content – Page 24
-
 News
NewsNewly discovered antimicrobial could prevent or treat cholera
Natural antimicrobials called microcins are produced by bacteria in the gut and show promise in fighting infection. A study identifies the first known microcin that targets the strains of bacteria that cause cholera.
-
 News
NewsNew phage editing technology could lead to alternative treatments for antibiotic-resistant bacteria
Scientists have developed a technology that lets them edit the genomes of phages in a streamlined and highly effective way, giving them the ability to engineer new phages and study how the viruses can be used to target specific bacteria.
-
 News
NewsWound peptides can help detect dangerous infections more quickly
After identifying unique peptide patterns and changes in these patterns based on different types of bacteria in wounds, researchers can now assess the severity of the infection, a new study reveals.
-
 News
NewsGame-changing purple bacteria can become bioplastic factories
Two new studies highlight one potential source of game-changing materials: purple bacteria that, with a little encouragement, can act like microscopic factories for bioplastics.
-
 News
NewsResearchers discover key gene regulating virulence of fungus that causes severe lung infections
Scientists have found a potential target for novel therapeutic strategies to combat fungal infections caused by Aspergillus fumigatus and are now looking for a molecule that inactivates the protein expressed by the gene as a basis for a drug.
-
 News
NewsSevere COVID-19 can involve either exacerbated lung inflammation or high viral replication
Researchers report a study based on autopsies of 47 patients who died after being infected by the ancestral strain of SARS-CoV-2. The findings will support clinical decisions on the treatment of critical cases.
-
 News
NewsScientists unlock the secret behind a decades-old dengue mystery
A study has pinpointed a mutation in the dengue virus’ genome as the root cause of a 1970s outbreak of dengue in the South Pacific, which impaired the virus’ ability to replicate in human cells, resulting in a low virus load and asymptomatic infections in patients.
-
 News
NewsWaging war on ‘superbugs’ in aged care
A new study explores the link between the widespread use of antibiotics in residential aged care and the resulting antibiotic resistant bacteria in the gut that can be passed on to other residents
-
 News
NewsNew discovery of how bacteria navigate their environment could change how we treat infection
Scientists have found that bacteria can directly measure differences in chemical concentration across the length of their cell bodies, contrary to decades of established scientific belief.
-
 News
NewsScientists unveil first complete image of the PARIS system
A new study explores the PARIS immune system, which bacteria use to protect themselves against viral infections and which stands for Phage Anti-Restriction Induced System.
-
 News
NewsA human-centered AI tool to improve sepsis management
A proposed artificial intelligence tool to support clinician decision-making about hospital patients at risk for sepsis has an unusual feature: accounting for its lack of certainty and suggesting what data it needs to improve its predictive performance.
-
 News
NewsCreature the size of a dust grain found hiding in California’s Mono Lake
Researchers have now found an unusual creature lurking in the shallows of Mono Lake — a choanoflagellate that could tell scientists about the origin of animals more than 650 million years ago.
-
 News
NewsCRISPR gene scissors switch off with built-in timer
Researchers have discovered a timer integrated into the CRISPR gene scissors that enables the gene scissors to switch themselves off.
-
 News
NewsNew method pinpoints virus that targets Ecuador fruit crop
Scientists in Ecuador have developed a new method to detect and diagnose a virus that devastates crops of babaco, a fruit plant of economic importance to local farmers.
-
 News
NewsScientists uncover how microbial enzymes lap up carbon dioxide
The remarkable affinity of the microbial enzyme iron nitrogenase for the greenhouse gas CO2 makes it useful for future biotechnology, a new study suggests.
-
 News
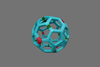
NewsNanoparticle platform offers step toward more effective Covid and HIV vaccines
Researchers have developed a nanoparticle platform that could make existing vaccines more effective, including those for influenza, COVID-19, and HIV.
-
 News
News‘Tiny biome tales’: playing a game to understand the human microbiome
Researchers have developed an interactive computer game that explains how important the microbiome is for our health and how it is influenced by our lifestyle and everyday decisions, such as playing in a sandbox, getting a pet or kissing someone.
-
 News
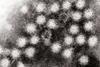
NewsResearch aims to streamline the detection of foodborne viruses
A research team has received a USDA grant to develop rapid, portable, single-tube technology to help maintain safety of the food supply.
-
 News
News3D bioprinting advances research on respiratory viruses
A research team has successfully created artificial lungs, designed to study infections and test drugs for respiratory diseases including COVID-19.
-
 News
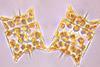
NewsResearchers manufacture bioinks from microalgae for 3D laser printing
An international research team has succeeded for the first time in manufacturing inks for printing complex biocompatible 3D microstructures from the raw materials extracted from microalgae.
