All Harvard University articles
-
 News
NewsHow did Bronze Age plague spread? Ancient sheep might solve the mystery
Researchers have found the first evidence of a Bronze Age plague infection in a non-human host. The scientists discovered Y. pestis DNA in a 4,000-year-old domesticated sheep from Arkaim, a fortified settlement located in the Southern Ural Mountains of present-day Russia.
-
 News
NewsMetabolites produced in the intestine play a central role in controlling obesity and diabetes
A study has identified a group of metabolites that travel from the intestine to the liver and then to the heart, where they are pumped throughout the body. These metabolites play an important role in controlling metabolic pathways in the liver and insulin sensitivity.
-
 News
NewsERC Synergy Grant awarded to physicist Michael Lässig and virologist Florian Klein
Researchers have been awarded a Synergy Grant by the European Research Council (ERC) for the project CoEvolve, which investigates the co-evolution of viruses and the immune system.
-
 News
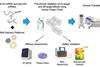
NewsHuman Organ Chip technology sets stage for pan-influenza A CRISPR RNA therapies
Human lung alveolus chip infection model enables investigation of viral replication, inflammatory responses, and genetic off-target effects of a novel pan-influenza CRISPR therapy.
-
 News
NewsMeta-analysis: COVID-19 vaccination during pregnancy is safe and beneficial for mother and infant
Vaccination is associated with better neonatal outcomes without added maternal risk, according to research presented during the American Academy of Pediatrics 2025 National Conference & Exhibition.
-
 News
News4,000-year-old sheep reveals that livestock played a role in prehistoric plague infections
An ancient Yersinia pestis genome recovered from sheep sheds new light on a mysterious infectious disease that plagued prehistoric Eurasia for over 2000 years.
-
 News
NewsBroad-spectrum coronavirus drug developed through AI-enabled dynamic modeling
Multidisciplinary AI- and physics-driven modeling of the viral fusion process enables discovery of an orally available drug inhibiting infection with multiple coronaviruses.
-
 News
NewsStudy indicates that severe forms of COVID-19 infection in children may increase cardiovascular disease risks
Scientists analysed blood samples from 147 children across different COVID-19 conditions and identified significant metabolic disruptions beyond the acute viral infection phase. These alterations affect how the body processes fats (triglycerides and cholesterol) critical to healthy heart structure.
-
 News
NewsScientists track pneumonia-causing bacteria as they infect the blood stream
A new study has shown various dissemination patterns can be adopted by Klebsiella pneumoniae that causes systemic infection, i.e. bacteremia.
-
 News
NewsBiotin may shield brain from manganese-induced damage, study finds
New research showing the mechanisms by which manganese inflicts damage to the central nervous system suggests that the vitamin biotin - synthesized by gut bacteria - may have a protective effect, potentially mitigating manganese-induced damage.
-
 News
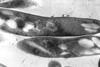
NewsRule-breaking tuberculosis bacteria challenge growth norms
The rod-shaped tuberculosis (TB) bacterium is the first single-celled organism ever observed to maintain a consistent growth rate throughout its life cycle, a new study reports, hinting at why the pathogen so readily outmaneuvers our immune system and antibiotics.
-
 News
NewsClimate change responsible for 19% of today’s rising dengue burden - but Wolbachia offers hope
Climate change is having a massive global impact on dengue transmission, accounting for 19% of the current dengue burden, with a potential to spark an additional 40%-60% spike by 2050 — and by as much as 150%-200% in some areas.
-
 News
NewsMicrobes: atmospheric methane increase during pandemic due primarily to wetland flooding
A new analysis of satellite data finds that the record surge in atmospheric methane emissions from 2020 to 2022 was driven by increased inundation and water storage in wetlands, combined with a slight decrease in atmospheric hydroxide (OH).
-
 News
NewsWyss Institute selected to develop biologically engineered broad-spectrum antimicrobial therapeutic
The Wyss Institute for Biologically Inspired Engineering at Harvard University received a contract for up to $12M from the new SHIELD program which aims to develop a prophylactic treatment that can rapidly clear multiple bloodborne bacterial and fungal pathogens.
-
 News
NewsStudy identifies protein that helps COVID-19 virus evade immune system
Discovery of a new viral evasion mechanism, and of a monoclonal antibody that subverts it, is an advance in immunotherapy that offers the prospect of effective host-directed treatment to combat infections.
-
 News
NewsGenome research reveals the global march of malaria
Researchers have reconstructed ancient Plasmodium genome-wide data from 36 malaria-infected individuals spanning 5,500 years of human history on five continents, reconstructing the worldwide spread of malaria and its historical impact.
-
 News
NewsHuman cervix modeled in microfluidic organ chip helps target bacterial vaginosis
Engineered cervix with in vivo-like mucus production, hormone sensitivity, and associated microbiome creates novel testbed for bacterial vaginosis therapeutics and other treatments.
-
 News
NewsMimicking infection in pregnant mice provokes persistent changes in juvenile brains
No parent wants to risk their child having a serious infection, least of all while still in the womb, but did you know that the immune response to a viral infection during pregnancy could also affect the development of the unborn offspring? Scientists from Harvard University in ...
-
 News
NewsMarine plankton behaviour could predict future marine extinctions, study finds
Marine communities migrated to Antarctica during the Earth’s warmest period in 66 million years long before a mass-extinction event.
-
 News
NewsFermentation may have driven human brain evolution
While some have theorized that the use of fire and the invention of cooking gave our ancestors enough nourishment for our larger-brained ancestors to become dominant, a new theory points to a different spark - fermentation.
