All Johns Hopkins University articles
-
 News
NewsOlder age, chronic kidney disease and cerebrovascular disease linked with increased risk for paralysis and death after West Nile virus infection
Older people with a history of chronic kidney disease or conditions affecting blood flow to the brain such as stroke face about double the risk for developing neuroinvasive disease that can lead to paralysis and death following infection with West Nile virus, new research finds.
-
 News
NewsMalaria parasites move on right-handed helices
After penetrating the skin, the malaria parasite moves with helical trajectories, almost always turning toward the right. Researchers demonstrated that the pathogen uses these right-handed helices to control its motion as it transitions from one tissue compartment to another.
-
 News
NewsGroundbreaking new projects launched to lower the cost of monoclonal antibody production
LifeArc and the Gates Foundation have awarded more than $5m to seven projects aimed at developing cheaper and more efficient ways to produce monoclonal antibody (mAb) treatments. The innovative approaches include using filamentous fungus to produce mAbs.
-
 News
NewsStudy finds COVID-19 mRNA vaccine sparks immune response to fight cancer
Patients with advanced lung or skin cancer who received a COVID-19 mRNA vaccine within 100 days of starting immunotherapy drugs lived significantly longer than those who did not get the vaccine, researchers have found.
-
 News
NewsStealth genetic switch in mosquitoes halts malaria spread
Biologists have created a CRISPR-based gene-editing system that changes a single molecule within mosquitoes, stopping the malaria-parasite transmission process. Genetically altered mosquitoes are still able to bite those with malaria, but the parasites can no longer be spread to other people.
-
 News
NewsMediterranean bacteria may harbor new mosquito solution
Researchers recently identified bacteria in Crete producing metabolites that quickly kill mosquito larvae in lab tests. The compounds might be useful for the development of new biopesticides, though developing the right formulations and delivery method remains a challenge.
-
 News
NewsNew AI reimagines infectious disease forecasting
A new AI tool to predict the spread of infectious disease outperforms existing state-of-the-art forecasting methods. The tool could revolutionize how public health officials predict, track and manage outbreaks of infectious diseases including flu and COVID-19.
-
 News
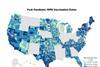
NewsNew data shows MMR vaccination rate decline across US
A new county-level dataset reveals a national decline in the measles-mumps-rubella (MMR) vaccination rate among U.S. children since the start of the COVID-19 pandemic.
-
 News
NewsSARS-CoV-2 corrupts some white blood cells to suppress immune system, suggesting path to severe COVID
A study found that neutrophils may be altered by SARS-CoV-2, the virus that causes COVID-19, to cease their normal function of destroying pathogens in the body and, instead, significantly inhibit other immune cells critical for fighting the virus.
-
 News
NewsNovel antibiotic BTZ-043 also reaches tuberculosis bacteria hiding in dead lung tissue
Researchers have shown that the novel antibiotic BTZ-043 effectively penetrates tubercolous lesions and accumulates there in high concentrations. Consequently, the drug can fight Mtb bacteria even in hard-to-reach areas.
-
 News
NewsCould we engineer stability in the microbiome? New research opens the door
New work could revolutionize our understanding of how the composition of the gut microbiome is determined and open the door to microbiome engineering.
-
 News
NewsStudy untangles how COVID-19 wreaks widespread damage in the body
A new study sheds light on the pathways that drive organ damage and death in severe COVID-19 and helps explain why survivors of the disease can experience long-term complications.
-
 News
NewsGlobal antibiotic consumption has increased by more than 21 percent since 2016
An analysis of antibiotic sales data from 67 countries from 2016-2023 shows a decrease in consumption in high-income countries countered by an increase in middle-income countries.
-
 News
NewsExtreme microbe reveals how life’s building blocks adapt to high pressure
An AI tool has helped scientists discover how the proteins of a heat-loving microbe respond to the crushing conditions of the planet’s deepest ocean trenches, offering new insights into how building blocks of life might have evolved under early Earth conditions.
-
 News
NewsRecreational tubing and swimming leave microbial impact on streams
Researchers found that swimming and tubing on a Colorado creek over a busy Labor Day weekend can have a short-term effect, increasing the levels of metals, human gut-associated microbes and substances from personal care products.
-
 News
NewsLong Covid continues to evade diagnosis
A national cohort study of adult US participants with and without prior SARS-CoV-2 infection found that there are no objective tests to accurately diagnose post-acute sequelae of SARS-CoV-2 infection (PASC), also known as Long Covid.
-
 News
NewsScientists probe molecular cause of COVID-19 related diarrhea, revealing potential treatments
Working with human stem cells that form a kind of ’mini intestine-in-a-dish’, scientists say they have found several molecular mechanisms for COVID-19-related diarrhea, suggesting potential ways to control it.
-
 News
NewsFuture enterovirus outbreaks could be exacerbated by climate change
A common set of drivers can explain the timing of outbreaks of both hand, foot and mouth disease and polio, according to a recent study which suggests these summertime outbreaks may hint at implications for climate change.
-
 News
NewsNew lab test to detect persistent HIV strains in Africa may aid search for cure
A multinational team has developed a test that will help measure the persistence of HIV in people affected by viral strains found predominantly in Africa—a vital tool in the search for an HIV cure that will benefit patients around the world.
-
 News
NewsWomen need better treatments for bacterial vaginosis: call
Researchers at the University of Maryland School of Medicine are calling for robust studies for a treatment already used in Europe.
