Latest News in WAAW – Page 39
-
 News
NewsInter-species interactions may stymie antibiotics
A new study suggests that between-species interactions within the gut microbiome may impact the efficacy of antibiotics aimed at treating C. difficile infections.
-
 News
NewsEye drops cause infection long before CDC warning
A patient was diagnosed with a dangerous Pseudomonas aeruginosa eye infection caused by contaminated eye drops, months before the CDC issued warnings against using the product.
-
 News
NewsTobacco plant engineered to act as drug factory
Researchers have engineered a close relative of tobacco, Nicotiana benthamiana, to churn out peptides with antibiotic activity against some of the nastiest pathogens known to medicine.
-
 News
NewsSleep supplement impairs action of gut microbiota
Despite its antioxidant effects and role in regulating sleep cycles, tests show melatonin can worsen inflammation of the intestine and impair the action of gut microbiota.
-
 News
NewsCRISPR-based drug candidate targets the microbiome
Scientists have engineered the first published CRISPR-based candidate for a drug - a combination of phages - that targets E. coli directly and leaves the microbiome intact.
-
 News
NewsWarning as entire ICU contaminated with superbug
Researchers have called for urgent measures to protect hospitals after an entire ICU was contaminated with an outbreak of antibiotic-resistant bacteria.
-
 News
NewsConcerns raised over popular Covid disinfectants
The Covid-19 pandemic has boosted the unnecessary use of antimicrobial chemicals linked to health problems, antimicrobial resistance, and environmental harm, scientists warn.
-
 News
NewsChild IBD risk linked to antibiotics and diet
Children and adolescents face greater risk of inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) when exposed to antibiotics or a Western diet at early ages, or when their family has higher socioeconomic status, according to a study being presented today at Digestive Disease Week® (DDW) 2023. “Pediatric IBD cases are ...
-
 News
NewsAntibiotics should be halted upon incision closure
New guidelines: antibiotics administered before and during surgery should be discontinued immediately after a patient’s incision is closed, according to updated recommendations for preventing surgical site infections.
-
 News
NewsSloth fur may carry antibiotic-producing bacteria
The fur of Costa Rican sloths appears to harbour antibiotic-producing bacteria that may hold a solution to the growing problem of antimicrobial resistance.
-
 News
NewsFungal diseases threaten global food security
Scientists have warned of the “devastating” impact that fungal disease in crops will have on global food supply unless agencies across the world come together to find new ways to combat infection.
-
 News
NewsPreemie infections may come from gut microbiomes
Dangerous bacterial bloodstream infections in premature babies may originate from the infants’ gut microbiomes, according to researchers.
-
 News
NewsRare yeast pathogen causing neonatal outbreaks
Scientists studying the stubborn and dangerous rare yeast pathogen behind two outbreaks in a neonatal intensive care unit in Delhi, India, have found that while infected patients can be treated with antifungal medications, the yeast is remarkably resistant to the strong disinfectant bleach commonly used to sanitize hospital rooms.
-
 News
NewsAntibiotic resistance genes can be carried by clouds
A research team from Université Laval and Université Clermont Auvergne has shown that anbiotic resistance genes can be transported by clouds.
-
 News
NewsPhage delivers double whammy against biofilms
A novel bacteriophage isolated from sewage water not only kills its target bacteria in the Klebsiella oxytoca complex but was unexpectedly found to be capable of disrupting biofilms produced by these bacteria.
-
 News
NewsAntimicrobial foam targets bugs or oil spills
A versatile new foam material could significantly reduce health care-related infections caused by implanted medical devices - or drastically improve cleanup efforts following environmental disasters like oil spills.
-
 News
NewsSystem targets and degrades viral RNA to treat Covid infection
Researchers have developed a system that directly targets and degrades the viral RNA genome, reducing infection in mice. The method could be adapted to fight off many viruses, as well as treat various diseases.
-
 News
NewsGlobal prevalence of H. pylori infection declining
Researchers have found that Helicobacter pylori (H. pylori) infection around the world has been steadily declining over the past four decades, and that the use of antibiotics against it could alter the micro-organisms and the virus community present in the gut.
-
 News
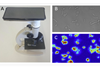
NewsFast and easy method detects antibiotic resistance
Scientists have developed a technique that obtains an antibiogram within 2-4 hours instead of the current 24 hours for the most common germs and one month for tuberculosis.
-
 News
NewsAntimicrobial use in agriculture can breed bacteria resistant to first-line human defences
A new study has shown that overuse of antimicrobials in livestock production can drive the evolution of bacteria more resistant to the first line of the human immune response.
