All malaria articles
-
 News
NewsNew tools saved a million lives from malaria last year but progress under threat as drug resistance rises
Wider use of new tools against malaria, including dual-ingredient nets and WHO-recommended vaccines helped to prevent an estimated 170 million cases and 1 million deaths in 2024, according to WHO’s annual World Malaria Report.
-
 News
News‘Creeping catastrophe’: Climate change is driving global rise in infectious diseases, leading health experts warn
Infectious diseases such as malaria, dengue, and tuberculosis are considered to pose as great a challenge to global health as new or emerging pathogens, according to a study. Participants reported that climate change, poverty, and drug resistance are combining to create an escalating health crisis.
-
 News
NewsResearchers warn: Climate change could expand habitats for malaria mosquitoes
A new study shows that future climate change could create more favourable conditions for malaria mosquitoes, exposing millions of people across large parts of Africa to more dangerous mosquito bites.
-
 News
NewsIs malaria messaging working? African biostatisticians have the data
New analysis shows malaria messaging works. Using advanced causal methods, researchers found that exposure to prevention messages increases insecticide-treated net use among women and children in Uganda, offering rare causal evidence to guide policy.
-
 News
NewsMalaria parasites move on right-handed helices
After penetrating the skin, the malaria parasite moves with helical trajectories, almost always turning toward the right. Researchers demonstrated that the pathogen uses these right-handed helices to control its motion as it transitions from one tissue compartment to another.
-
 News
NewsResearchers diagnose disease with a drop of blood, a microscope and AI
Scientists have developed an automated, high-throughput system that relies on imaging droplets of biofluids for disease diagnosis in an attempt to reduce the number of consumables and equipment needed for biomedical testing.
-
 News
NewsAI and citizen science reveal potential first detection of invasive malaria mosquito in Madagascar
Researchers used AI and citizen science to identify what may be the first Anopheles stephensi mosquito ever detected in Madagascar — a species capable of spreading deadly malaria across urban Africa. A single smartphone photo submitted through NASA’s GLOBE Observer app led to the discovery.
-
 News
NewsWarmer Nordic springs double the incidence of avian malaria
A unique long-term study, in which biological samples were collected from the same population of blue tits over a 30-year period, shows that rising spring temperatures have doubled the incidence of avian malaria in southern Sweden.
-
 News
NewsMalaria risk in the Amazon is higher in regions with intermediate forest degradation
Research shows that areas with 50% deforestation near residential areas or fragmented vegetation allow greater contact between mosquitoes and humans. The study helps us understand the link between forest destruction and the spread of the disease.
-
 News
NewsNew compound cuts off protein supply to parasites
There is an urgent need for new active ingredients that are capable of circumventing existing resistances in malaria. Researchers have now identified a new drug candidate, ’Substance 31’, which could enable the development of a new malaria drug.
-
 News
NewsNew insights into malaria could reshape treatment
A sodium pump essential to the malaria parasite’s survival, PfATP4, has emerged as one of the most attractive drug targets. A new study presents the first high-resolution 3D structure of PfATP4 and identifies a previously unknown but essential binding partner.
-
 News
NewsNew monoclonal antibody shows promise for preventing malaria infections
A new early-stage clinical trial has found that a novel monoclonal antibody provided dose-dependent full protection against the malaria parasite with minimal side effects.
-
 News
NewsToxoplasmosis: how the pathogen exploits its own envelope
Researchers have developed a novel imaging technique that allows reliable visualization of the process of endocytosis in Toxoplasma for the first time. The material enters the pathogen through a micropore in its cell membrane.
-
 News
NewsParasite paparazzi take millions of photos of secret malaria proteins
Using millions of microscope images magnified up to 130,000 times, researchers have unraveled the structure of two key proteins in the malaria parasite. With this knowledge, scientists are developing new vaccines that block the transmission of parasites via mosquitoes.
-
 News
NewsTropical diseases: Global health meeting showcases resilience of field under fire
At a moment of monumental challenges for global health, thousands of researchers, clinicians and public health professionals from over 100 countries will gather in Toronto for the 2025 Annual Meeting of the American Society of Tropical Medicine and Hygiene (ASTMH).
-
 News
NewsAcross eight Amazon countries, forests on Indigenous lands reduce spread of 27 diseases
New research finds that municipalities in the Amazon region closest to healthy forests on Indigenous lands face less risk from rising cases of two categories of disease: cardiovascular and respiratory diseases due to forest fires and illnesses.
-
 News
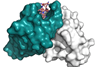
NewsMalaria vaccine mimics natural immunity with high precision
A detailed analysis reveals one of the reasons why the R21/Matrix-M malaria vaccine works so well: the antibodies generated following vaccination are indistinguishable from those found in people who have been infected by the parasites.
-
 News
NewsChemical trick could turn losing malaria drug into a winner
A new generation of malaria drugs failed clinical trials, in part because they were hard to swallow. Chemists have remodeled their structures to make them more soluble, while maintaining their effectiveness against drug-resistant parasites.
-
 News
NewsRevealed: New vaccine target to block malaria transmission
Researchers have visualised a key protein complex in malaria parasites for the first time, uncovering a new target for next-generation vaccines that could help stop the disease from spreading.
-
 News
NewsVaccination could mitigate climate-driven disruptions to malaria control
Tropical cyclones in Madagascar lead to sharp spikes in malaria infections – particularly in children – due to interruptions in control efforts, according to a new study. However, newly introduced long-lasting vaccines can help to mitigate these gaps.
