All McMaster University articles
-
 News
NewsNew antibiotic targets IBD — and AI predicted how it would work before scientists could prove it
The new antibiotic, enterololin, attacks and kills only a specific group of disease-causing bugs, which includes the type of E. coli that drives Crohn’s disease. It is a promising new treatment option for people affected by Crohn’s and other IBD-related conditions.
-
 News
NewsResearchers discover all-new antifungal drug candidate in university greenhouse
A research team at McMaster University has discovered a new drug class that could someday lead to breakthrough treatments for dangerous fungal infections. The new molecules, dubbed coniotins, were isolated from a plant-dwelling fungus called Coniochaeta hoffmannii — the samples of which were collected from the McMaster ...
-
 News
NewsTrapping gut bacteria’s hidden fuel improves blood sugar and liver health, study shows
Scientists have discovered a surprising new way to improve blood sugar levels and reduce liver damage: by trapping a little-known fuel made by gut bacteria before they wreak havoc on the body. It could open the door to new therapies to treat metabolic diseases.
-
 News
NewsNature’s toolkit: Scientists breed mushrooms to build versatile natural substitutes for commonly used materials
Scientists have shown that natural genetic variations in a common species of mushroom can be used to create new strains capable of making customized, biodegradable replacements for fabric, plastic, packaging and other environmentally harmful materials.
-
 News
NewsHow the plague bacillus became less virulent, prolonging the duration of two major pandemics
Scientists have discovered that the evolution of a gene in the bacterium that causes bubonic plague, Yersinia pestis, may have prolonged the duration of two major pandemics. Modifying the copy number of a specific virulence gene increases the length of infection.
-
 News
NewsFungi dwelling on human skin may provide new antibiotics
Researchers have uncovered a molecule produced by yeast living on human skin that showed potent antimicrobial properties against a pathogen responsible for a half-million hospitalizations annually in the United States.
-
 News
NewsBreakthrough as researchers discover new class of antibiotics
Researchers have identified a strong candidate to challenge even some of the most drug-resistant bacteria on the planet: a new molecule called lariocidin.
-
 News
NewsMcMaster leads Canada’s first-ever guidelines for Post COVID-19 Condition
A team of experts from McMaster University has led the creation of Canada’s first-ever comprehensive guidelines for diagnosing, managing, preventing, and treating post COVID-19 condition (PCC), more commonly known as long COVID.
-
 News
NewsInhaled COVID vaccine study begins recruitment for phase-2 human trials
Researchers have started a phase-2 clinical trial on a next-generation, inhaled COVID-19 vaccine. Findings from the phase-1 trial indicate that the vaccine is more effective at inducing immune responses than traditional injected vaccines are.
-
 News
NewsOvercoming resistance: McMaster researchers find new utility for old antibiotics
In a recent study, researchers found that zinc plays a vital role in how some of the world’s most dangerous bacteria resist antibiotics.
-
 News
NewsResearchers develop a simple lab-free test to detect bacteria in fluids from water to urine
A novel new test for bacteria in fluids makes it as easy as observing a colour change to confirm the presence of disease-causing pathogens, promising much easier diagnostic tests and greater food safety.
-
 News
NewsBacteria and fungi found on bat wings that could help fight deadly white-nose syndrome
Bacteria and fungi from the wings of bats could play a significant role in saving them from white-nose syndrome (WNS), a fungal disease affecting the skin of wings and muzzle, which has nearly wiped out vulnerable bat populations across North America.
-
 News
NewsMajor antimicrobial power boost as phages form into surprising flower shapes
Researchers treated bacteria-eating viruses so they could be viewed alive under an electron microscope and coaxed them to join together into flower-like shapes - discovering that this made them 100 times more efficient.
-
 News
NewsResearchers develop a way to make lifesaving phages accessible, transportable and much easier to use
Researchers have developed a simple new way to store, identify, and share phages, making them more accessible to patients who need them.
-
 News
NewsResearchers invent artificial intelligence model to design new superbug-fighting antibiotics
Researchers have invented a new generative artificial intelligence model which can design billions of new antibiotic molecules that are inexpensive and easy to build in the laboratory.
-
 News
NewsResearchers discover molecular ‘barcode’ used by bacteria to secrete toxins
Researchers have discovered a molecular “barcode” system used by disease-causing bacteria to distinguish between beneficial and toxic molecules.
-
 News
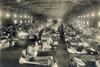
NewsRemains of 1918 flu pandemic victims contradict belief that healthy young adults were particularly vulnerable
New analysis of the remains of victims of the 1918 influenza pandemic, which killed an estimated 50 million people worldwide, contradicts the widespread belief the flu disproportionately impacted healthy young adults.
-
 News
NewsPackaging tray can signal Salmonella contamination before food is unwrapped
Researchers have created a new packaging tray that can signal when Salmonella or other dangerous pathogens are present in packages of raw or cooked food such as chicken.
-
 News
NewsDrug-resistant fungi thriving in the most remote regions of Earth
New research has found that a disease-causing fungus — collected from one of the most remote regions in the world — is resistant to a common antifungal medicine used to treat infections.
-
 News
NewsAI deployed to find promising antibiotic to fight evasive hospital superbug
Scientists have used artificial intelligence to discover a new antibiotic which could be used to fight a deadly, drug-resistant pathogen that strikes vulnerable hospital patients.
