All Michigan State University articles
-
 News
NewsPostharvest apple immunity: a key factor in shelf life and fruit quality
New research sheds light on how the immune system of apple fruits interacts with their microbiomes during storage, playing a crucial role in maintaining fruit health and preventing spoilage.
-
 News
NewsMichigan cherry farmers find a surprising food safety ally: falcons
By shooing cherry-pecking birds away, kestrels also keep them from contaminating crops with their droppings, a new study shows. Kestrels were associated with a 3-fold reduction in droppings spotted on branches.
-
 News
NewsFlower to fruit: tracking the changing fungal community on blueberry plants
A study identifies how fungal diversity changes over time and across tissue types in highbush blueberry, revealing dynamic transitions in the phyllosphere from buds to ripe fruits. Early-season buds and flowers harbor the highest fungal diversity, while unripe green fruits display the lowest.
-
 News
NewsAncient chemical clues reveal Earth’s earliest life 3.3 billion years ago
A new study uncovered fresh chemical evidence of life in rocks more than 3.3 billion years old, along with molecular traces showing that oxygen-producing photosynthesis emerged nearly a billion years earlier than previously thought. Researchers paired cutting-edge chemistry with artificial intelligence to reveal faint chemical “whispers” of biology locked inside ancient rocks.
-
 News
NewsScientists reveal how cyanobacteria use ’sunscreen’ to adapt to climate
Using single particle spectroscopy, researchers revealed insights into how different types of photosynthetic bacteria can use a shared mechanism to protect themselves from too much sunlight.
-
 News
NewsWhen faucets rest: hidden microbial risks emerge in hours
Stagnant water in building plumbing systems is a well-known driver of microbial growth and contamination, including L. pneumophila. A new study highlights a short “microbial safety window” of 2–4 hours, after which risks increase significantly.
-
 News
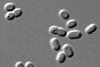
NewsScientists discover regulatory pathway behind cyanobacteria’s carbon-fixing factories
A new study illuminates a key regulatory pathway between cyanobacteria’s light-harvesting systems and the inner compartments where carbon fixation happens, helping us to understand how cyanobacteria balance their energy demands.
-
 News
NewsStudy finds tiny microbes shape brain development
New research finds that microbes play an important role in shaping early brain development, specifically in a key brain region that controls stress, social behavior, and vital body functions.
-
 News
NewsNew study reveals how corals teach their offspring to beat the heat
A new study shows that rice coral, an important reef-building species, passes on thermal resistance to their offspring and avoids coral bleaching. Understanding this is important to building healthier coral reefs and protecting their future.
-
 News
NewsHidden bacterial redundancy could be antibiotic game-changer
Staphylococcus aureus possesses a surprising level of metabolic redundancy, allowing it to survive even when key enzymes are knocked out, a new study finds. However, when two specific enzymes are removed, staph doesn’t infect its host as readily.
-
 News
NewsHow superfungus Candida auris rebuilds its cell walls to withstand antifungal treatment
A groundbreaking study has revealed how the multidrug-resistant superfungus Candida auris uniquely reconstructs its cell wall to survive antifungal treatments.
-
 News
NewsScientists find two brain biomarkers in long COVID sufferers may be what’s causing brain fog
A new study that compares inflammation and brain stress responses in long COVID-19 patients with individuals who have fully recovered shows those with cognitive issues have a lower ability to adapt to stress and higher levels of inflammation in their brains.
-
 News
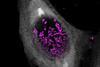
NewsDiscovery opens up for new ways to treat chlamydia
Researchers have discovered a type of molecule that can kill chlamydia bacteria but spare bacteria that are important for health.
-
 News
NewsGlycan-coated magnets: A game-changer for safer food supply chains
A new method using glycan-coated magnetic nanoparticles (gMNPs) is poised to change the way we detect foodborne pathogens like Escherichia coli and Salmonella in complex food matrices such as melons, lettuce, and raw chicken.
-
 News
NewsScientists discover new microbe phylum cleaning the water in Earth’s deep soil
Scientists have discovered a new phylum of microbes in the Earth’s Critical Zone, an area of deep soil that restores water quality. Ground water, which becomes drinking water, passes through where these microbes live, and they consume the remaining pollutants.
-
 News
NewsWorried about a pregnant woman’s stress and mental health? Her saliva may hold the key.
New research has found that the number and type of microbes present in the saliva of pregnant women differ according to whether they are experiencing life stress and symptoms of anxiety, depression and post-traumatic stress disorder.
-
 News
NewsNew research could pave way for vaccine against deadly wildlife disease
A researcher has been awarded a $2.4 million grant from the National Institutes of Health’s National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases to study the cause of Bang’s disease, Brucella abortus.
-
 News
NewsOral microbiome varies with life stress and mental health symptoms in pregnant women
The number and type of microbes present in the saliva of pregnant women differ according to whether they are experiencing life stress and symptoms of anxiety, depression and post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD), finds a study published in the open access journal BMJ Mental Health. Although several studies ...
-
 Careers
CareersMeet the Global Ambassadors: Our Q&A with Ashley Shade
The Microbiologist chats with our new Global Ambassador for France, Ashley Shade, who is Director of Research with Le Centre National de la Recherche Scientifique (CNRS) at the Universite Claude Bernard Lyon 1.
-
 News
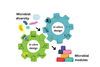
NewsComputer-aided biology can be deployed to develop tailored microbe communities
Researchers inspired by natural lichens want to develop the microbial networking manifested here as an example for future applications, as a contribution toward establishing interdisciplinary methods and technologies for CO2-negative processes.
