More News – Page 92
-
 News
NewsA new test will make it possible to detect the parasite responsible for trichomoniasis more quickly and inexpensively
A sensitive, cheap and rapid test is developed to detect the parasite, Trichomonas vaginalis, which causes one of the world’s most common sexually transmitted infections, using an innovative approach that targets highly specific molecules with short nucleic acid sequences.
-
 News
NewsWorld first clinical trial will study specialized ‘poop pills’ to improve treatment of advanced pancreatic cancer
A world-pioneering fecal microbiota transplantation pill will undergo a clinical trial, aiming to improve immune responses by remodifying the gut microbiome in patients with advance pancreatic cancer.
-
 News
NewsDemocratic Republic of the Congo deepens investigation on cluster of illness and community deaths in Equateur province
Health authorities in the Democratic Republic of the Congo and experts from World Health Organization (WHO) are carrying out further investigations to determine the cause of another cluster of illness and community deaths in Equateur province.
-
 News
NewsA blueprint for making cereal crops more resistant to fungal disease
Researchers have uncovered the structural interactions between a type of barley immune receptor that helps the crop to fight against devastating fungal disease, powdery mildew and other plant pathogens.
-
 News
NewsGastric bacteria ‘leaking across stomach lining’ could indicate risk of gastric cancer
A new discovery in the roles of gastric microbiota bacteria and Helicobacter pylori across the stomach lining during pre-cancerous stage of gastric cancer development could be the missing link for engineering future therapeutic intervention.
-
 News
NewsThe International Space Station is overly sterile - so making it ‘dirtier’ could improve astronaut health
The International Space Station (ISS) has a much lower diversity of microbes compared to human-built environments on Earth, and the microbes that are present are mostly species carried by humans onto the ISS, suggesting that the presence of more microbes from nature could help improve human health in the space station.
-
 News
NewsHidden fungal allies strengthen defenses of black poplars and influence insect interactions
Endophytic fungi inside the leaves strengthen the chemical defenses of black poplars and influence the interactions between insect populations living on the trees.
-
 News
NewsGenomic tools provide clearer view of health for endangered bats
Researchers have used advanced molecular tools to survey the health status of endangered Indiana bats, identifying microbiome changes resulting from parasitic infections.
-
 News
NewsNew method developed to dramatically enhance bioelectronic sensors
In a breakthrough that could transform bioelectronic sensing, researchers have developed a new method to dramatically enhance the sensitivity of enzymatic and microbial fuel cells using organic electrochemical transistors (OECTs).
-
 News
NewsImmunity against seasonal H1N1 flu reduces bird flu severity in ferrets, study suggests
Pre-existing immunity against seasonal H1N1 flu might help explain why most reported human cases of H5N1 bird flu in the U.S. have not resulted in lethal outcomes, suggests a new study.
-
 News
NewsResearch reveals hidden risks from plastic-coated fertilizers in soil
A study focuses on the microplastic pollution generated by polymer-coated, control-release fertilizers, highlighting the need for biodegradable alternatives.
-
 News
NewsA rapid and reproducible method for generating germ-free Drosophila melanogaster
Scientists have introduced a refined method for the production of germ-free Drosophila, complemented by a straightforward verification process to ascertain its efficacy.
-
 News
NewsA*STAR spin-off NalaGenetics implements nationwide drug reaction screening for leprosy patients in Indonesia
NalaGenetics, a spin-off from A*STAR Genome Institute of Singapore (A*STAR GIS), will be transforming leprosy treatments in Indonesia with a nationwide genetic screening programme with their PGx1301 diagnostic kit.
-
 News
NewsMicrobiologist calls for urgent action on the danger of raw sewage in UK seas
A microbiologist has described how he contracted a type of bacterial pneumonia following a swim in the sea that was likely connected to an incident of sewage dumping in the area.
-
 News
NewsNew 3D imaging approach reveals intricate steps of virus assembly
A new integrated 3D imaging approach combines cryo-light microscopy and cryo-soft X-ray tomography to reveal the intricate ultrastructure of herpes simplex virus-1 (HSV-1) assembly.
-
 News
NewsNew insights into how specific gut cells respond to bacterial toxins
Researchers have characterized a specific gut cell type, BEST4/CA7+ cells, with the ability to interact with immune cytokine interferon-γ (IFNγ), and its regulation in cellular electrolyte and water balance, in response to bacterial toxins.
-
 News
NewsNew insights into phage–bacteria interactions in the gut microbiome
Researchers studied the interactions between bacteria and phages within the gut microbiome and highlighted the significance of the phage community to shape the microbiome that contributes to host health and diseases.
-
 News
NewsDesigning self-destructing bacteria to make effective tuberculosis vaccines
Preclinical studies have demonstrated a more effective tuberculosis (TB) vaccine through engineering bacteria to self-destruct and swiftly stops the infection on cue, which activates a more robust immune response.
-
 News
NewsScientists build robot to track plant-fungal trade networks, revealing nature’s underground supply chains
New research uses advanced robotics to track the hyper-efficient supply chains formed between plants and mycorrhizal fungi as they trade carbon and nutrients across the complex, living networks that help regulate the Earth’s atmosphere and ecosystems.
-
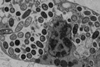 News
NewsBacteria consumed by immune cells become part of the cell
Immune cells that eat bacteria in the body don’t stash them in specialized compartments as once thought, but turn them into critical nutrients that build proteins, create energy and keep the cells alive, according to a new study.
