Researchers from the Organoid group at the Hubrecht Institute have found that specific gut cells, BEST4/CA7+ cells, regulate electrolyte and water balance in response to bacterial toxins that cause diarrhea. Their findings, published in Cell Stem Cell, show that these cells greatly increase in number when exposed to the cytokine interferon-γ (IFNγ), presenting a promising target for therapeutic strategies.
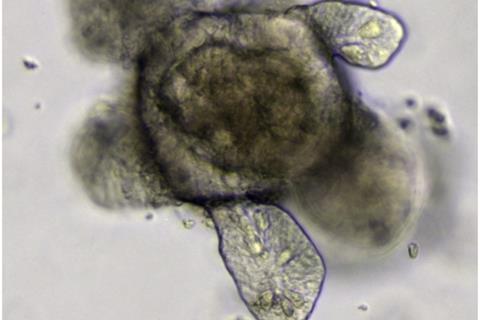
In the gut, a variety of cell types collaborate to keep a balance of electrolyte and water. Bacterial infections can disrupt this balance, leading to diarrhea. Yet, it was unclear which cells were mainly affected by these toxins. “In this study, we looked at the recently identified BEST4/CA7+ cells, a specific type of cell in the intestinal lining that highly expresses CFTR, an important ion channel for electrolyte balance”, says Daisong Wang, lead author of the study.
Understanding how BEST4/CA7+ cells develop and its role in diarrhea
While researchers previously identified the presence of BEST4/CA7+ cells, their development and function are not well understood due to the lack of study models. Wang and his colleagues overcame this by creating human intestinal organoids, mini organ-like structures cultured in a dish. They used these organoids to experimentally assess the response of BEST4/CA7+ cells to various specific signals.
“Using cell-type specific reporter organoids and CRISPR-mediated genetic modifications, we found that the Notch signaling pathway and a master regulator named SPIB are crucial for these cells’ development,” Wang notes.
READ MORE: Children’s gut bacteria - and a superfood grain - may hold the key to diarrhea treatment
READ MORE: Diarrheal diseases remain a leading killer for children under 5, adults 70+
The team previously observed swelling of the organoid when the ion channel CFTR was activated. “However, we saw that organoids lacking BEST4/CA7+ cells did not show this swelling, confirming the vital role of these cells in controlling fluid balance,” Wang explains. This shows that BEST4/CA7+ cells are key targets in diarrhea.
Unexpected growth in response to IFNγ
The researchers then added the type I immune factor called IFNγ which is present during bacterial infections. What they observed was remarkable: “Though these cells only represent a small portion of the intestinal lining, we observed their numbers increase over eightfold in organoids exposed to IFNγ”, Wang explains.
“This is the first time that a type I immune-responsive cell type has been identified in the human gut and the significant growth of BEST4/CA7+ cells underscore their roles in immunity. On the other hand, when treated with a drug called rapamycin, we saw that the number of these cells goes down,” he adds. This could suggest a promising pharmacological strategy for naturally regulating the number of BEST4/CA7+ cell.
The insights from this study not only advance our understanding of gut biology but also open new doors for therapeutic strategies. “Identifying BEST4/CA7+ cells as the primary targets of bacterial toxins might allow us to control fluid release more effectively, either by changing the number of BEST4/CA7+ cells or by targeting their intracellular functional mechanisms,” Wang notes. While initial laboratory results are promising, further research is necessary to determine the efficacy of these strategies in real-world applications.






No comments yet