All Research News articles – Page 180
-
 News
NewsMagnetic resonance imaging shows how infection progresses in strawberry crown
Researchers from the Department of Technical Physics and the Department of Environmental and Biological Sciences at the University of Eastern Finland have used magnetic resonance imaging, MRI, to investigate how the pathogen Phytophthora cactorum affects the growth and development of strawberry plants. This pathogen causes crown rot in strawberries and ...
-
 News
NewsResearchers investigate immune response of a man who received 217 Covid vaccinations
Researchers who examined a man who has received more than 200 vaccinations against Covid-19 say there were no negative impacts on his immune system.
-
 News
NewsStudy supports disease-challenged broiler chickens through nutrition
New research suggests diet changes might help to ensure optimal growth during outbreaks of the parasitic infection coccidiosis in broiler chickens.
-
 News
NewsStudy shows new class of antivirals that works against SARS-CoV-2
Researchers have uncovered a new class of drugs with the potential to prevent or treat infections in a future viral outbreak.
-
 News
NewsZika vaccine safe, effective when administered during pregnancy
A vaccine against Zika virus is safe and effective when administered both before and during pregnancy, according to new research.
-
 News
NewsMussel-based coating protects joints from bacteria
Scientists have successfully developed a coating material for implants. Based on mussel adhesion proteins, this material is designed to release antibiotics in response to bacterial invasion.
-
 News
NewsSpecial insecticide paint may help curb zika and dengue fever outbreaks
Scientists showed that insecticide paint could effectively decrease mosquito presence in Cabo Verde (Cape Verde) for up to one year, making this paint a potential strategy to decrease the transmission of vector-borne diseases.
-
 News
NewsNitrogen has been underestimated in lake ecosystems, researchers warn
A new study shows that algae growth in shallow lakes around the world is affected not only by phosphorus but also by nitrogen.
-
 News
NewsResearchers unveil new method for measuring electrical conductivity in microorganisms
Researchers investigating electro-activity in biofilms have developed a straightforward experimental setup in which a microbial colony, a form of biofilm, was grown on agar and directly pressed onto an electrode to assess its electrical conductivity.
-
 News
NewsScientists discover 18 new species of gut microbes in search for origins of antibiotic resistance
Scientists have found 18 novel species of a type of bacteria called enterococci, which are gut microbes found in most land animals.
-
 News
NewsMicrobial viruses act as secret drivers of climate change
In a new study, scientists have discovered that viruses that infect microbes contribute to climate change by playing a key role in cycling methane, a potent greenhouse gas, through the environment.
-
 News
NewsStudy reveals convergent evolution of algal CO2-fixing organelles
Various pyrenoid-associated proteins have been reported among the algae studied, suggesting that CO2-fixing organelles evolved independently in each algal group.
-
 News
NewsResearchers uncover how virus causes cancer, point to potential treatment
Kaposi sarcoma-associated herpesvirus activates a specific pathway to drive viral persistent infection and cell growth, paving the way for tumors to form.
-
 News
NewsScientists reveal how first cells could have formed on Earth
A new phospholipid discovery brings researchers closer to understanding how primordial cells emerged during origin of life.
-
 News
NewsScientists target seed microbes to improve seed resilience
Fonio (Digitaria exilis), a type of millet, is the oldest indigenous crop in West Africa and one of the fastest maturing cereals. Despite its low yield, the combination of quick maturation and drought tolerance and its ability to thrive in poor soils make it a useful model for understanding how ...
-
 News
NewsResearchers develop a new toolkit in fruit flies to study Zika virus
To study how Zika virus proteins hijack and disrupt host developmental pathways during infection and disease progression, scientists have generated a toolkit of transgenic flies expressing all ten Zika virus proteins.
-
 News
NewsResearchers shine light into the darkness of photosynthesis
Researchers have now succeeded for the first time in visualising the copying machine of chloroplasts, the RNA polymerase PEP, in high-resolution 3D.
-
 News
NewsRefrigerate lettuce to reduce risk of E. coli contamination, researchers say
Leafy green vegetables are important sources of dietary fiber and nutrients, but they can harbor harmful pathogens. In particular, lettuce has often been involved in outbreaks of foodborne illness across the U.S. A new study from the University of Illinois Urbana-Champaign examines factors that affect E. coli ...
-
 News
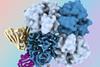
NewsNew antibodies target “dark side” of influenza virus protein
Researchers have identified antibodies targeting a hard-to-spot region of the influenza virus, shedding light on the relatively unexplored “dark side” of the neuraminidase (NA) protein head.
-
 News
NewsProtective human monoclonal antibody targets a conserved site of spike glycoprotein of SARS-CoV-2 Omicron variants
Scientists report that mAb-39 greatly improved the neutralizing activity of anti-RBD antibody, the same type of EUA therapeutic monoclonal antibodies, against the highly neutralization-resistant Omicron variants.
