Research – Page 144
-
 News
NewsGut microbiome can increase risk and severity of HIV and EBV disease
Researchers have shown that the microbiome has a significant impact on the acquisition of Epstein-Barr virus (EBV) and human immunodeficiency virus-1 (HIV) infection and plays a role in the course of disease.
-
 News
NewsGut microbiome diversity boosts survival in children receiving stem cell transplants
Researchers have shown that among children who have undergone a donor stem cell transplant, the presence of diverse species of micro-organisms in the intestinal tract beforehand resulted in significantly better overall patient survival and fewer complications.
-
 News
NewsScientists reveal inner workings of Ebola’s ‘viral factories’
A new study reveals how the Ebola virus’s replication machinery forms fascinating microscopic structures inside host cells that become viral factories.
-
 News
NewsSome phytoplankton can blitz neurotoxin methylmercury - even in the dark
In the search for ways to fight methylmercury in global waterways, scientists have discovered that some forms of phytoplankton are good at degrading the potent neurotoxin - even in the absence of sunlight.
-
 News
NewsMolnupiravir dose of human effect size-equivalent blocks Covid transmission in ferrets
Two oral drugs provide equivalent therapeutic benefit in preventing severe COVID-19 in animal models, but only molnupiravir efficiently blocked SARS-CoV-2 transmission when administered at a human effect size-equivalent dose.
-
 News
NewsHigh-tech microscope using AI detects malaria in returning travellers
Researchers have tested the accuracy of an automated microscope combined with AI software to identify malaria parasites in blood samples – an additional diagnostic approach to disease detection.
-
 News
NewsInflammation slows malaria parasite growth and reproduction in the body
Researchers have found that inflammation in the body can slow down the development of malaria parasites in the bloodstream.
-
 News
NewsCo-infection by novel species of parasite found in visceral leishmaniasis patient
Genome sequencing of clinical samples from a child has revealed the simultaneous presence of the protozoan Leishmania infantum and an as-yet unnamed parasite that was identified earlier in a fatal case of visceral leishmaniasis.
-
 News
NewsModulating type 1 Interferon may expand treatment options for COVID-19
Researchers have, for the first time in nonhuman primates, studied how modulating the signaling of type 1 Interferon (IFN-I), one of the body’s initial defenses against infection, impacts SARS-CoV-2 viral replication and disease progression.
-
 News
NewsScientists discover broadly neutralizing antibodies that contribute to HIV control
Researchers have investigated and revealed how neutralizing antibodies, including those described as broadly neutralizing, contribute to HIV control.
-
 News
NewsResearchers find chink in the armour of tuberculosis pathogen
Discovery of drug resistance network could clear way for developing a drug to prevent pathogen from resisting and tolerating tuberculosis treatment.
-
 News
NewsAMR poses threat in all 35 countries in the Americas
569,000 deaths were linked to bacterial antimicrobial resistance in all 35 countries of the WHO Region of the Americas, according to a new study.
-
 News
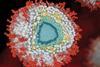
NewsResearchers reveal how the herpes virus HCMV deceives its host cells
Researchers have created a detailed map of the spatial interactions between viral and host cell proteins within HCMV particles, revealing that certain host cell proteins are recruited by viral proteins and play a role in viral replication.
-
 News
NewsEgyptian cotton gene grants powerful resistance to resurging blight
An overlooked gene found in Egyptian cotton confers powerful resistance to bacterial blight, a plant disease that is threatening cotton production worldwide.
-
 News
NewsFlu deaths rise when pro sports teams move into cities
West Virginia University economists, whose research shows flu deaths increase when a city becomes home to a new professional sports team, say their data should make even the biggest fans reconsider support for taxpayer-funded stadium subsidies.
-
 News
NewsAspergillus fumigatus adapts to life in humans - and shapes their lung microbiome
Aspergillus fumigatus strains that infect humans have a significantly altered metabolism compared to other strains in the environment. At the same time, infection with the fungus leads to an apparent change in the human lung microbiome. Source: CDC Photomicrograph revealing ultrastructural morphology exhibited by the fungal organism Aspergillus ...
-
 News
NewsCurrent estimates of Lake Erie algae toxicity may miss the mark
A new study of the annual harmful algal bloom (HAB) in Lake Erie suggests that the toxicity of the bloom may be overestimated in earlier warm months and underestimated later in the summer.
-
 News
NewsResearchers using synthetic microbiomes to protect aquatic communities from bacteria
Scientists have been awarded a grant to create synthetic microbiomes – communities of microorganisms – that will better protect aquatic environments from bacteria.
-
 News
NewsChanges in gut microbiome alters rewarding effects of cocaine and cravings
Scientists have provided the first evidence that changes in the gut microbiome have significant effects on cocaine use and cravings after withdrawal.
-
 News
NewsHigh diversity of cell appendages found in hospital superbug
Bioinformaticians have detected an unexpectedly wide diversity of certain cell appendages in hospital pathogen Acinetobacter baumannii that are associated with pathogenicity.
