All USA & Canada articles – Page 78
-
 News
NewsBioengineered mussel-inspired sticky microorganisms to help break down plastic waste
Scientists have tapped into nature’s adhesive genius, the sticky power of mussels, to create bioengineered microorganisms with powerful cling that could help transform environmental cleanup.
-
 News
NewsStudy probes disparities in hepatitis C care for reproductive-aged women to break cycle of viral transmission
Researchers and clinicians are working to minimize racial and ethnic disparities in hepatitis C testing and treatment for women with opioid use disorder and their children through innovative programs.
-
 News
NewsResearchers confront new US and global challenges in vaccinations of adults
Decreasing vaccination rates now threaten the huge beneficial impacts of vaccinations in the U.S. and globally. Researchers discuss the barriers including increasing vaccine hesitancy and new clinical and public health challenges in vaccinations of U.S. adults.
-
 News
NewsAsteroid that doomed dinosaurs created fungus farming among ants
Scientists analyzed genetic data from 475 species of fungi and 276 species of ants to craft detailed evolutionary trees, allowing them to pinpoint when ants began cultivating fungi millions of years ago, a behavior that some ant species still exhibit today.
-
 News
NewsPlastic-eating enzyme identified in wastewater microbes
Plastic pollution is everywhere, and a good amount of it is composed of polyethylene terephthalate (PET, ♳). This polymer is used to make bottles, containers and even clothing. Now, researchers report in ACS’s Environmental Science & Technology that they have discovered an enzyme that breaks apart PET ...
-
 News
NewsIn lab tests, dietary zinc inhibits AMR gene transmission
Genes responsible for antimicrobial resistance (AMR) can spread from microbe to microbe through plasmids, and this lateral transfer occurs in the gut - but transmission of some AMR plasmids may be inhibited by dietary zinc supplements.
-
 News
NewsBacteria-fighting viruses team up to treat drug-resistant superbugs
Researchers screened a library of bacteriophages to find combinations of the viruses that can work together to fight antibiotic-resistant Klebsiella pneumoniae infections.
-
 News
NewsScientists reveal how doxycycline for STI prevention affects the gut microbiome
Taking a dose of the oral antibiotic doxycycline after a high-risk sexual encounter has dramatically reduced the incidence of sexually transmitted infections (STIs) in places where the strategy is being tried. Source: NIAID Capsules of the antibiotic doxycycline Despite its effectiveness, the new strategy, known ...
-
 News
NewsGut bacteria engineered to act as tumor GPS for immunotherapies
Cancer researchers have engineered gut derived E. coli bacteria to express immune-activating cytokines on their surfaces, with the idea that the bacteria would move into tumors and induce potent immune responses.
-
 News
NewsExperts propose key criteria to classify prebiotics
A group of eight leading international scientists has developed a comprehensive framework that outlines the criteria for establishing prebiotic status, providing much-needed clarity in this evolving field.
-
 News
NewsZooplankton go ‘Eew!’ to cleaning feces-contaminated water
Scientists were recently surprised to find that the natural community of zooplankton — tiny, aquatic animals known to graze on bacteria — present in freshwater and saltwater do not clean water that is contaminated with fecal microorganisms.
-
 News
NewsStudy identifies potential novel drug to treat tuberculosis
A new study demonstrates that a novel semi-synthetic compound can be derived from natural compounds to produce potent activity against Mycobacterium tuberculosis, including multi-drug resistant strains.
-
 News
NewsWastewater bacteria can break down plastic for food
Researchers have discovered how cells of a Comamonas bacterium break down plastic for food. First, they chew the plastic into small pieces, then secrete an enzyme that breaks down the plastic further, and finally use a ring of carbon atoms as a food source.
-
 News
NewsPlant compound used in traditional medicine may help fight tuberculosis
A compound found in African wormwood — a plant used medicinally for thousands of years to treat many types of illness — could be effective against tuberculosis, according to a new study.
-
 News
NewsNSF to invest $5 million to Biofoundries project
The U.S. National Science Foundation and partner agencies in the U.S., Canada, Finland, Japan, the Republic of Korea (ROK), and the United Kingdom have announced funding awards in their Global Centers competition. One of the centers, the Reliable and Scalable Biofoundries for Biomanufacturing and Global Bioeconomy, includes researchers from the ...
-
 News
NewsA tool to enhance taste and texture of sourdough and study the complexity of microbiomes
Researchers explore how acetic acid bacteria shapes emergent properties of sourdough, with implications across complex microbial systems.
-
 News
NewsResearchers identify likely culprit that turns classical Klebsiella pneumoniae into a drug-resistant killer
A hypervirulent strain of Klebsiella pneumoniae can infect and severely sicken otherwise healthy people. Researchers have identified a likely culprit that is causing the hypervirulence.
-
 News
NewsBovine H5N1 influenza may spread via milking
Milking practices may be linked to the transmission of bovine H5N1 influenza virus, which affects dairy cattle and was first detected in the U.S. in spring 2024.
-
 News
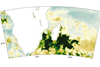
NewsPlankton bloom off Madagascar linked to drought in South Africa
Researchers show that dust from drought-stricken Southern Africa caused a bloom of marine phytoplankton off the southeast Madagascar coast from November 2019 through February 2020.
-
 News
NewsAntibodies in breast milk provide protection against common GI virus
A study has found that breast milk provides protection against rotavirus, a common gastrointestinal disease that causes diarrhea, vomiting and fever in infants.
