All Algae articles
-
 News
NewsNew study reveals cyanobacteria may help spread antibiotic resistance in estuarine ecosystems
Scientists have discovered that cyanobacteria may play a major role in spreading antibiotic resistance genes in coastal environments. The findings highlight a previously overlooked link between natural nutrient cycling and the global challenge of antibiotic resistance.
-
 News
NewsLab-grown algae removes microplastics from water
Scientists have applied a revolutionary strain of algae toward capturing and removing harmful microplastics from polluted water. The aim is to repurpose the collected microplastics into safe, bioplastic products such as composite plastic films.
-
 News
NewsSediment core yields evidence of an unexpected climate feedback in Antarctica
Researchers have concluded that global warming may lead to reduced uptake of carbon dioxide than at present in the Pacific sector of the Southern Ocean if the West Antarctic Ice Sheet, which is considered unstable, continues to shrink.
-
 News
NewsFrom sea to soil: Molecular changes suggest how algae evolved into plants
A research team used cryo-electron microscopy to look at the three-dimensional structure and function of Lhcp, a unique prasinophyte LHC, from the microscopic alga Ostreococcus tauri. The team compared their results to LHCII, which is found in terrestrial plants.
-
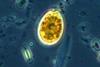 News
NewsResearchers uncover hidden toxin risks during nutrient-starved algal blooms
Researchers have shown that extended nutrient deprivation can significantly increase toxin content per cell in the benthic dinoflagellate Prorocentrum lima, even when cell numbers remain relatively stable. Toxin risk may increase quietly under nutrient-poor conditions without obvious bloom expansion.
-
 News
NewsNatural sunscreen compounds show potential to support skin health and blood pressure
Researchers have discovered that natural ‘sunscreen’ compounds found in algae and cyanobacteria may also support skin and heart health.
-
 News
NewsMachine learning reveals how to maximize biochar yield from algae
Researchers have developed a powerful machine learning framework that can accurately predict and optimize biochar production from algae, offering a faster and more sustainable path toward carbon rich materials for climate mitigation, soil improvement, and environmental applications.
-
 News
NewsMineral dust accelerating melting of Greenland ice sheet
Scientists have found that airborne mineral dust and other aerosols are directly connected to how much algae grows on the ice. The algae interfere with albedo, or the reflection of the sun’s rays, exacerbating melting.
-
 News
NewsFirst known lichen in the fossil record helped structure terrestrial ecosystems
A group of researchers has confirmed the identity of the first lichens to inhabit Earth, Spongiophyton, around 410 million years ago, in great detail for the first time. The study confirms that the symbiosis between fungi and algae that dissolves rocks helped form the first soils.
-
 News
NewsScientists advance commercial production of nutrient-rich spirulina
Sultan Qaboos University (SQU) has achieved a significant milestone in the commercial production of spirulina, a highly nutritious microalgae increasingly recognized worldwide for its role in food security, health supplements, and sustainable production systems.
-
 News
NewsRare microbial wrinkle structures - signs of ancient life - turn up in an unexpected place
Deep water sediment layers in the Dadès Valley in the Central High Atlas Mountains of Morocco have revealed rare microbial wrinkle structures formed far from sunlight.
-
 News
NewsFrom sediment to surface: How invisible plumes trigger harmful algal blooms
A new study shows that algal blooms can begin days earlier than previously recognized, originating from chlorophyll-rich plumes rising from lake sediments before any surface discoloration appears.
-
 News
NewsResearchers eye goal of turning garden and crop waste into plastics
A research team will combine eco-friendly and application-oriented approaches to develop a cost-effective, energy-efficient technology for making innovative plastics based on polybutylene succinate (PBS) which are made entirely out of organic waste.
-
 News
NewsDeep ocean earthquakes drive Southern Ocean’s massive phytoplankton blooms, study finds
Researchers have uncovered evidence that deep underwater earthquakes can spur the growth of massive phytoplankton blooms at the ocean surface. The new findings point to a previously unknown relationship between the ocean floor and life at the surface.
-
 News
NewsA coral reef’s daily pulse reshapes microbes in surrounding waters
A new study shows that coral reefs don’t just provide a home for ocean life, they also help set the daily “schedule” for tiny microbes living in the water nearby. Over the course of a single day, the quantity and types of microbes present can shift dramatically.
-
 News
NewsMicroalgal–Bacterial granules show resilience to estrogen pollution but face structural collapse at high contamination levels
A study reveals both the adaptive biodegradation potential and the vulnerability of MBGS under estrogenic stress, offering new insights for developing robust, biologically based wastewater treatment technologies.
-
 News
NewsStrengthening asphalt roads with a unique green ingredient: Algae
Researchers propose a figurative and literal green solution to improve the durability of roads and sidewalks: an algae-derived asphalt binder. For temperatures below freezing, results indicated that the algae binder reduced asphalt cracks when compared to a conventional, petroleum-based binder.
-
 News
NewsRising heat reshapes how microbes break down microplastics, new review finds
A new review examines how high and extreme temperatures influence the ability of microorganisms to degrade microplastics. The authors show that heat can both accelerate and suppress microbial breakdown of plastic particles, depending on conditions and the organisms involved.
-
 News
NewsBreakthrough AI speeds up discovery of life-supporting microbes
Scientists have developed a powerful new artificial intelligence tool called LA⁴SR that can rapidly identify previously overlooked proteins in microalgae - tiny organisms that produce much of the Earth’s oxygen and support entire aquatic ecosystems.
-
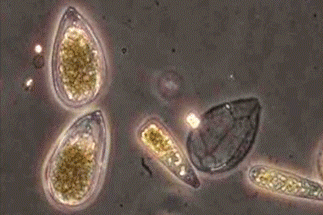 News
NewsScientists discover fungus that kills toxic algae threatening human health
A team of researchers have discovered a previously unknown species of marine fungus that can kill harmful, bloom-forming algae. The new species, Algophthora mediterranea, is a form of microscopic chytrid fungus that can occupy a broad range of hosts.
