All One Health Content – Page 161
-

-
 News
NewsWarning as entire ICU contaminated with superbug
Researchers have called for urgent measures to protect hospitals after an entire ICU was contaminated with an outbreak of antibiotic-resistant bacteria.
-
 News
NewsConcerns raised over popular Covid disinfectants
The Covid-19 pandemic has boosted the unnecessary use of antimicrobial chemicals linked to health problems, antimicrobial resistance, and environmental harm, scientists warn.
-
 News
NewsChild IBD risk linked to antibiotics and diet
Children and adolescents face greater risk of inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) when exposed to antibiotics or a Western diet at early ages, or when their family has higher socioeconomic status, according to a study being presented today at Digestive Disease Week® (DDW) 2023. “Pediatric IBD cases are ...
-
 News
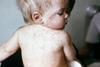
NewsMeasles surge sparks UK government vaccine call
The UK government has urged parents to make sure their children’s MMR vaccine is up to date following a rise of measles cases.
-
 Careers
CareersBiomedical scientist for hire, will travel!
Insights and advice for people looking to work as locum scientists.
-
 News
NewsHealthy diet promotes sound gut microbiome
A new study suggests that following the Dietary Guidelines for Americans (DGA) promotes a gut microbiota composition that may support overall health.
-
 News
NewsRed light aids growth of Haematococcus pluvialis
Researchers have proved that red light can promote photoautotrophic growth of Haematococcus pluvialis and investigated the related carbon fixation mechanism.
-
 News
NewsAntibacterial treatment solves radiotherapy skin problem
A new study shows that a low-cost antibacterial regimen can prevent acute radiation dermatitis.
-
 News
NewsAntibiotics should be halted upon incision closure
New guidelines: antibiotics administered before and during surgery should be discontinued immediately after a patient’s incision is closed, according to updated recommendations for preventing surgical site infections.
-
 News
NewsSloth fur may carry antibiotic-producing bacteria
The fur of Costa Rican sloths appears to harbour antibiotic-producing bacteria that may hold a solution to the growing problem of antimicrobial resistance.
-
 News
NewsPreemie infections may come from gut microbiomes
Dangerous bacterial bloodstream infections in premature babies may originate from the infants’ gut microbiomes, according to researchers.
-
 News
NewsQuantum entanglement doubles microscope resolution
Using a ‘spooky’ phenomenon of quantum physics, Caltech researchers have discovered a way to double the resolution of light microscopes.
-
 News
NewsDeep neural network spots pathogens in real time
Scientists have developed a deep neural network that can accurately identify biomarker signals in real time, on a system that is relatively cheap and portable for point-of-care applications.
-
 News
NewsLiverpool begins first human trial of Zika vaccine
The first participant has received a dose of a new Zika virus vaccine being trialled by the University of Liverpool.
-
 News
NewsFitness landscape explains Covid variant origins
Researchers have uncovered the mechanisms behind the emergence of new and dangerous coronavirus variants, such as Alpha, Delta, Omicron, and others.
-
 News
NewsHIV targeted with novel dual gene-editing approach
Gene-editing therapy aimed at two targets – HIV-1, the virus that causes AIDS, and CCR5, the co-receptor that helps the virus get into cells – can effectively eliminate HIV infection, new research shows.
-
 News
NewsRare yeast pathogen causing neonatal outbreaks
Scientists studying the stubborn and dangerous rare yeast pathogen behind two outbreaks in a neonatal intensive care unit in Delhi, India, have found that while infected patients can be treated with antifungal medications, the yeast is remarkably resistant to the strong disinfectant bleach commonly used to sanitize hospital rooms.
-
 News
NewsIntestinal ecosystem directly affects anorexia
Severe changes in the intestinal ecosystem of bacteria and viruses directly affect the development and maintenance of anorexia nervosa
-
 News
NewsPreviously unknown intracellular electricity may power biology
Newly discovered electrical activity within cells could change the way researchers think about biological chemistry
