Food security – Page 2
-
 News
NewsMichigan cherry farmers find a surprising food safety ally: falcons
By shooing cherry-pecking birds away, kestrels also keep them from contaminating crops with their droppings, a new study shows. Kestrels were associated with a 3-fold reduction in droppings spotted on branches.
-
 News
NewsFestive cheer: Soaked raisins ferment to turn water into wine
Scientists have discovered that soaking sun-dried raisins in water is a successful method of creating wine. It was thought that ancient wine production relied on the natural fermentation process of storing crushed grapes in jars, but Saccharomyces cerevisiae rarely colonizes grape skins.
-
 News
NewsNew Arkansas Clean Plant Center partnership to boost Indian agriculture
The University of Arkansas System Division of Agriculture has entered a five-year agreement with the Indian National Horticulture Board and Ministry of Agriculture and Farmers Welfare to help farmers in India improve agricultural production by limiting spread of pathogens.
-
 News
NewsMicrobial nano-selenium breakthrough boosts tea quality and safety
Scientists developing selenium-enriched tea have identified a powerful selenium-reducing bacterium, Raoultella ornithinolytica S-1, capable of converting inorganic selenium into selenium nanoparticles (SeNPs) while simultaneously promoting plant growth.
-
 News
NewsScientists reveal molecular cause behind “stuck” beer fermentation
Premature yeast flocculation (PYF) is a persistent issue in beer brewing, where yeast settles too early during fermentation. New research identifies multiple differential metabolites and confirmed galangin as a key factor that promotes early yeast aggregation.
-
 News
NewsLivestock manure linked to the rapid spread of hidden antibiotic resistance threats in farmland soils
Scientists have uncovered how even “low-risk” organic fertilizers like dried poultry manure can inadvertently drive a dramatic surge in dangerous antibiotic resistance genes, once released into vegetable plots used for food crops.
-
 News
NewsImpact of pasteurization on dairy calves’ gut microbiota: A study of milk feeding and early microbial colonization
A new study highlights the impact of pasteurization on microbial diversity in dairy calves, underlining the importance of balancing pathogen safety and microbial health. It suggests that while pasteurization prevents pathogen transmission, it also reduces beneficial microbial transfer.
-
 News
NewsGenetically engineered fungi are protein packed, sustainable, and taste similar to meat
Researchers used CRISPR to increase a fungus’s production efficiency and cut its production-related environmental impact by as much as 61%—all without adding any foreign DNA. The genetically tweaked fungus tastes like meat and is easier to digest than its naturally occurring counterpart.
-
 News
NewsFlower to fruit: tracking the changing fungal community on blueberry plants
A study identifies how fungal diversity changes over time and across tissue types in highbush blueberry, revealing dynamic transitions in the phyllosphere from buds to ripe fruits. Early-season buds and flowers harbor the highest fungal diversity, while unripe green fruits display the lowest.
-
 News
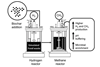
NewsBiochar boosts clean energy output from food waste in novel two-stage digestion system
A new study from researchers at the University of Western Australia and Universitas Brawijaya has found that adding biochar to advanced food waste recycling systems can significantly increase the clean energy yields of hydrogen and methane. This breakthrough offers promising strategies for municipalities and industries aiming to turn food scraps ...
-
 News
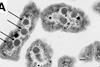
NewsNew blueprint for nature’s carbon-capturing nanomachines revealed
Researchers have uncovered how bacterial organelles assemble, opening new routes for bioengineering and climate innovation. The team has unveiled the most detailed picture yet of how bacteria construct microscopic compartments known as carboxysomes – natural nanomachines that play a vital role in capturing and converting carbon dioxide (CO₂).
-
 News
NewsFirst-in-North-America resource touts research into health benefits of fermented foods
A one-stop network, the first of its kind in North America, has begun sharing easily digested research, recipes and other resources about the health benefits of fermented foods. The new Canadian Fermented Foods Initiative (CFFI) launches officially on Nov. 17.
-
 News
NewsStudy finds high rates of antibiotic-resistant bacteria in raw milk
Raw cow and sheep milk is frequently contaminated with antibiotic-resistant bacteria that could pose a threat to human and animal health, reports a new study.
-
 News
NewsWild grass offers new genetic clues to combat deadliest pathogen of wheat
A new study has identified Aegilops cylindrica, a wild grass closely related to wheat, as a powerful genetic reservoir for resistance against the devastating fungal pathogen Zymoseptoria tritici—the cause of Septoria tritici blotch (STB).
-
 Features
FeaturesClostridioides difficile: the unseen passenger from farm to fork
Once known as a hospital superbug, Clostridioides difficile is now turning up in surprising places – production animal farms, soil, retail meats, vegetables, ready-to-eat salads, and even household kitchens. Recent research suggests this gut pathogen may not be confined to just hospital wards but is moving through our food chain, raising questions regarding how C. difficile finds its way to our plates, and what might be the result.
-
 News
NewsHorizon Awards 2025: Professor Joana Falcao Salles named as winner of Basil Jarvis Award
Professor Joana Falcao Salles, a professor of Microbial Community Ecology at the University of Groningen, has been named as the newest winner of the Basil Jarvis Food Security and Innovation Award.
-
 News
NewsMicrobiome around Xanthomonas infection in tomato plants signposts scientists to the bacterium of its downfall
Scientists have uncovered a bacterium in the microbiome of tomato leaves that can be used to fight back against infection by Xanthomonas, a disease that poses a major challenge to tomato growers worldwide.
-
 News
NewsTwo amino acids help plants decide whether to welcome or repel nitrogen-fixing bacteria
Researchers are one step closer to understanding how some plants survive without nitrogen - a breakthrough that could eventually reduce the need for artificial fertilizer in crops such as wheat, maize, or rice.
-
 Careers
CareersSummer studentship: Taiwo uncovers native strains for mycotoxin control in stored nuts
Taiwo Boluwatife Omowunmi reports back on her AMI-sponsored summer studentship which assessed native microbial strains for mycotoxin biocontrol in stored nuts.
-
 News
NewsFoxtail barley serves as a host for fungal pathogens attacking barley
Researchers report that foxtail barley (Hordeum jubatum), a wild relative of the cultivated crop, can harbor several fungal pathogens and may play a role in the disease epidemiology of barley, potentially serving as reservoirs of inoculum to initiate some diseases.
