More clean water – Page 7
-
 News
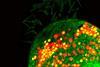
NewsWarming stops tiny organisms working together
The single-celled organism Paramecium bursaria can absorb and host algae (Chlorella spp), providing benefits for both, but when scientists made the water 5°C warmer, the partnership stopped working – and the algae may even become parasitic.
-
 News
NewsAMAST Network launches to battle AMR in the agrifood system
AMAST – the AMR in Agrifood Systems Transdisciplinary Network, has been created to harness perspectives from across agrifood stakeholders and prepare new ways to tackle these challenges.
-
 News
NewsStudy sheds light on patterns of Leptospirosis infection
Part of a multi-year project, the study seeks to identify demographic, socioeconomic and environmental factors in a high transmission setting in Brazil.
-
 News
NewsSmall animals acquire genes from bacteria that can produce antibiotics
A group of small, freshwater animals protect themselves from infections using antibiotic recipes “stolen” from bacteria, according to new research.
-
 News
NewsMicrobes found to destroy certain ‘forever chemicals’
Scientists have discovered specific bacterial species that can destroy certain kinds of “forever chemicals,” a step further toward low-cost treatments of contaminated drinking water sources.
-
 News
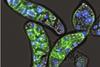
NewsAncient microbes offer clues to how complex life evolved
A single-celled organism, a close relative of animals, harbors the remnants of ancient giant viruses woven into its own genetic code, shedding light on how complex organisms may have acquired some of their genes.
-
 Features
FeaturesA community approach to clean water
The link between water and disease has been recognised for nearly two centuries. Despite this, the current global water situation remains dire. When a top-down approach will not work, community involvement is essential for effective water and sanitation projects.
-
 News
NewsScientists prioritize 6 key pathogens for wastewater surveillance ahead of the Paris 2024 Olympic and Paralympic Games
French health authority researchers have identified priority pathogens that could be suitable for wastewater surveillance (WWS) during the Paris 2024 Olympic and Paralympic Games taking place from 26 July to 11 August and 28 August to 8 September.
-
 News
NewsHot spring microbe delivers nitrite-driven anaerobic ethane oxidation
A microbial culture capable of nitrite-driven anaerobic ethane oxidation was enriched through long-term operation of a nitrite-and-ethane-fed bioreactor, a new study shows.
-
 News
NewsStudy reveals environmental impact of artificial sweeteners on water microbes
A new study demonstrates how sucralose affects the behavior of cyanobacteria — an aquatic photosynthetic bacteria — and diatoms, microscopic algae that account for more than 30% of the primary food production in the marine food chain.
-
 News
NewsMicromachines are powered by tiny, active microorganisms
Researchers have created tiny, vehiclelike structures which can be maneuvered by microscopic algae. The algae are caught in baskets attached to the micromachines, which have been carefully designed to allow them enough room to continue swimming.
-
 Opinion
OpinionCholera: vaccination or better infrastructure?
Vibrio cholerae continues to challenge public health systems worldwide. Should we prioritize vaccination or infrastructure improvements?
-
 News
NewsModel shows how plankton survive in a turbulent world
A researcher studying how particles move in turbulent fluids has created a model including various hydrodynamic factors to study how these particles handle and even utilise turbulence.
-
 Features
FeaturesChanging the culture of Legionella testing
Examining the history of laboratory culture for Legionella spp., and whether it’s time for change.
-
 News
NewsResearchers discover genetic collaboration in harmful algae
A breakthrough study of freshwater harmful algal communities led by Dave Hambright, a Regents’ Professor of Biology at the University of Oklahoma, has discovered that complementary genes in bacteria and algae living in the same algal colonies coordinate the use and movement of nutrients within the colony. This research, funded ...
-
 News
NewsMesocosms allow scientists to study the biodiversity of aquatic organisms
With a new facility funded by the Gips-Schüle Foundation, researchers at the University of Konstanz’s Limnological Institute can now study the development of biodiversity of bodies of water, such as Lake Constance.
-
 News
NewsTiny predator owes its shape-shifting ability to origami-like cellular architecture
For a tiny hunter of the microbial world that relies on extending its neck up to 30 times its body length to release its deadly attack, intricate origami-like cellular geometry is key.
-
 Careers
CareersCan you use a dishwasher instead of a steriliser?
Wondering whether you can sterilise baby bottles in a dishwasher — or use a dishwasher to safely clean bowls, spoons and other baby weaning equipment? AMI microbiologists provide expert advice to Helen Brown of Made for Mums on what you can and can’t do, depending on your baby’s age.
-
 News
NewsResearchers to study links between Great Lakes algal blooms and human health
University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill researcher Hans W. Paerl will join researchers at the University of Michigan for a $6.5 million, five-year federal grant to host a center for studying links between climate change, harmful algal blooms and human health. Source: Aerial Associates Photography, Inc. by ...
-
 News
NewsU-M lands $6.5 million center to study links between Great Lakes algal blooms, human health
Great Lakes researchers at the University of Michigan have been awarded a $6.5 million, five-year federal grant to host a center for the study of links between climate change, harmful algal blooms and human health.
