More Economic Equality – Page 6
-
 News
NewsTiny heroes and innovative technology can fight back against antibiotic-resistant biofilms
Researchers show that antibiotic-infused silver nanoparticles can effectively break down biofilms and also unveil a new sensing method to assess antimicrobial activity.
-
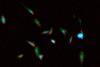 News
NewsInfrared light can pick out biomolecules in living cells
To accelerate biotechnology innovations, such as the development of lifesaving drug therapies, scientists strive to develop faster, more quantitative and more widely available ways to observe biomolecules in living cells. Source: Y. Lee/NIST An image of biomolecules, such as nucleic acids, lipids and proteins, in live cells ...
-
 News
NewsSaline nasal drops reduce the duration of the common cold in young children by two days
Using hypertonic saline nasal drops can reduce the length of the common cold in children by two days, according to a study that will be presented at the European Respiratory Society (ERS) Congress.
-
 News
NewsSmart mask monitors breath for signs of disease and infection
Researchers have developed a prototype for a smart mask that can be used to monitor a range of medical conditions, including respiratory ailments, such as asthma, COPD (chronic obstructive pulmonary disease), and post-COVID-19 infections.
-
 News
NewsUC Santa Barbara to lead $22M NSF-funded center on exceptional microbes
UC Santa Barbara, UC Riverside, and Cal Poly Pomona receive a six-year, $22 million grant to establish a first-of-its-kind BioFoundry that focuses on largely untapped and unexplored extreme microbes.
-
 News
NewsFungus-controlled robots tap into the unique power of nature
By harnessing the innate electrical signals of fungal mycelia, researchers have discovered a new way of controlling ‘biohybrid’ robots that can potentially react to their environment better than their purely synthetic counterparts.
-
 News
NewsTIny microbe rewired to upcycle excess carbon dioxide
Researchers have rewired a microbe to help tackle greenhouse gases in the atmosphere: It takes in carbon dioxide (CO2) gas and produces mevalonate, a useful building block for pharmaceuticals.
-
 News
NewsCRISPR gene scissors switch off with built-in timer
Researchers have discovered a timer integrated into the CRISPR gene scissors that enables the gene scissors to switch themselves off.
-
 News
NewsScientists to investigate why men and women are hit by the flu differently
Turns out that there is a biological reason why women and men suffer viral infections like influenza differently – and a team of scientists are extending their research to better understand why and how to design better, possible sex-specific treatments.
-
 News
NewsScientists uncover how microbial enzymes lap up carbon dioxide
The remarkable affinity of the microbial enzyme iron nitrogenase for the greenhouse gas CO2 makes it useful for future biotechnology, a new study suggests.
-
 News
NewsLens-free fluorescence instrument detects deadly microorganisms in drinking water
A new approach promises low-cost, real-time water quality monitoring for developing countries, disaster areas and rapid testing needs at events like the Paris Olympics.
-
 Opinion
OpinionWheat straw and muncipal waste - how next generation biofuels can save the world
With greenhouse gas emissions peaking, the search for renewables is intensifying. AMI Healthy Land Scientific Advisory Group member Juan Luis Ramos and his colleagues Estrella Duque and Patricia Godoy take a look at the future of biofuels.
-
 Careers
CareersThe role of fungi in the Amazonian bioeconomy
The term bioeconomy is entering the mainstream and has brought discussions on sustainable development into the spotlight, in particular for the Amazon region.
-
 News
NewsStudy highlights factors associated with higher tuberculosis risk in South Africa
Tuberculosis is the world’s top infectious killer. About 10 million people fall ill with the disease every year, and roughly 1.5 million people die because of it, according to the World Health Organization. Additionally, about one-quarter of the world’s population is infected with the disease’s causative agent Myctuberobacterium tuberculosis. ...
-
 News
NewsResearchers find new way to turn bacteria into cellulose-producing mini-factories
A new approach to turning microorganisms into living mini-factories has been developed, allowing scientists to produce tens of thousands of variants of the bacterium very quickly.
-
 News
NewsApplied Microbiology International unveils 11 new Global Ambassadors
AMI has announced that it has recruited 11 new Global Ambassadors from around the world. Global ambassadors have a range of expertise and knowledge across regions and sectors, and support and promote applied microbiology and our organisation.
-
 News
NewsNew FAIRY rapid method determines virus infectivity
A new method that can rapidly determine whether a virus is infectious or non-infectious could revolutionise the response to future pandemics.
-
 News
NewsIt’s not just humans — bacteria have memory too
Beneficial bacteria — used in probiotics and biological pest control to fight harmful bacteria — possess memory, and even pass information on to future generations.
-
 News
NewsUse of synthetic microbial communities has stalled - but we can get moving again
Use of synthetic microbial communities outside the lab is rare - but a more systematic approach could improve confidence in their long-term behaviour and address ethical considerations. Source: Sarah Keetch and Alex Fedorec That’s the message from a review of the field by scientists at University College ...
-
 News
NewsRhizobacteria identified to combat striga and boost sorghum yields in Ethiopia
Researchers have identified potential Striga-suppressing rhizobacteria associated with sorghum, which have been shown to significantly reduce Striga seed germination rates.
