More News – Page 298
-
 News
NewsScientists find new eco-friendly source of nanoparticles in edible seaweed
An edible seaweed could provide a potential environmentally friendly source of silver nanoparticles for antibacterial and anticancer applications.
-
 News
NewsBacteria flourish in plumes of deep ocean volcanoes
Deep down in the ocean at tectonic plate boundaries, hot fluids rise from so-called hydrothermal vents. The fluids are devoid of oxygen and contain large amounts of metals such as iron, manganese or copper. Some may also transport sulphides, methane and hydrogen. Source: HACON cruise 2021, REV Ocean ...
-
 News
NewsMicrobes can create a more peaceful world: Scientists call to action
Microorganisms should be ‘weaponised’ to stave off conflicts across the globe, according to a team of eminent microbiologists. The paper ‘Weaponising microbes for peace’ by Anand et al, outlines the ways in which microbes and microbial technologies can be used to tackle global and local challenges that could otherwise ...
-
 News
NewsStudy shows New York City rats carry SARS-CoV-2
Wild rats in the New York City municipal sewer systems and elsewhere in the city have been exposed to SARS-CoV-, a new study has revealed.
-
 News
NewsEngineered bacteria track down tumours, then signal the immune cells
Researchers have created a ’bacterial suicide squad’ that targets tumours, attracting the host’s own immune cells to the cancer to destroy it.
-
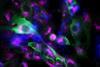 News
NewsFungal spores bind to lung cell protein to escape human defences
The pathogenic fungus Aspergillus fumigatus escapes elimination from surface cells of the human lung by binding to a human protein.
-
 News
NewsEating more live microbes leads to better health and lower weight
A new study shows lower weight and better overall health in those who consume more live microorganisms daily - including those in raw fruit and vegetables.
-
 News
NewsScientists unlock indole in soil bacteria to create prodrugs
Researchers from Bochum and Leipzig have successfully used a soil bacterium to specifically produce prodrugs. The key to this step was a detailed understanding of the metabolisation of indole, a natural compound which first must be activated in microorganisms. To do this, they needed a monooxygenase, the molecular structure of ...
-
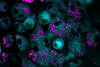 News
NewsScientists develop novel combination therapy for treating vancomycin-resistant bacterial infections
Researchers have developed a novel combination therapy using an anticancer agent, mitoxantrone (MTX), together with an antibiotic, vancomycin, for treating bacteria that are resistant to the vancomycin.
-
 News
NewsGeoactive fungus mines rare earth elements from monazite ore
Researchers have demonstrated that geoactive fungi can play a significant role in bioweathering of the phosphate mineral monazite, opening a route to biorecovery of important rare earth elements (REEs).
-
 News
NewsScientists reveal molecular structure of bacterial gas vesicles
For the first time, scientists have described the molecular structure of gas vesicles, used by some water-based bacteria to regulate their floatability.
-
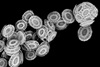 News
NewsTiny chalk discs in oceans play key role in earth’s carbon cycle by propagating viruses
Researchers find biomineral structures formed by marine algae foment viral infection, contributing positively to capture CO2.
-
 News
NewsCommercial water purification system may have caused Mycobacterium infection in 4 hospitalized patients
A study of four cardiac surgery patients in one hospital found that they developed Mycobacterium abscessus infections, a multidrug-resistant nontuberculous mycobacteria, potentially due to a commercial water purifier.
-
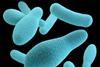 News
NewsStudy sheds fresh light on how wet heat kills bacterial spores
Researchers have shed new light on a possible mechanism whereby bacterial spores are killed by wet heat, potentially paving the way to more effective ways of killing spores.
-
 News
NewsClinical trial finds temperature-stable TB vaccine is safe and prompts immune response
A clinical trial testing a freeze-dried, temperature-stable experimental tuberculosis (TB) vaccine in healthy adults found that it was safe and stimulated both antibodies and responses from the cellular arm of the immune system.
-
 News
NewsIntellifoods Labs, LLC teams with Mason scientists to cut food bacterial contamination detection time
Mason Associate Professor of Infectious Diseases and Microbiology, Ramin M Hakami has received $35,000 in grants from Intellifoods Labs, LLC to continue examining methods to reduce the time to detect the presence of bacteria in food samples.
-
 News
NewsFertilizer additive makes slurry more climate-friendly
Scientists have found that combining farm slurry with calcium cyanamide brings the production of greenhouse gas mathane to an almost complete halt.
-
 News
NewsAMI welcomes prospect of Horizon re-entry following Brexit deal
Applied Microbiology International (AMI) has welcomed the EU Commission President’s recent mention of starting work on associating the UK to the €100bn (£88.6bn) Horizon Europe programme.
-
 News
NewsGut microbes spur immune cells to mend damaged muscles
Researchers have found that gut microbes spur the production of a class of regulatory T cells that play a role in repairing injured muscles and mending damaged livers.
-
 News
NewsInkjet printer tech inspires faster and cheaper way to identify bacteria in fluids
An innovative adaptation of the technology in an old inkjet printer plus AI-assisted imaging leads to a faster, cheaper way to spot bacteria in blood, wastewater, and more.
