All Research News articles – Page 122
-
 News
NewsA lung pathogen’s dilemma: infect or resist antibiotics?
Research has uncovered how Pseudomonas aeruginosa manages the trade-off between colonizing and surviving during infection by switching between biofilm formation for antibiotic protection and a more mobile, “planktonic” state to spread and access nutrients.
-
 News
NewsGut bacteria transfer genes to disable weapons of their competitors
New research shows how common gut bacteria tame their antagonistic neighbors by transferring genes that change their weapon systems.
-
 News
NewsBeneficial gut microbe has surprising metabolic capabilities
To address childhood malnutrition — which affects 200 million children globally — researchers at Washington University School of Medicine in St. Louis developed a therapeutic food that nourishes the collections of beneficial microbes that reside in the gut, and improves children’s growth and other measures of their health. ...
-
 News
NewsBacteria and fungi found on bat wings that could help fight deadly white-nose syndrome
Bacteria and fungi from the wings of bats could play a significant role in saving them from white-nose syndrome (WNS), a fungal disease affecting the skin of wings and muzzle, which has nearly wiped out vulnerable bat populations across North America.
-
 News
NewsA metabolic secret of ethane-consuming archaea unraveled
Scientists have presented a study on the degradation of ethane, the second most abundant alkane in seeps on the deep seafloor. They characterized enzymes involved in the process and found that their reaction breaks an established dogma in the field of anaerobic biochemistry.
-
 News
NewsLyme borreliosis: New approach for developing targeted therapy
A research team has made significant progress in understanding the mechanism of Lyme borreliosis infection and identified a potential way forward for the development of targeted therapies that do not rely on antibiotics.
-
 News
NewsUnnoticeable electric currents could reduce skin infections
Using a few zaps of electricity to the skin, researchers can stop bacterial infections without using any drugs. For the first time, researchers have designed a skin patch that uses imperceptible electric currents to control microbes.
-
 News
NewsStudy yields evidence of oldest confirmed photosymbiosis in corals
Researchers have demonstrated, using nitrogen isotope analyses, that some extinct corals from the Middle Devonian period were already symbiotic. This represents geochemical evidence of the oldest confirmed photosymbiosis in corals.
-
 News
NewsMaternal antibodies interfere with malaria vaccine responses
Maternal antibodies passed across the placenta can interfere with the response to the malaria vaccine, which would explain its lower efficacy in infants under five months of age, according to research.
-
 News
NewsRepeated COVID vaccines enhance mucosal immunity against the virus
New work has found that repeated Covid-19 vaccinations lead to the presence of mucosal antibodies, for example, inside the nose.
-
 News
NewsPolar bears’ exposure to pathogens is increasing as their environment changes
As the Arctic warms, polar bears now face a greater risk of contracting several pathogens than bears three decades ago, a new study reveals.
-
 News
NewsStructural biology analysis of a Pseudomonas bacterial virus reveals a genome ejection motor
Bacterial viruses, known as phages, are the most abundant biological entities on the planet and are increasingly used as biomedicines to eradicate antibiotic-resistant pathogenic bacteria.
-
 News
NewsChemists pioneer metallodrug-antibiotic combination strategy to combat superbugs
A combination of different types of antibiotics with bismuth-based drugs, such as Pepto-Bismol, disrupts bacterial iron homeostasis, effectively restoring the bactericidal function of multiple antibiotics.
-
 News
NewsScientists discover how fungi interact with soil actinomycetes
Discovery of a unique microbial interaction offers potential for environmentally friendly control of rice blast disease.
-
 News
NewsTire-wear particles disrupt gut-liver function in aquatic organisms
Researchers have uncovered the adverse health effects of tire-wear particles (TWPs) on aquatic organisms. The study focused on the hepatotoxicity of TWP leachates, revealing significant impacts on the gut-liver axis and oxidative stress levels in test organisms.
-
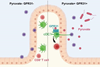 News
NewsStudy reveals how our gut cells detect harmful invaders
Researchers hve found that the GPR31 path in ‘gut surveillance’ cells detects bacterial metabolites and triggers immune responses, opening new possibilities for drug development, vaccines, and probiotics to fight infections.
-
 News
NewsFloor swabbing could help prevent COVID-19 outbreaks in hospitals
In two Ontario hospitals, high levels of SARS-CoV-2 on floors correlated with COVID-19 cases among healthcare workers and patients, suggesting floor swabbing as a potential method to prevent outbreaks.
-
 News
NewsPlastic mulch is contaminating agricultural fields
Using plastic sheets for weed control, even under current best management practices, pollutes soil with macro- and micro-plastics and negatively affect critical soil functions, according to a study.
-
 News
NewsBeyond gut health: prebiotics promise mental wellness
Research shows a prebiotic supplement can reduce inflammation. This could help with symptoms of stress, anxiety, and depression in people with metabolic syndrome.
-
 News
NewsArtificial ‘nose’ can sniff out damaged fruit and spoiled meat
The smell of cut grass, or the fumes from refueling your car, are all the result of volatile organic compounds. A new approach to antenna technology can actually detect and identify them.
