All Research News articles – Page 214
-
 News
NewsResearchers reveal how microbes return after a wildfire
A study suggests that dispersal - through air or rain, for example - plays a major role in microbial succession after a destructive fire.
-
 News
NewsClimate warming could impact forest resilience by disrupting fungal networks
Researchers find that warming trends will likely result in major disturbances of networks of fungi, potentially harming forest resilience.
-
 News
NewsAssays for rapid and visual detection of monkey B virus
Two recombinase polymerase amplification (RPA) assays have been developed for Monkey B virus that target two conserved genes combined with a one-off, closed visualization strip device
-
 News
NewsNew research reveals gut microbiota link to colitis - and therapetic strategies
Researchers have revealed a new and critical role of Axin1 in regulating intestinal epithelial development and microbial homeostasis.
-
-
 News
NewsNanoparticle vaccine candidate shows promise against emerging tick-borne virus
Researchers have used nanoparticles to develop a potential vaccine candidate against Dabie Bandavirus, formerly known as Severe Fever with Thrombocytopenia Syndrome Virus (SFTSV), a tick-borne virus that has no prevention, treatment or cure.
-
 News
NewsHops compound reduces abundance of gut microbe associated with metabolic syndrome
Researchers have shown in a mouse model and lab cultures that a compound derived from hops reduces the abundance of a gut bacterium associated with metabolic syndrome.
-
 News
NewsDiscovery in mosquitoes could lead to new strategy against dengue fever
Researchers have discovered that a protein in the mosquito Aedes aegypti , Argonaute 2, has a key role - via several biological mechanisms - in keeping mosquitoes healthy and active despite the presence of viral infections like dengue and Zika.
-
 News
NewsCOVID-19 could hold key to spotting viruses with pandemic potential
Certain SARS-CoV-2 variants of concern are evolving to do a better job of shutting down human innate immune responses, according to new research.
-
 News
NewsUnzipping mRNA rallies plant cells to fight infection
Scientists studying a plant called Arabidopsis thaliana have discovered short snippets of folded RNA that are unzipped in the presence of a pathogen to allow plant cells to make defense proteins to fight infection.
-
 News
NewsResearch on bee virus origins uncovers buzz-worthy breakthrough
A study of deformed wing virus, a key driver in declines among European honey bee populations, show that one of the most common strains, DWV-A, originated in Asia and not Europe, as previously suggested.
-
 News
NewsUnderstanding bacterial motors may lead to more efficient nanomachine motors
Scientists have identified the FliG molecule in the flagellar layer, the ‘motor’ of bacteria, and revealed its role in the organism, potentially suggesting ways in which future engineers could build nanomachines with full control over their movements.
-
 News
NewsPotential spoilage microbe found in microfiltered milk
A new filtration process that aims to extend milk’s shelf life can result in a pasteurization-resistant microbacterium passing into fluid milk if equipment isn’t properly cleaned early, scientists have found.
-
 News
NewsSyphilis transmission networks and AMR in England uncovered using genomics
Scientists use genomics to uncover syphilis transmission patterns in England, in a pioneering new approach for STI surveillance.
-
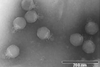 News
News25 new phage viruses IDed in Barcelona’s wastewaters
Scientists have identified 25 new viruses that infect bacteria in the human intestinal tract in wastewaters around the city’s metropolitan area and in some towns nearby.
-
 News
NewsDeadly frog disease more prevalent in central Florida than expected
As climate change alters temperature and rainfall patterns in North America, researchers say more areas could experience conditions favorable to the disease known as amphibian Perkinsea.
-
 News
NewsNew SARS-CoV-2 variant Eris on the rise
The EG.5 lineage of SARS-CoV-2, known as Eris, which has been spreading globally, has been found to be able to escape neutralizing antibodies better than other currently circulating SARS-CoV-2 lineages.
-
 News
NewsPolar experiments reveal seasonal cycle in Antarctic sea ice algae
A new study provides the first measurements of how sea-ice algae and other single-celled life adjust to seasonal changes, offering clues to what might happen as this environment shifts under climate change.
-
 News
NewsNew enzyme reduces the carbon footprint of methane by converting it into methanol
A team led by Professor Osami Shoji at Nagoya University in Japan has developed a technology to convert methane, the principal component of natural gas, into methanol at room temperature in water. They used an enzyme that can be easily mass-produced, offering the possibility of a cheap and effective ...
-
 News
NewsLife in boiling water similar in far-flung locations
Scientists studied hot springs on different continents and found similarities in how some microbes adapted despite their geographic diversity, yeilding clues to the evolution of life.
