All university of exeter articles
-
 News
NewsCandida auris: genetic process revealed which could be treatment target for deadly fungal disease
Scientists have discovered a genetic process which could unlock new ways to treat a mysterious and deadly fungal infection which has shut down multiple hospital intensive care units.
-
 News
NewsMicroplastics pose a human health risk in more ways than one
A new study shows that microplastics in the natural environment are colonised by pathogenic and antimicrobial resistant bacteria. The study team calls for urgent action for waste management and strongly recommends wearing gloves when taking part in beach cleans.
-
 News
NewsNew research confirms HPV vaccination prevents cervical cancer
Two new Cochrane reviews show strong and consistent evidence that HPV vaccines are effective in preventing cervical cancer and pre-cancerous changes, especially when given to young people before they are exposed to the virus.
-
 News
News‘Cocktails’ of common pharmaceuticals in our waterways may promote antibiotic resistance
New research has shown, for the first time, how mixtures of commonly used medications which end up in our waterways and natural environments might increase the development of antibiotic resistant bacteria.
-
 News
NewsCoral reefs set to stop growing as climate warms, scientists warn
Most coral reefs will soon stop growing and may begin to erode – and almost all will do so if global warming hits 2°C, according to a new study in the western Atlantic.
-
 News
NewsNew research reveals ancient alliance between woody plants and microbes has potential to protect precious peatlands
New research shows that during historic periods of drying the growth of woody plants in a subtropical Chinese peatland improved the quality of organic matter and suppressed decomposing microbial activity.
-
 News
NewsBeetroot juice lowers blood pressure in older people by changing oral microbiome
The blood pressure lowering effect of nitrate-rich beetroot juice in older people may be due to specific changes in their oral microbiome, according to the largest study of its kind.
-
 News
NewsNew test could save lives from deadly fungal infection that spiked during pandemic
A new lateral-flow test could one day save lives across the world through early detection of a deadly fungal disease which dramatically spiked during the COVID-19 pandemic.
-
 News
NewsNew pests and diseases will cut UK tree growth
The arrival of new plant pests and diseases is likely to severely damage UK trees and woodlands in the coming decades, new research shows.
-
 News
NewsScientists uncover how bacterial resistance to synergistic drug treatments is arising
Scientists investigating the potential of combined and more powerful drug treatments have found that antimicrobial resistance to these is arising via the vitamin B2 synthesis pathway.
-
 News
NewsPlague transmission may have begun a century before the Black Death, study shows
Evidence from 13th-century chroniclers and physicians indicates plague may have been involved in epidemics a century before the Black Death, a new study shows. Source: Dschingis Khan und seine Erben (exhibition catalogue), München 2005, p. 253 Conquest of Baghdad by the Mongols 1258. Right part of a double-page ...
-
 News
NewsStudy shows some species are susceptible to broad range of viruses
A study of fruit flies shows some species are highly susceptible to a wide range of viruses. But fly species that were resistant to one virus were generally resistant to others – including very different types of virus.
-
 News
NewsOral microbiome may affect cognitive function as we age
The microbial ecosystems within our mouths may affect our cognitive function as we age, according to a study. Interventions such as prebiotics, including dietary nitrate, have potential for delaying cognitive decline.
-
 News
NewsExeter launches second round of global funding to tackle antifungal drug resistance
A University of Exeter funding scheme designed to combat the global challenge of fungal antimicrobial resistance (fAMR) has announced a new call for applications.
-
 News
NewsSpecialist under-ice species at risk as Arctic warms
’Specialist’ lifeforms that live under Arctic sea ice are at risk as the ice retreats, new research shows. Scientists studied microscopic organisms in four environments – open ocean, river mouths, coasts and under sea ice – in the sea off northern Canada.
-
 News
NewsBacteria breakthrough could accelerate mosquito control schemes
Mosquito larvae grow faster if they’re exposed to particular bacteria, according to a new study that could help global health programmes.
-
 News
NewsKeeping fewer friends protects ageing monkeys from diseases
New research shows becoming less sociable protects older monkeys from getting ill.
-
 News
NewsScientists have successfully bred corals to improve their heat tolerance
A new study has shown that selective breeding can lead to a modest rise in coral heat tolerance. The study documents the world’s first effort to selectively breed adult corals for the ability to survive intense marine heatwaves.
-
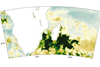 News
NewsPlankton bloom off Madagascar linked to drought in South Africa
Researchers show that dust from drought-stricken Southern Africa caused a bloom of marine phytoplankton off the southeast Madagascar coast from November 2019 through February 2020.
-
 News
News‘Invisible forest’ of algae thrives as ocean warms
An ‘invisible forest’ of phytoplankton is thriving in part of our warming ocean, new research shows. The study examined phytoplankton at the ocean surface and the ‘subsurface’ – a distinct layer of water beneath – to see how climate variability is affecting them.
