All The Microbiologist articles in Web Issue – Page 196
-
 News
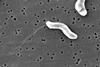
NewsUnderstanding bacterial motors may lead to more efficient nanomachine motors
Scientists have identified the FliG molecule in the flagellar layer, the ‘motor’ of bacteria, and revealed its role in the organism, potentially suggesting ways in which future engineers could build nanomachines with full control over their movements.
-
 News
News Fast-track strain engineering for speedy biomanufacturing
The time and money required to engineer microbes to produce vital medicines and chemicals can be dramatically reduced with a new model-based method.
-
 News
NewsPotential spoilage microbe found in microfiltered milk
A new filtration process that aims to extend milk’s shelf life can result in a pasteurization-resistant microbacterium passing into fluid milk if equipment isn’t properly cleaned early, scientists have found.
-
 Opinion
OpinionHas a viral contribution to Alzheimer’s disease been in front of our noses this whole time?
The concept that a viral infection may induce pathology in regions far from its active location is gaining traction. Could this phenomenon also be at play in Alzheimer’s disease?
-
 Careers
CareersPost-doc appreciation week 2023
AMI’s Policy Team sits down with Thomas Thompson for a short interview about the experience of doing a post-doc in microbiology.
-
 Features
FeaturesPostdoc Appreciation Week
We held a Q&A for postdocs from the University of Liverpool and The Quadram Institute to showcase their skills beyond research, and their views on the importance of postdocs within microbiology.
-
 News
NewsTiny nanocarriers could prove the magic bullet for acne sufferers
A new antibacterial compound was encased in tiny, soft nanoparticles 1000 times smaller than a single strand of human hair and applied in a gel form to targeted acne sites.
-
 News
NewsSyphilis transmission networks and AMR in England uncovered using genomics
Scientists use genomics to uncover syphilis transmission patterns in England, in a pioneering new approach for STI surveillance.
-
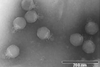 News
News25 new phage viruses IDed in Barcelona’s wastewaters
Scientists have identified 25 new viruses that infect bacteria in the human intestinal tract in wastewaters around the city’s metropolitan area and in some towns nearby.
-
 News
NewsScientists pioneer dual trojan horse approach to combat superbugs
In the relentless battle against antibiotic-resistant superbugs, science continues to unveil ingenious strategies to address their vulnerability. Like other bacteria, superbugs have a unique weakness – their dependence on iron for growth and survival. Iron serves as an essential nutrient that bacteria utilise for various cellular processes, including DNA replication, ...
-
 News
NewsDeadly frog disease more prevalent in central Florida than expected
As climate change alters temperature and rainfall patterns in North America, researchers say more areas could experience conditions favorable to the disease known as amphibian Perkinsea.
-
 News
NewsNew SARS-CoV-2 variant Eris on the rise
The EG.5 lineage of SARS-CoV-2, known as Eris, which has been spreading globally, has been found to be able to escape neutralizing antibodies better than other currently circulating SARS-CoV-2 lineages.
-
 News
NewsGenetically modified bacteria break down plastics in saltwater
Researchers have genetically engineered a marine microorganism to break down plastic in salt water - specifically, polyethylene terephthalate (PET), a plastic used in everything from water bottles to clothing.
-
 News
NewsNICER than CRISPR: new gene editor reduces unintended mutations
Researchers led by Osaka University develop a new gene modification technique known as NICER that significantly reduces off-target mutations in DNA.
-
 News
NewsPolar experiments reveal seasonal cycle in Antarctic sea ice algae
A new study provides the first measurements of how sea-ice algae and other single-celled life adjust to seasonal changes, offering clues to what might happen as this environment shifts under climate change.
-
 News
NewsMajority rule in complex mixtures
Göttingen University researchers use mathematical model to identify new mechanism for control of phase separation.
-
 News
NewsNew enzyme reduces the carbon footprint of methane by converting it into methanol
A team led by Professor Osami Shoji at Nagoya University in Japan has developed a technology to convert methane, the principal component of natural gas, into methanol at room temperature in water. They used an enzyme that can be easily mass-produced, offering the possibility of a cheap and effective ...
-
 News
NewsLife in boiling water similar in far-flung locations
Scientists studied hot springs on different continents and found similarities in how some microbes adapted despite their geographic diversity, yeilding clues to the evolution of life.
-
 News
NewsLack of maternal care affects development, microbiome and health of wild bees
Most wild bees are solitary, but one tiny species of carpenter bees fastidiously cares for and raises their offspring, an act that translates into huge benefits to the developing bee’s microbiome, development and health.
-
 News
NewsScientists uncover COVID’s weakness - the need for human cells
New UC Riverside research has revealed COVID’s Achilles heel — its dependence on key human proteins for its replication — which can be used to prevent the virus from making people sick.
