Healthy land
Land has a wide variety of uses: agricultural, residential, industrial, and recreational. Microbes play a key role in the terrestrial ecosystem, providing symbiotic relationships with plants. Human use of land has led to the exhaustion of nutrients in soils, contamination of land, and a reduction in biodiversity. Applying our knowledge of microbes will be essential in restoring the biodiversity of affected ecosystems. Greater research into how microbes impact human life on land could all have a positive impact, by increasing crop production, repurposing areas of land and improving microbial biodiversity in soil, land, and water.
News
Corpses leave microbial fingerprints behind in the soil long after they’re gone
Researchers have found that trace elements of a cadaver linger at an original dump site even after an extensive amount of time. These elements can provide insights into postmortem processes, helping forensic investigators uncover clandestine burials and relocate the remains of murder victims.
Read story- News
Ticks carrying more than one pathogen are on the rise in US Northeast
Tick-borne diseases are on the rise in the northeastern US, with many ticks carrying more than one pathogen. Most commonly found together were Borrelia burgdorferi and Babesia microti. Co-infection with these two pathogens was more frequent than expected, approaching 11% by the end of the study.
- News
Scientists design metal-enhanced biochar to boost clean hydrogen production from agricultural waste
A new study reports that specially engineered biochar made from agricultural waste could significantly increase biohydrogen production by improving the way microbes transfer electrons during fermentation.
- News
Island birds reveal surprising link between immunity and gut bacteria
Scientists have uncovered a hidden link between gut health and the immune system, all thanks to a tiny island bird. They collected the poo of the Seychelles warbler to analyse their gut bacteria – and found that their immune genes influence which gut microbes thrive.
More Healthy Land
News
Machine learning reveals when biochar helps or harms soil life
Researchers have shown that biochar can either help or harm soil organisms depending on how it is produced and applied. The research analyzed results from dozens of previous experiments to better understand how biochar affects plants, microbes, and soil animals.
- News
Scientists trace crop viruses back to the last Ice Age
Long before humans cultivated crops or sailed between continents, a group of plant viruses was already evolving among wild plants in Eurasia. Tthe ancestors of modern tymoviruses likely emerged before the last Ice Age, a new study reveals.
- News
Tiny vesicles, big risk: Environmental sweeteners trigger antibiotic resistance transfer
A new study reveals that mixtures of artificial sweeteners can stimulate soil bacteria to release microscopic extracellular vesicles that carry antibiotic resistance genes (ARGs).
- News
Shifting from biotic to abiotic drivers of urban microbial multifunctionality under drought and rehydration
Scientists conducting microcosm experiments on Zoysia japonica, a common urban turfgrass, simulated four drought intensities and recovery by rehydration. They analyzed alteration in microbial communities and biochemical cycling to pinpoint the drivers of urban microbial multifunctionality.
- News
Soybeans recruit beneficial soil microbes to defend against major pest
Researchers report that resistant soybean varieties actively recruit beneficial soil microorganisms that help suppress soybean cyst nematode. Even more striking, those protective microbes can be transferred to soil to help defend susceptible soybean plants.
- News
Scientists successfully harvest chickpeas from ‘moon dirt’
Scientists have successfully grown and harvested chickpeas using simulated “moon dirt,” the first instance of this crop produced in this medium. They added vermicompost and coated the chickpeas with the fungi arbuscular mycorrhizae before planting.
- News
Hidden viral networks in soil microplastics may shape the future of sustainable agriculture
A new scientific review highlights the complex interactions between soil microbes and viruses that occur on the surface of microplastic particles. The study reveals that these microscopic relationships may influence soil health, ecosystem recovery, and the long term sustainability of agriculture.
- News
Diversification of termite diets was made possible by genome modifications
Study reveals that evolutionary divergence occurred before ecological divergence, enabling these insects to feed on both wood and soil. Future discoveries may be applied to the production of biofuels.
- News
One Health antimicrobial resistance modelling: from science to policy
Researchers have identified fundamental gaps in current mathematical modelling approaches that prevent translation of science into policy, including data limitations, knowledge gaps about AMU-AMR relationships, and the absence of international coordination mechanisms similar to climate change efforts.
- News
New study reveals how hygienic honey bees show unique advantages in fighting infectious pathogens in adult bees
For the first time, research shows that a key social trait in honey bees is linked to measurable physiological advantages that can improve colony survival. The study uncovers how hygienic honey bee colonies mount stronger individual immune defenses against Nosema ceranae.
- News
Pig farm ammonia pollution may indirectly accelerate climate warming, new study finds
A new study shows that ammonia released from intensive livestock farms can significantly increase nearby soil emissions of nitrous oxide, a powerful greenhouse gas that contributes to climate change and ozone depletion.
- News
Nitrous oxide, a product of fertilizer use, may harm some soil bacteria
While some nitrous oxide is produced naturally at the plant root, agricultural practices can increase its levels. While it has long been believed that nitrous oxide doesn’t meaningfully interact with living organisms, a new paper shows that it may in fact shape microbial communities.
- News
Modified biochar helps compost retain nitrogen and build richer soil organic matter
A new study reports that specially engineered biochar can significantly improve compost quality by reducing nitrogen loss and accelerating the formation of stable humic substances. The findings offer a promising strategy for transforming organic waste into more effective fertilizers while lowering environmental emissions.
- News
Growing buildings in space: researchers test fungi as construction material for moon, Mars
A NASA-funded project will investigate whether certain fungi can be combined with regolith — loose rock and soil found on the surface of the moon and other planets — to create materials that could one day support construction in places other than Earth.
- News
Prolonged drought linked to instability in key nitrogen-cycling microbes in Connecticut salt marsh
A prolonged drought in southeastern Connecticut reduced the stability of microorganisms responsible for a critical step in the nitrogen cycle in a coastal salt marsh, according to new research.
- News
Underground fungal map of the world’s oldest, slowest-growing rainforest trees can boost the resilience of Earth’s long-term carbon sinks
Protecting and conserving old trees will protect hundreds, if not thousands, of mycorrhizal and other fungal species that inhabit soils around these giants, each of which play a role we might not fully understand in keeping these forests healthy and resilient.
- News
Biodegradable mulch isn’t disappearing as expected, new study warns
Scientists investigated how soybean roots influence the degradation of PBAT microplastics in soil. They tracked both polymer loss and monomer accumulation over a full 70-day plant growth cycle, revealing size-dependent and condition-specific rhizosphere effects.
- News
Editing for timing, not overdrive: A new genetic route to fire blight resistance in apple
Fire blight remains one of the most destructive bacterial diseases threatening global apple production. A new study identifies a family of inducible lectin genes, MdAGGs, as critical components of apple immune defense and demonstrates that their precise activation timing is key to effective resistance.
- News
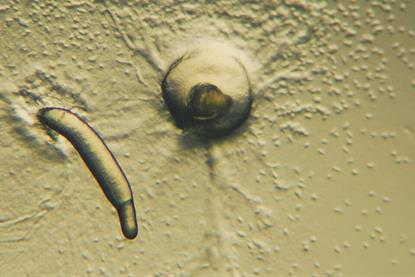
A common CRISPR platform enables comparative studies of multicellularity in social amoebae
Researchers have established a CRISPR genome editing technique that enables comparative analysis of the evolution of multicellularity across different species of social amoebas (cellular slime molds). Until now, genetic studies had been largely restricted to a single model species.