All Editorial articles – Page 61
-
 News
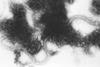
NewsMushroom chemical teams with phages to deliver a one-two punch to MRSA
A chemical found in mushrooms can be teamed with bacteriophages to deliver a one-two punch to antibiotic-resistant infections, reveals a study presented at MLS Future Forum 2025.
-
 News
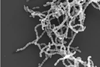
NewsEven healthy children can be severely affected by RSV
It is not only premature babies and children with underlying diseases who suffer from serious respiratory syncytial virus (RSV) infections. Even healthy, full-term babies are at significant risk of intensive care or prolonged hospitalisation – especially during the first three months of life.
-
 News
NewsCan the ‘good’ bacteria in your mouth act as probiotic cavity fighters?
Discovery of clumping molecules made by gene clusters in the oral microbiome may lead to ways to reengineer the microbes in plaque, a new study shows.
-
 News
NewsCan a healthy gut microbiome help prevent childhood stunting?
Researchers find gut microbiome turnover in children is linked to poor growth outcomes, pointing to microbiome-based diagnostics for malnutrition.
-
 News
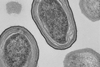
NewsGiving food waste fermentation a ‘jolt’ increases chemical production
Adding an electrical jolt to fermentation of industrial food waste speeds up the process and increases the yield of platform chemicals that are valuable components in a wide range of products, new research shows.
-
 News
NewsOcean warming puts vital marine microbe Prochlorococcus at risk
A new study finds that Prochlorococcus prefers ocean water between 66 and 86 degrees and doesn’t tolerate water much warmer. Climate models predict that subtropical and tropical ocean temperatures will exceed that threshold in the next 75 years.
-
 News
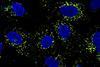
NewsNew insight into yam disease defense: how leaf traits and ABA stop anthracnose
A research team has isolated the anthracnose pathogen infecting greater yam and identified it as Colletotrichum alatae—the first report of this species in yam.
-
 News
NewsStudy reveals how dengue rewires the immune system, reshaping vaccine response
Just as a computer’s operating system can be rewritten after a major update, dengue infection can ‘re-programme’ the body’s immune system, leaving a long-lasting genetic imprint that influences how people respond to future infections—an effect not seen with vaccination.
-
 News
NewsStudy shows how diet and gut microbiota can counter the baby blues
Microbiome diversity and relative abundance of butyrate-producing bacteria were associated with high levels of depressive mood. But a diet rich in fermented foods, soy products, mushrooms, and seaweed may help regulate the gut environment and contribute to preventing depression.
-
 News
NewsCoral-inspired pill offers a new window into the hidden world of the gut
Marine corals have evolved intricate, porous structures that shelter diverse microbial communities. Researchers have borrowed this biological blueprint to create an ingestible pill that can sample bacteria from one of the most inaccessible regions of the human body: the small intestine.
-
 News
NewsPeanut shell biochar composite shows promise for removing antibiotic-resistant bacteria from aquaculture wastewater
Researchers have developed a novel, low-cost catalyst that efficiently removes antibiotic-resistant bacteria (ARB) from aquaculture wastewater, offering a potential new solution to one of today’s most pressing environmental and public health challenges.
-
 News
NewsFrailty fuels gut imbalance and post-surgery gastrointestinal risks
Scientists found that residual intra-abdominal microbes, especially in frail patients, drive gastrointestinal complications after bladder cancer surgery.
-
 News
NewsStudy shows not all dietary proteins are digested the same way
As protein-rich diets become increasingly popular, a new study suggests that categorizing dietary proteins as either animal- or plant-based fails to effectively capture the source-specific differences in their composition, digestive efficiency and accessibility to the gut microbiota.
-
 News
NewsDe-mystifying common misconception about the prevalence of Legionella bacteria
There is a common misconception that Legionella is only found in air conditioners and water towers - however, a new study has found people are likely exposed to the bacteria through other sources, including through soil.
-
 News
NewsNew antibiotic to fight superbug C. diff proves effective in clinical trial
As the effectiveness of antibiotics meant to fight the deadly superbug Clostridioides difficile wanes, a research team is seeing positive results of a new antibiotic on the scene – ibezapolstat – which is proving successful in fighting these infectious bacteria in clinical trials.
-
 News
NewsScientists unveil viral mechanism behind nasopharyngeal cancer spread
Researchers have discovered that the Epstein-Barr virus (EBV), a common human virus closely linked to nasopharyngeal carcinoma (NPC), can change the 3D structure of the human genome inside cancer cells, much like assembling building blocks.
-
 News
NewsA survival kit for smallpox viruses
Scientists have discovered a previously unknown type of assembly chaperone during their analysis of poxviruses, and they have decoded its function in full detail. This is the first known chaperone that is not formed by a protein but by a nucleic acid — specifically RNA.
-
 News
NewsResearchers map key human proteins that power coronavirus replication, pointing to new treatment strategies
Scientists have pinpointed dozens of human proteins that SARS-CoV-2 needs to complete its full life cycle, from entering a cell to replicating and releasing new viral particles.
-
 News
NewsIn extensive sequencing study, scientists find few links between cancer and microbiome
Scientists say a study that sequenced human cancers found far less microbial DNA sequences than earlier studies reported in the same cancer tissue samples.
-
 News
NewsFungi–biochar partnership boosts soil health and crop growth under cadmium stress
A study reports that combining arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi (AMF) with biochar can reshape soil microbiomes, reduce cadmium uptake, and dramatically improve plant growth, offering a sustainable strategy for restoring farmland contaminated with heavy metals.
