All Helmholtz Institute for RNA-based Infection Research articles
-
 News
NewsNew genome editing method inspired by bacteria’s defense strategies
Researchers have developed a new method for precisely editing DNA. Their aim was to make genetic changes in bacteria, plants, and human cells even more accurate and gentle.
-
 News
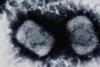
NewsA survival kit for smallpox viruses
Scientists have discovered a previously unknown type of assembly chaperone during their analysis of poxviruses, and they have decoded its function in full detail. This is the first known chaperone that is not formed by a protein but by a nucleic acid — specifically RNA.
-
 News
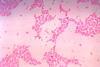
NewsResearchers establish link between form and function of gut bacterium
New insights into the functional differences between the various morphotypes of Bacteroides thetaiotaomicron could open up new possibilities for medicine. A better understanding of their diversity could lay the foundation for novel microbiome-based therapies.
-
 News
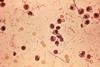
NewsCultured mini-organs reveal the weapons of aggressive Shigella bacteria
Thanks to lab-grown miniature intestines, researchers have successfully mapped how aggressive Shigella bacteria infect the human gut. The study opens the door to using cultured human mini-organs to investigate a wide range of other serious infections.
-
 News
NewsBacteria: Recording gene activity more efficiently
Researchers have presented a step-by-step protocol for creating single bacterial transcriptomes with MATQ-seq. The protocol also includes the experimental and computer-aided analysis of the data.
-
 News
NewsNovel compound inhibits the growth of tumor-associated Fusobacteria
Researchers seeking ways to eliminate fusobacteria in carcinomas have made an unexpected discovery: their control compound, FUS79, which did not target a specific transcript, exhibited strong activity against five fusobacterial strains without affecting other tested bacterial species.
-
 News
NewsScientists unveil novel anti-CRISPR protein mechanism
Apart from their counter-defensive function, anti-CRISPR proteins hold great promise for enabling more precise control over CRISPR technologies. Researchers have now further elucidated the function of an important yet so far uncharacterized anti-CRISPR protein.
-
 News
NewsDecoding HIV genomic tactics in viral replication
Research on HIV-1 unravels the viral and host translational regulations during viral replications through the identification of RNA structures and previously unrecognized genetic elements - this could bring potential therapeutic interventions to counter the viral manipulations.
-
 News
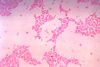
NewsResearchers uncover control mechanisms of polysaccharide utilization in gut bacterium
Polysaccharide utilization loci (PULs) complexes enable bacteria to bind, break down, and import specific polysaccharides, contributing to successful gut colonization. A new study explores how PULs are regulated post-transcriptionally to adapt to environmental changes.
-
 News
NewsResearchers unlock gateway to open up more bacterial species for research
Researchers have introduced a novel approach that can make many more bacteria amenable to genetic engineering. Their method, called IMPRINT, uses cell-free systems to enhance DNA transformation across various bacterial strains.
-
 News
NewsMissing puzzle piece discovered that influences sensitivity of gut bacterium to antibiotics
Scientists identify the small RNA that influences the sensitivity of the intestinal pathogen Bacteroides thetaiotaomicron to certain antibiotics.
-
 News
NewsScientists shine a new light on the tug-of-war between virus and host
Researchers have recently developed a new method that, for the first time, enables the discovery of interactions for specific regions within a target RNA molecule.
