All Infectious Disease articles – Page 31
-
 News
NewsAntibody-making cells reveal new function in response to flu infection
A study has uncovered a new function of the immune cells that are known for making antibodies. Researchers determined that, in response to flu infection, a specialized set of B cells produce a key signaling molecule that the immune system needs to develop a robust, long-term response to fight off infections.
-
 News
NewsInfectious disease modelling teams invited to strengthen global response to highly pathogenic avian influenza
An international modelling challenge is calling on experts across disciplines to help tackle one of Europe’s most pressing health threats: highly pathogenic avian influenza (HPAI). The initiative, which is now open for applications, seeks to improve outbreak modelling readiness and to foster international collaboration among researchers and decision makers.
-
 News
NewsOne dose of antibiotic treats early syphilis as well as three doses
Researchers have found that a single injection of the antibiotic benzathine penicillin G (BPG) successfully treated early syphilis just as well as the three-injection regimen used by many clinicians. These findings from a late-stage clinical trial suggest the second and third doses of conventional BPG therapy do not provide a health benefit.
-
 News
NewsThe cling of doom: How staph bacteria latch onto human skin
Scientists have discovered the strongest natural protein bond ever recorded, explaining how Staphylococcus aureus clings so tightly to human skin and pointing to new ways to fight antibiotic resistance.
-
 News
NewsCARB-X to support lower respiratory tract infection diagnostic by Zeteo
CARB-X has awarded Zeteo Tech, Inc. US$1M to execute a workplan for its noninvasive diagnostic platform that aims to evaluate whether exhaled breath can diagnose lower respiratory tract infections (LRTIs) in high-risk populations within critical care environments.
-
 News
NewsClinical study shows that nasal spray containing azelastine reduces risk of coronavirus infection by two-thirds
In addition to showing a marked reduction in coronavirus infections, the azelastine group also displayed fewer symptomatic SARS-CoV-2 infections, a lower overall number of confirmed respiratory infections, and, unexpectedly, a reduced incidence of rhinovirus infections, another major cause of respiratory illness.
-
 News
NewsLess is more: Gene loss drives adaptive evolution of a pandemic bacterium
A study reveals a surprising evolutionary insight: sometimes, losing genes rather than gaining them can help bacterial pathogens survive and thrive. The research focused on Vibrio parahaemolyticus, a bacterium behind many of the seafood-related infections worldwide.
-
 News
NewsTherapeutic vaccination against HPV-related tumors: Nanoparticles make the difference
Researchers have developed a therapeutic vaccination concept that can mobilize the immune system to target cancer cells. Virus peptides coupled to silica nanoparticles can elicit effective T-cell responses against HPV-related tumors. In a mouse model, the nanoparticle-based vaccine was able to partially or completely suppress HPV-related tumors.
-
 News
NewsOne shot of RSV vaccine effective against hospitalization in older adults for two seasons
One shot of an RSV vaccine protects adults ages 60 or older from RSV-associated hospitalization and critical illness during two consecutive RSV seasons, according to a new study.
-
 News
NewsCARB-X backs neonatal sepsis diagnostic platform by Quantamatrix
CARB-X has awarded QuantaMatrix Inc. US$2.85M to execute a workplan to develop its rapid diagnostic platform to detect sepsis, especially in vulnerable neonates. The test aims to deliver results within just 6 hours from very small blood samples of 1 to 2 milliliters.
-
 News
NewsNew sepsis diagnostic could reduce critical time to save patients
A new diagnostic method would confirm sepsis infections earlier, cutting critical hours in the “race against time” to save patients’ lives. The process uses a centrifuge to separate bacteria from blood cells, and automatic microscopy for detection.
-
 News
NewsNew ‘cough simulator’ mimics TB transmission with unprecedented accuracy
Researchers have developed a new experimental system called Transmission Simulation System (TSS) that replicates the airborne transmission of TB – by simulating the human cough – with unparalleled realism and never-before-seen precision.
-
 News
NewsGuideline on respiratory infections in leukemia revised
People with leukemia have a weakened immune system due to the disease itself and treatment, which leads to an increased susceptibility to infections. In a revised guideline, experts summarize the findings of the past ten years on all viruses that cause respiratory infections.
-
 News
NewsMERIT grant awarded to study cure for HIV
A scientific team has received an NIH MERIT Award to provide long-term grant support to study a handful of people who have managed to clear HIV after a stem cell transplant and those who did not.
-
 News
NewsPertussis resurgence in Tuscany outlines importance of timely vaccination in Italy
Research analysing 2016-2024 data from all pertussis-related hospitalisations in Tuscany, Italy, finds a ninefold increase in pertussis cases in 2024 among children and adolescents.
-
 News
NewsDeadly infectious bone disease wiped out long-necked dinosaurs in Brazil
Researchers found sauropod bones with signs of osteomyelitis, an infectious disease that can be caused by viruses, bacteria, fungi, or protozoa and that killed the animals quickly. The discovery suggests that favorable conditions for the disease existed.
-
 News
NewsNew bacterium discovered in the Amazon is closely related to Andean species that causes human bartonellosis
A new species of bacteria of the genus Bartonella has been found in the Amazon National Park in the state of Pará, Brazil, in phlebotomine insects, also known as sand flies. Its DNA is similar to that of two other Andean species of bacteria.
-
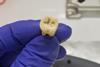 News
NewsNew research rewrites origins of world’s first recorded pandemic - the Plague of Justinian
For the first time, researchers have uncovered direct genomic evidence of the bacterium behind the Plague of Justinian — the world’s first recorded pandemic — in the Eastern Mediterranean, where the outbreak was first described nearly 1,500 years ago.
-
 News
NewsNext-generation ‘molecular scissors’ may offer hope for chronic hepatitis B sufferers
Researchers have developed engineered precision ’molecular scissors’ that can permanently disable the genetic blueprint of the hepatitis B virus (HBV). The approach directly targets covalently closed circular DNA (cccDNA), the stubborn viral reservoir.
-
 News
NewsMyocardial infarction may be an infectious disease
A pioneering study has demonstrated for the first time that myocardial infarction may be an infectious disease. This discovery challenges the conventional understanding of the pathogenesis of myocardial infarction and opens new avenues for treatment.
