Latest News in WAAW – Page 52
-
 News
NewsAntimicrobial foam targets bugs or oil spills
A versatile new foam material could significantly reduce health care-related infections caused by implanted medical devices - or drastically improve cleanup efforts following environmental disasters like oil spills.
-
 News
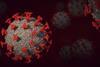
NewsSystem targets and degrades viral RNA to treat Covid infection
Researchers have developed a system that directly targets and degrades the viral RNA genome, reducing infection in mice. The method could be adapted to fight off many viruses, as well as treat various diseases.
-
 News
NewsGlobal prevalence of H. pylori infection declining
Researchers have found that Helicobacter pylori (H. pylori) infection around the world has been steadily declining over the past four decades, and that the use of antibiotics against it could alter the micro-organisms and the virus community present in the gut.
-
 News
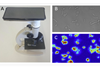
NewsFast and easy method detects antibiotic resistance
Scientists have developed a technique that obtains an antibiogram within 2-4 hours instead of the current 24 hours for the most common germs and one month for tuberculosis.
-
 News
NewsAntimicrobial use in agriculture can breed bacteria resistant to first-line human defences
A new study has shown that overuse of antimicrobials in livestock production can drive the evolution of bacteria more resistant to the first line of the human immune response.
-
 News
NewsStool transplants more effective than antibiotics for treating recurring, life-threatening gut infections
A new Cochrane Review has found that, compared with standard antibiotic treatment, stool transplantation can increase the number of people recovering from Clostridioides difficile infection from 40% to 77%.
-
 News
NewsNew biologic effective against major infection in early tests
Researchers have shown in early tests that a bioengineered drug candidate can counter infection with Staphylococcus aureus – a bacterial species widely resistant to antibiotics and a major cause of death in hospitalized patients.
-
 News
NewsBacteria’s antibiotic-evading super polymers do best in harsh conditions of the gut
New research has shown that gut bacteria’s extracellular appendages known as F-pili are stronger in the turbulent conditions of the gut, helping the bacteria transfer resistance genes to each other more efficiently and to clump into ‘biofilms’ – protective bacterial consortia – that help them fend off antibiotics.
-
 News
News‘Antibiotic culture’ permeates US hospital ICUs, study finds
A new study reveals that there continues to be an ’antibiotic culture’ in US hospitals, meaning that the preference for antibiotics is related to their perceived role as ’magic bullets’.
-
 News
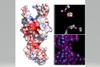
News New cell-killing toxin discovered in an environmental pathogen
An international research team has discovered how a bacterial toxin, known as Ssp, is capable of entering and killing a wide range of living cells, including human cells.
-
 News
NewsUnraveling the secret microbial power within medicinal plants
A new review uncovers how medicinal plants interact with their endophytes at a molecular and metabolic level - and examines the potential of these endophytes for use in therapeutics.
-
 News
NewsNew treatment for multidrug-resistant bacteria blocks toxins involved in infection
A new type of drug could provide a way to treat multidrug-resistant bacteria - rather than targeting the bacteria directly, the drug blocks key toxins involved in the infection process.
-
 News
NewsWARNING - GRAPHIC IMAGES: War in Ukraine fuelling rise in injuries infected with multi-drug resistant bacteria
New research being presented at this year’s ECCMID highlights the devastating impact of war injuries with complex bone and soft-tissue multidrug-resistant infections suffered by 13 civilians and one soldier during the war in Ukraine, who were transferred to Germany for specialist treatment.
-
 News
NewsPolymer discovery stops bacterial virus contamination
A new discovery by researchers at the University of Warwick could help stop bacteria being contaminated with viruses, reducing disruption and decreasing costs in industry and research.
-
 News
NewsWomen, city dwellers and those on higher incomes found to have more antibiotic resistance genes
A genetic study analysing the microbiome of a large nationally representative sample of the Finnish population finds that geographic, demographic, diet, and lifestyle factors are driving the spread of antibiotic resistance in the general population.
-
 News
NewsStudy suggests antibiotic-resistant “superbugs” are being passed between dogs and cats and their owners
Evidence that multidrug-resistant bacteria are being passed between pet cats and dogs and their owners will be presented at this year’s European Congress of Clinical Microbiology & Infectious Diseases (ECCMID) in Copenhagen, Denmark (15-18 April).
-
 News
NewsInternational consensus highlights importance of molecular testing for AMR in TB management
A multidisciplinary group of tuberculosis experts from the TBnet and RESIST-TB networks have reached a consensus on key issues related to the molecular prediction of Mycobacterium tuberculosis antibiotic sensitivity or resistance and its clinical implications.
-
 News
NewsHigh-level discussion urges political action for AMR research
Government leaders, policymakers and scientists from across the globe have united to address the need for strong partnerships between policy and research in developing solutions for one of the greatest health threats facing our world today, AMR.
-
 News
NewsA polychromatic light device has an antibacterial effect in blood
Polychromatic light administered by device into blood delivers a moderate antibacterial effect, according to a multidisciplinary team of researchers.
-
 News
NewsGold-based antibiotics shine through in battle against multi-drug resistant superbugs
Several gold-based compounds with the potential to treat multidrug-resistant ’superbugs’ have been identified in new research being presented at this year’s ECCMID.
