All Leibniz Institute for Natural Product Research and Infection Biology articles
-
 News
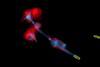
NewsFungal toxin offers colonization support - in small doses
The yeast fungus Candida albicans not only uses the toxin candidalysin to cause infections, but also to colonize the oral mucosa inconspicuously – but only in finely balanced amounts. Too little toxin prevents oral colonization, too much triggers the immune system.
-
 News
NewsMagic mushrooms invent active compound twice
A study shows that fungi have developed the ability to produce psilocybin at least twice independently of each other. While Psilocybe species use a known enzyme toolkit for this purpose, fiber cap mushrooms employ a different biochemical arsenal – and yet arrive at the same molecule.
-
 News
NewsCandida’s hidden toolbox: Scientists discover a previously unknown infection strategy
A new study shows that the common blood protein albumin can turn otherwise harmless fungal strains of Candida albicans into dangerous pathogens.
-
 News
NewsChemical radar enables bacteria to detect and kill predators
Researchers have identified a previously unknown defense mechanism of Pseudomonas syringae. They were able to show how the bacterium uses a chemical radar to recognize and eliminate hostile amoebae.
-
 News
NewsInactive mushroom toxin can become poison when eaten
Muscarine can be stored as a harmless precursor in mushrooms and only be released when mushrooms get injured.
-
 News
NewsBacterium becomes a permanent resident in a fungus
Researchers developed an innovative method for the precise implantation of bacteria into fungal cells and used evolutionary experiments to show how the symbiosis can be stabilised.
-
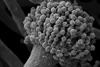 News
NewsFungus uses surface protein of its spores to weaken human immune system
An international research team discovered a special enzyme on the surface of the spores of Aspergillus fumigatus apparently suppresses the release of pro-inflammatory substances by immune cells, making it easier for the pathogen to spread in the tissue.
-
 News
NewsPandemic stranding ended up helping to solve mystery of synthetic polymers and fungi
A chemistry PhD student who was stranded during the pandemic used the time for research on Candida albicans, leading to a successful collaboration between natural product researchers and infection biologists from Germany and Australia.
-
 News
NewsCandida albicans toxin plays a special role in the colonization of the digestive tract
Comparative studies on mice with a complete microbiome and a microbiome reduced by antibiotics now show that the previous assumption that the yeast form of Candida albicans is better suited for colonization needs to be revised.
-
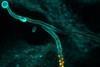 News
NewsInsights into release of fungal toxin promise progress in treating infections
The toxin Candidalysin of the yeast Candida albicans is incorporated into an unusual protein structure during an infection, and researchers have now succeeded in deciphering the function of this unusual arrangement.
-
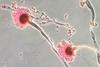 News
NewsAspergillus fumigatus adapts to life in humans - and shapes their lung microbiome
Aspergillus fumigatus strains that infect humans have a significantly altered metabolism compared to other strains in the environment. At the same time, infection with the fungus leads to an apparent change in the human lung microbiome. Source: CDC Photomicrograph revealing ultrastructural morphology exhibited by the fungal organism Aspergillus ...
-
 News
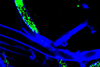
NewsJust one single molecule can disrupt symbiosis
Researchers have found that the bacterial species Mycetohabitans rhizoxinica lives happily in the hyphae of the fungus Rhizopus microsporus only when the bacteria produce a certain protein.
-
 News
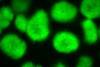
NewsStreptomycetes reveal their arsenal of signalling compounds
Streptomyces bacteria produce a group of signalling molecules that trigger a variety of processes, a new study shows.
-
 News
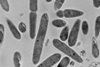
NewsHydrogen-fuelled bacteria can produce wide range of chemicals
Researchers probing microbial electrosynthesis have confirmed experimentally for the first time that the bacteria use electrons from hydrogen and can produce more chemical substances than previously known.
-
 News
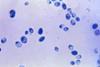
NewsIntestinal bacteria influence the growth of fungi
The bacteria present in the intestine provide information about the quantities of fungi of the potentially disease-causing Candida genus - among them, surprisingly, are lactic acid bacteria that are known for their protective effect against fungal infections.
-
 News
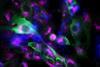
NewsFungal spores bind to lung cell protein to escape human defences
The pathogenic fungus Aspergillus fumigatus escapes elimination from surface cells of the human lung by binding to a human protein.
-
 News
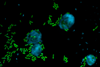
NewsDeadly Keanu-inspired bacterial compound delivers excellent anti-fungal protection to plants
Researchers have proved that an antimicrobial natural product produced by Pseudomonas - and named after Keanu Reeves - is effective against both plant fungal diseases and human-pathogenic fungi.
