All articles by Linda Stewart – Page 5
-
 News
NewsChemically ‘stapled’ peptides used to target difficult-to-treat cancers
Researchers have developed a new technology that uses bacteria to build, chemically stabilise, and test millions of potential drug molecules inside living cells. The bacteria produce vast libraries of peptide molecules, and chemically stabilise them into defined shapes while they are being tested inside the cell.
-
 News
NewsUnderground fungal map of the world’s oldest, slowest-growing rainforest trees can boost the resilience of Earth’s long-term carbon sinks
Protecting and conserving old trees will protect hundreds, if not thousands, of mycorrhizal and other fungal species that inhabit soils around these giants, each of which play a role we might not fully understand in keeping these forests healthy and resilient.
-
 News
NewsResearchers find a gentler way to treat aggressive gum disease
Researchers have discovered that the primary bacterium driving gum disease carries an internal “genetic brake” that controls its own aggression. By locking this brake in place, future treatments could silence the pathogen while leaving beneficial bacteria untouched.
-
 News
NewsBiodegradable mulch isn’t disappearing as expected, new study warns
Scientists investigated how soybean roots influence the degradation of PBAT microplastics in soil. They tracked both polymer loss and monomer accumulation over a full 70-day plant growth cycle, revealing size-dependent and condition-specific rhizosphere effects.
-
 News
NewsEditing for timing, not overdrive: A new genetic route to fire blight resistance in apple
Fire blight remains one of the most destructive bacterial diseases threatening global apple production. A new study identifies a family of inducible lectin genes, MdAGGs, as critical components of apple immune defense and demonstrates that their precise activation timing is key to effective resistance.
-
 News
NewsA common CRISPR platform enables comparative studies of multicellularity in social amoebae
Researchers have established a CRISPR genome editing technique that enables comparative analysis of the evolution of multicellularity across different species of social amoebas (cellular slime molds). Until now, genetic studies had been largely restricted to a single model species.
-
 News
NewsAncient symbiosis between plants and fungi: Important insights for sustainable agriculture
Almost all plants live in close symbiosis with so-called mycorrhizal fungi – an important symbiosis for absorbing essential nutrients. Scientists have discovered that this mycorrhizal symbiosis is very sensitive to imbalances of certain nutrients in the soil.
-
 News
NewsTiny plastics, green solutions: How algae could help clean polluted waters
A new review examines how algae interact with microplastics in aquatic systems. Importantly, it highlights how their biological interactions could be harnessed to mitigate microplastic pollution, offering new perspectives for sustainable aquatic environmental management.
-
 News
NewsNanoparticle vaccine approach takes on a new target: Hepatitis C virus
Scientists have engineered a native-like, stabilized version of Hepatitis C virus’s E1E2 complex and used it to build a nanoparticle-based vaccine candidate. It uses a technology called self-assembling protein nanoparticles, which organizes copies of the proteins into virus-like clusters that the immune system can recognize.
-
 News
NewsDiisobutyl phthalate at environmental concentration promotes conjugative transfer of antibiotic resistance genes
Researchers investigating the ecological safety risks posed by dibutyl phthalate (DBP), in aquatic environments found it significantly increased conjugative transfer frequency in both intragenus (E. coli DH5α to E. coli HB101) and intergenus (E. coli DH5α to B. subtilis WB100N) systems.
-
 News
NewsToxic algal bloom takes heavy toll on mental health
The year-long algal bloom along the South Australian coastline has not only devastated marine life and triggered health risks for humans and pets: it has also had a significant psychological impact on local residents, according to new research.
-
 News
NewsBig and small dogs both impact indoor air quality - just differently
An initial study reports that dogs — both big and small — impact indoor air quality. The researchers found that small active dogs produced more airborne particles, but larger animals released more microbes into the air than people did.
-
 News
NewsLife forms can planet hop on asteroid debris – and survive
The extremophile bacterium Deinococcus radiodurans can survive the pressures developed during ejection from Mars as a result of massive asteroid impact, a study shows. It means microorganisms can survive more extreme conditions than previously thought, including launch across space after major impacts.
-
 News
NewsTestosterone increases severity of bacterial skin infections
Men are more susceptible than women to skin infections caused by Staphylococcus aureus bacteria, but the biological basis for this disparity has remained unclear. A new study is the first to reveal testosterone, present at higher levels in males, as a key driver of infection.
-
 News
NewsHuge toll: Bird flu rampant among black vultures
More than four out of every five dead black vultures examined by University of Georgia researchers tested positive for highly pathogenic avian influenza, according to a new study. Their indiscriminate scavenging appears to sustain transmission of the virus beyond the typical bird flu season.
-
 News
NewsFecal transplants from older mice significantly improve ovarian function and fertility in younger mice
A new study details how fecal transplants from older female mice significantly improve ovarian function and fertility in young mice. The surprising results reveal a direct link between the microbiome of the gut and ovarian health and function.
-
 News
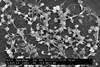
NewsUltrasound-activated ‘nanoagents’ kill superbugs hiding in biofilms
Scientists have designed nanoagents that act like smart drug‑delivery capsules – carrying an antibiotic deep into bacterial infection sites and releasing it only when activated by gentle ultrasound.
-
 News
News10 Years, 70% shift: Wastewater upgrades quietly transform river microbiomes
Researchers investigated how the upgrade of a WWTP influenced nitrogen-cycling microorganisms and DNA viruses in its receiving river. The research compared the river whose WWTP was upgraded during the study period against the river whose upgrade occurred prior to the study.
-
 News
NewsScientists identify therapeutic target that would curb the spread of coronaviruses
Coronaviruses not only use the machinery of the human cells they infect: they modify it to achieve optimal conditions to produce viral proteins and thus spread more quickly, according to a study identifying enzymes that modify transfer RNAs as key elements for coronavirus infection.
-
 News
NewsAlgal blooms: New AI algorithm enables scientific monitoring of ‘blue tears’
‘Blue tears’ chasing has become a popular tourism activity along coasts to witness the spectacular natural phenomenon. However, the occurrence and movement of algal blooms are unpredictable - but scientists have developed an innovative real-time video monitoring algorithm named BT-YOLO.
