More News – Page 28
-
 News
NewsZoo poo might hold the secrets to new medical treatments
Scientists are hoping the collection of poo from tigers, elephants, giraffes and other exotic animals, could contain the secret to finding new medical treatments. Although a waste product to the animals, hidden amongst it are thousands of phages which are potentially capable of fighting bacterial infections.
-
 News
NewsUnlocking how bacteria bounce back after antibiotics
A groundbreaking study has uncovered how Escherichia coli (E. coli) persister bacteria survive antibiotics by protecting their genetic instructions. The work offers new hope for tackling chronic, recurring infections.
-
 News
NewsLess is more: Gene loss drives adaptive evolution of a pandemic bacterium
A study reveals a surprising evolutionary insight: sometimes, losing genes rather than gaining them can help bacterial pathogens survive and thrive. The research focused on Vibrio parahaemolyticus, a bacterium behind many of the seafood-related infections worldwide.
-
 News
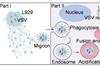
News‘Migrion’ – a chimeric structure of virus and migrasome, a novel unit for intercellular viral transmission
Researchers found that in infected cells, nucleic acids and proteins of vesicular stomatitis virus (VSV) are actively transported into migrasomes, newly characterized cellular structures generated specifically during cell migration.
-
 News
NewsTherapeutic vaccination against HPV-related tumors: Nanoparticles make the difference
Researchers have developed a therapeutic vaccination concept that can mobilize the immune system to target cancer cells. Virus peptides coupled to silica nanoparticles can elicit effective T-cell responses against HPV-related tumors. In a mouse model, the nanoparticle-based vaccine was able to partially or completely suppress HPV-related tumors.
-
 News
NewsResearchers uncover relationship between gut fungi, human genetic variation and disease risk
A study uncovers evidence of the first ternary relationships between human genetic variation, variation in gut mycobiome, and risk of developing chronic disease.
-
 News
NewsAncient mammoth remains yield the world’s oldest host-associated bacterial DNA
An international team has uncovered microbial DNA preserved in woolly and steppe mammoth remains dating back more than one million years. The analyses reveal some of the world’s oldest microbial DNA ever recovered, as well as the identification of bacteria that possibly caused disease in mammoths.
-
 News
NewsStudy detects multidrug-resistant KPC-producing bacteria in Chilean wastewater for the first time
A team of Chilean researchers has identified, for the first time in the country, the presence of KPC-type carbapenemase-producing bacteria in wastewater samples from the Greater Concepción Metropolitan Area.
-
 News
NewsMicroalgae are more significant for carbon dioxide absorption in the Southern Ocean than previously thought
14,000 years ago, algal blooms in the Southern Ocean helped to massively reduce the global carbon dioxide content of the atmosphere – as has now been revealed by new analyses of ancient DNA. Declines in sea ice pose a serious threat to these algae.
-
 News
NewsNew pimple patches deliver a powerful remedy to unwanted zits
Researchers have designed a two-stage pimple patch set with an array of tiny spikes that grabs onto the pimple and delivers antibacterial or anti-inflammatory compounds. Human clinical trials confirmed that the pimples disappeared after seven days of treatment.
-
 News
NewsTiny ocean partnership between algae and bacteria reveals secrets of evolution
The microscopic alliance between algae and bacteria offers rare, step-by-step snapshots of how bacteria lose genes and adapt to increasing host dependence, a new study shows.
-
 News
NewsOne shot of RSV vaccine effective against hospitalization in older adults for two seasons
One shot of an RSV vaccine protects adults ages 60 or older from RSV-associated hospitalization and critical illness during two consecutive RSV seasons, according to a new study.
-
 News
NewsUnder The Lens: Raquel Peixoto reveals how tourists armed with probiotics could save world’s coral reefs
A fascinating conversation between Applied Microbiology International President Professor Jack Gilbert and Professor Raquel Peixoto examines how understanding and leveraging coral microbiomes is leading to innovative probiotic solutions to boost coral resilience.
-
 News
NewsChronic wound infection model is much closer to real life - and cuts back on animal testing
Thousands of lab animals are used every year to test wound treatments. But one lab in Wales is pointing the way towards a more humane model of research, with the work it is carrying out on in vitro/animal replacement models.
-
 News
NewsCARB-X backs neonatal sepsis diagnostic platform by Quantamatrix
CARB-X has awarded QuantaMatrix Inc. US$2.85M to execute a workplan to develop its rapid diagnostic platform to detect sepsis, especially in vulnerable neonates. The test aims to deliver results within just 6 hours from very small blood samples of 1 to 2 milliliters.
-
 News
NewsMicrobiologists uncover bacteria that remove toxic sulfide and use iron minerals for growth
An international team of scientists has discovered a new microbial metabolism: so-called MISO bacteria “breathe” iron minerals by oxidizing toxic sulfide. The previously unknown biological process sees versatile microbes remove toxic sulfide and use it for their growth.
-
 News
NewsBacteria survive dust storms and introduce new genetic traits into our air
Bacterial communities carried from Africa to Israel survive their airborne journey, arriving with genes that may affect human health and the environment, a new study reveals.
-
 News
NewsBroad-specificity enzyme targets glycans from across the kingdoms of life
Researchers have found a new enzyme that has a much broader specificity than the leading alternatives. This analysis resulted in the identification of the PNGaseL enzyme taken from Flavobacterium akiainvivens, which is a microbe isolated from decaying wood of a Hawai’ian plant.
-
 News
NewsStudy finds significant health benefits from gut microbes transfer
A cohort of overweight teens who received fecal transfer eight years ago were found to have reduced risk for a series of metabolic changes which can lead to heart disease, stroke and diabetes, compared with the participants who received the placebo.
-
 News
NewsNew study finds concerning sea star response to an algal neurotoxin
Researchers found potentially concerning concentrations of the neurotoxin domoic acid in sea stars even in the absence of the algal blooms that are thought to drive DA outbreaks.
