More Ocean Sustainability
-
 News
NewsBreakthrough AI speeds up discovery of life-supporting microbes
Scientists have developed a powerful new artificial intelligence tool called LA⁴SR that can rapidly identify previously overlooked proteins in microalgae - tiny organisms that produce much of the Earth’s oxygen and support entire aquatic ecosystems.
-
 News
NewsStudy showcases resilience and rapid growth of ‘living rocks’
South Africa is home to some of the oldest evidence of life on Earth, contained in rocky, often layered outcroppings called microbialites. Like coral reefs, these complex “living rocks” are built up by microbes absorbing and precipitating dissolved minerals into solid formations. Source: Rachel Sipler, Bigelow Laboratory for ...
-
 News
NewsPandemic ‘beneath the surface’ has been quietly wiping out sea urchins around the world
Over the last four years, an unrecognized pandemic that has been wiping out sea urchins around the world has hit the Canary Islands. The consequences on marine ecosystems aren’t yet fully known, but likely profound.
-
 Features
FeaturesThe smell of the sea: how microbes shape Earth’s sulfur story
That distinctive “sea breeze” scent we associate with the coast isn’t just nostalgia; it’s the smell of microbial chemistry at work. Behind it lies an intricate web of microbial pathways turning sulfur compounds into gases that help shape Earth’s climate.
-
 News
NewsHorseshoe crab fossil reveals early mass-burial event and ancient microbial attack
A remarkably preserved horseshoe crab fossil from North America offers rare insight into some of the earliest known cases of animal disease in a Late Carboniferous swamp – more than 300 million years before the age of dinosaurs.
-
 News
NewsClimate extremes triggered rare coral disease and mass mortality on the Great Barrier Reef
Marine biologists have identified a devastating combination of coral bleaching and a rare necrotic wasting disease that wiped out large, long-lived corals on the Great Barrier Reef during the record 2024 marine heatwave.
-
 News
NewsDeep sea microbes yield up their engineering secrets
A biomatrix of tiny tubes of protein, known as cannulae, link cells of the thermal vent-dwelling archaeon Pyrodictium abyssi together into a highly stable microbial community. A study reveals new details about the elegant design of the cannulae and their method of construction.
-
 News
NewsPreviously unrecognized pathway in plants and phytoplankton offers mercury-detox powers
Primary producers—including phytoplankton—possess a previously overlooked ability to internally break down and detoxify methylmercury. The demethylation pathway rapidly converts methylmercury into less toxic inorganic mercury, which is subsequently reduced to gaseous Hg⁰.
-
 News
NewsThe mystery of the missing deep ocean carbon fixers
New findings challenge the current view of how carbon dioxide is “fixed” in the sunless ocean depths. The study presents results that help to reconcile discrepancies in accounting for nitrogen supply and dissolved inorganic carbon (DIC) fixation at depth.
-
 News
NewsVIRE: a global data platform to better understand viruses
Researchers have released a comprehensive viral genome database covering diverse ecosystems to advance the understanding of viral evolution and ecosystem functions.
-
 News
NewsIsland-wide field surveys illuminate land-sea connections in Mo‘orea
A multi-year scientific expedition determined that land use on tropical islands can shape water quality in lagoons and rainfall can be an important mediator for connections between land and lagoon waters.
-
 News
NewsMicroplastics pose a human health risk in more ways than one
A new study shows that microplastics in the natural environment are colonised by pathogenic and antimicrobial resistant bacteria. The study team calls for urgent action for waste management and strongly recommends wearing gloves when taking part in beach cleans.
-
 News
NewsOceanographers present new conceptual framework to answer age-old question: What happens to carbon as it sinks through the ocean?
New research spanning multiple ocean regions has found upper ocean ecosystem conditions, such as nutrient availability and microbial interactions, play a major role in shaping the composition of carbon-rich particles sinking into the deep ocean.
-
 News
NewsNew study reveals how a common antibiotic disrupts nitrogen cycling and boosts greenhouse gas emissions in estuaries
Antibiotics may have far reaching impacts on wetland chemistry, according to a new study that identifies the bacteria responsible for breaking down the antibiotic sulfamethoxazole and links this process to increased emissions of nitrous oxide, a potent greenhouse gas.
-
 News
NewsMarine viruses use ‘hijacked’ genes to take over bacteria and exploit their energy systems
Marine viruses deploy a sophisticated Trojan horse maneuver that enables them to dismantle the energy systems of ocean bacteria and use the breakdown products for self-replication, according to a new study.
-
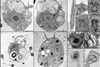 News
NewsClues to origins of complex life revealed with discovery of new unicellular organism and phylum
A new paper describes the discovery of Solarion arienae, a previously unknown unicellular organism that provides new insight into the earliest stages of complex life on Earth. This microscopic protist displays two distinct cell types and a unique predatory structure unlike any seen before.
-
 News
NewsTeam discovers cyanobacteria activate different genes by day and by night
By analyzing gene expression in the cyanobacterium Nostoc punctiforme, scientists discovered that during daylight, the cells focus on metabolism. But under cover of darkness, they turn to the control of genome repair and activate various genetic elements.
-
 News
NewsThe road ahead: why conserving the invisible 99% of life is fundamental to planetary health
A new paper outlines how scientists came together to put together the first microbial conservation roadmap under the leadership of Applied Microbiology International President, Professor Jack Gilbert.
-
 News
NewsThe leading causes of mass mortality events in sea urchins are pathogens, storms, and extreme temperatures
Researchers have identified the primary drivers of sea urchin mass mortality events over recent decades: pathogens, storms, and extreme temperatures. The team have developed an innovative method for genetic sampling in marine environments - using a swab similar to a COVID-19 test, to enable rapid and non-invasive monitoring of marine animals and underwater disease outbreaks.
-
 News
NewsPredicting the development of biological communities in different kinds of ecosystems
Researchers tested a mechanistic consumer-resource model and confirmed its high predictive capacity. Using the model, the researchers refined current rules on the coexistence of species, too. Their findings can be applied to any situation in which communities of organisms compete for resources.
