More USA & Canada News – Page 32
-
 News
NewsStudy resolves diatom tree of life - and could offer clues to Earth’s puzzle
A new study finds that diatoms evolved slowly for the first 100 million years of their existence. Then, 170 million years ago, they reached an inflection point characterized by a burst of rapid speciation orders of magnitude faster than anything that had preceded it.
-
 News
NewsLarge-scale immunity profiling grants insights into flu virus evolution
A new study has shown that person-to-person variation in antibody immunity plays a key role in shaping which influenza (flu) strains dominate in a population.
-
 News
NewsStudent discovers long-awaited mystery fungus sought by LSD’s inventor
A student has found a long sought-after fungus that produces effects similar to the semisynthetic drug LSD, which is used to treat conditions like depression, post-traumatic stress disorder and addiction.
-
 News
NewsNew mRNA vaccine is more effective and less costly to develop, Pitt study finds
A new type of mRNA vaccine is more scalable and adaptable to continuously evolving viruses such as SARS-CoV-2 and H5N1, according to a study.
-
 News
NewsDNA floating in the air tracks wildlife, viruses — even drugs
A new study reveals the power of DNA, vacuumed up from the air, which can track everything from elusive bobcats to illicit drugs. A simple air filter running for hours, days or weeks can pick up signs of nearly every species that grows or wanders nearby.
-
 News
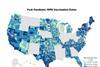
NewsNew data shows MMR vaccination rate decline across US
A new county-level dataset reveals a national decline in the measles-mumps-rubella (MMR) vaccination rate among U.S. children since the start of the COVID-19 pandemic.
-
 News
NewsNew study reveals bats are key players in cross-species spread of morbilliviruses
Researchers studying the spread of morbilliviruses in bats and monkeys in Brazil and Costa Rica have discovered new virus species and host switches from bats to other mammalian species.
-
 News
NewsStudy uncovers how certain antibodies help fight tuberculosis
Researchers collected the largest library of monoclonal antibodies to Mycobacterium tuberculosis (Mtb) and identified specific antibody features that significantly limit its growth.
-
 News
NewsCotton virus circulated undetected in US fields for nearly 20 years, study finds
A virus responsible for damaging cotton crops has been lurking in U.S. fields for nearly 20 years – undetected. Cotton leafroll dwarf virus (CLRDV), thought to be a recent arrival, was infecting plants in cotton-growing states as early as 2006.
-
 News
NewsHIV discovery could open door to long-sought cure
Scientists have uncovered a key reason why HIV remains so difficult to cure: Their research shows that small changes in the virus affect how quickly or slowly it replicates, and how easily or stubbornly it can reawaken from hiding.
-
 News
NewsRock record reveals oxygenation of ocean may have happened earlier than we thought
Researchers uncover evidence that oxygenation in the ocean—crucial for life as we know it—may have occurred earlier than previously thought, offering new insights into the evolution of our planet.
-
 News
NewsNew diagnostic tool uses bioluminescence to detect viruses
Researchers are shining a powerful new light into the viral darkness with the development of Luminescence CAscade-based Sensor (LUCAS), a rapid, portable, highly-sensitive diagnostic tool for processing complex biological samples.
-
 News
NewsHow the plague bacillus became less virulent, prolonging the duration of two major pandemics
Scientists have discovered that the evolution of a gene in the bacterium that causes bubonic plague, Yersinia pestis, may have prolonged the duration of two major pandemics. Modifying the copy number of a specific virulence gene increases the length of infection.
-
 News
NewsResearchers engineer a herpes virus to turn on T cells for immunotherapy
Researchers have identified herpes virus saimiri, which infects the T cells of squirrel monkeys, as a source of proteins that activate pathways in T cells that are needed to promote T cell survival - a promising tool in the fight against cancer.
-
 News
NewsBiologist examines growth patterns in bacteria to help develop more targeted, effective antibiotics
Among the new investigative projects at the University of Texas at Arlington is one headed by Dr. Cara Boutte, who is studying how certain bacteria grow by examining how they build their cell walls, an effort that could lead to the development of more effective antibiotics.
-
 News
NewsTrees vs. disease: Tree cover reduces mosquito-borne health risk
A new study shows that in Costa Rica, even modest patches of tree cover can reduce the presence of invasive mosquito species known to transmit diseases like dengue fever.
-
 News
NewsStudy links oral microbiome diversity with long sleep duration in teenagers and young adults
A new study to be presented at the SLEEP 2025 annual meeting found that oral microbiome diversity is positively associated with long sleep duration among teenagers and young adults.
-
 News
NewsZika virus uses cells’ ‘self-care’ system to turn against host
A new study reveals the biological secret to the Zika virus’s infectious success: Zika uses host cells’ own ‘self-care’ system of clearing away useless molecules to suppress the host proteins that the virus has employed to get into those cells in the first place.
-
 News
NewsMirror molecules deliver a one-two punch to superbugs to fight infections
Researchers have created mirror-image molecules that both kill pathogens outright and rally the immune system—an advance aimed at the growing crisis of antimicrobial resistance.
-
 News
NewsTwo-step method to prevent biofilm regrowth is a SLAM dunk
A new study reports a novel, two-step method to effectively dismantle bacterial biofilms and prevent regrowth.
