More USA & Canada News – Page 56
-
 News
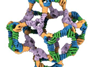
NewsVirus that threatened humanity opens the future
Researchers have developed an innovative therapeutic platform by mimicking the intricate structures of viruses using artificial intelligence.
-
 News
NewsSugar solution fights infection in dairy cows just as well as antibiotics
A concentrated sugar solution could be just as effective as antibiotics at treating a common infection in dairy cows, according to a new study.
-
 News
NewsStudy uncovers how a new gut microbe drives the gut-lung axis
New findings highlight how a little-known member of the gut microbiome reshapes the lung immune environment to have both beneficial and detrimental effects on respiratory health.
-
 News
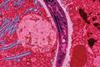
NewsResearchers discover novel class of anti-malaria antibodies
A novel class of antibodies that binds to a previously untargeted portion of the malaria parasite could lead to new prevention methods. The most potent of the new antibodies was found to provide protection against malaria parasites in an animal model.
-
 News
NewsMapping the gut microbiome to create personal nutrition plans
Researchers are developing methods of mapping the microbiome to help create personalized nutrition plans for individuals. They designed metabolomic analyses that are accessible and reusable for dietary research targets such as corn, wheat and citrus.
-
 News
NewsStudy reveals the fabrics most vulnerable to fungi attack during shipping - and the culprits
A new study could help consumer goods manufacturers to predict the likelihood of mold growth during shipping, enabling them to make informed decisions and mitigate economic losses.
-
 News
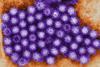
NewsResearchers discovered replication hubs for human norovirus
Researchers have reported the discovery of replication hubs for human norovirus, which could lead to designing antiviral drugs to prevent, control or treat these infections.
-
 News
NewsSeasonal flu vaccine study reveals host genetics’ role in vaccine response
Scientists have found that influenza subtype-bias is primarily driven by host genetics, particularly major histocompatibility complex (MHC) class-II polymorphisms, with prior exposure playing a secondary role.
-
 News
NewsPotentially harmful bacteria slip through antimicrobial showerheads
Researchers report that antimicrobial silver-containing showerheads are no ’silver bullet’. In real-world showering conditions, most microbes aren’t exposed to the silver long enough to be killed.
-
 News
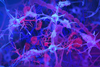
NewsThe surprising role of gut infection in Alzheimer’s disease
A new study implicates link between a common virus and the disease, which travels from the gut to the brain and may be a target for antiviral treatments.
-
 News
NewsTinkering with the ‘clockwork’ mechanisms of life
Scientists have successfully recreated and validated two distinct mechanisms that can program both the activation and deactivation rates of nanomachines in living organisms across multiple timescales.
-
 News
NewsNature’s instructions: How fungi make a key medicinal molecule
Scientists outline how they deciphered nature’s own instructions — namely, the genes of the mold Penicillium citrinum — to discover a previously unreported enzyme that catalyzes the creation of cyclopentachromone-containing compounds.
-
 News
News‘Unbreakable’ Lassa vaccine shows promising results
A live-attenuated vaccine candidate against Lassa virus completely protected guinea pigs exposed to an otherwise lethal dose of the virus, researchers have reported.
-
 News
NewsDiarrheal diseases remain a leading killer for children under 5, adults 70+
A new global study reports a 60% drop in global mortality from diarrheal diseases, but children and the elderly still have the highest death rates, particularly in sub-Saharan Africa and South Asia.
-
 News
NewsLiving in the deep, dark, slow lane: first global appraisal of microbiomes in earth’s subsurface environments
A new study reveals astonishingly high microbial diversity in some of the Earth’s deepest, darkest subsurface environments, including gold mines, in aquifers and deep boreholes in the seafloor.
-
 News
NewsNew discovery provides hope in fighting drug-resistant malaria
Researchers have described how they may have found a new target in Plasmodium falciparum, the deadliest malaria parasite: a cholesterol-managing protein called PfNCR1.
-
 News
NewsOcean microbe’s unusual pair of enzymes may boost carbon storage, study suggests
Scientists have discovered multiple forms of a ubiquitous enzyme in microbes that thrive in low-oxygen zones off the coasts of Central and South America.
-
 News
NewsGiant virus encodes key piece of protein-making machinery of cellular life
Researchers recently discovered that a virus, FloV-SA2, encodes one of the proteins needed to make ribosomes, the central engines in all cells that translate genetic information into proteins. This is the first eukaryotic virus found to encode such a protein.
-
 News
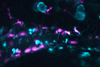
NewsBad bacteria can trigger painful gut contractions; new research shows how
After a meal of questionable seafood or a few sips of contaminated water, bad bacteria can send your digestive tract into overdrive. Your intestines spasm and contract, efficiently expelling everything in the gut. Source: Parthasarathy Lab and Guillemin Lab Immune cells (magenta) and cells expressing a reporter of ...
-
 News
NewsCases of whooping cough growing, but knowledge about it is lacking
Many in the public are not familiar with symptoms of whooping cough. Almost a third of respondents (30%) are not sure if pertussis is the same as whooping cough and not sure (30%) whether a vaccine exists to prevent it.
