More USA & Canada News – Page 71
-
 News
NewsDeeper corals may help shallow reefs recover in the Florida keys
Using the blushing coral star (Stephanocoenia intersepta), found throughout the Western Atlantic, researchers have investigated how coral populations at different depths and locations may be related or ‘connected’ to each other.
-
 News
NewsEradivir closes $10.25M Series A funding round for next stage of influenza therapeutic trials
Eradivir, a preclinical biotech company that develops antiviral therapeutics, has completed a $10.25 million Series A funding round which will be used to conduct a Phase 2a challenge study of its EV25 influenza treatment.
-
 News
NewsBacteria ‘doing their job’, as nitrogen fertilizer for soybeans offers limited yield benefits
Researchers tested whether modern high-yielding soybeans benefit from nitrogen fertilizer, with results suggesting additions are largely unnecessary.
-
 News
NewsMedical device could diagnose respiratory infections with breath
A proof-of-concept study promises the speedy diagnosis of lower respiratory tract infections through analysis of human breath.
-
 News
NewsFruit-only diet improves bats’ immune response to viruses
Fruit bats generate more diverse antibodies than mice, but overall have a weaker antibody response, according to a new study.
-
 News
NewsScientist studying parasite-derived vesicles in babesia virulence and vaccine development
Fatah Kashanchi, Professor of Virology at George Mason University, has received funding for the study: ’Parasite-Derived Vesicles in Babesia virulence and Vaccine Development’.
-
 News
NewsGood nutrition boosts honey bee resilience against pesticides and viruses
In a new study, researchers investigate how nutritional stress, viral infections and exposure to pesticides together influence honey bee survival. By looking at all three stressors together, the scientists found that good nutrition enhances honey bee resilience against the other threats.
-
 News
NewsWastewater monitoring can detect foodborne illness
Results of a new study suggest sewage monitoring could provide early warning of foodborne disease outbreaks to public health authorities.
-
 News
NewsResearch team discovers molecular mechanism for a bacterial infection
Researchers have discovered the mechanism by which the bacterial pathogen Shigella flexneri, the causative agent of dysentery, manipulates molecular activity to assure its survival against its host’s natural defenses.
-
 News
NewsResearchers awarded $3 million grant to explore gut health
A $3 million grant has been awarded to investigate the energy generating processes of gut Bacteroides and how they impact our well-being.
-
 News
NewsScientists ID combination of bacterial strains that could treat antibiotic-resistant gut infections
Researchers have isolated 18 bacterial strains from stool from healthy people that could potentially be an effective treatment for antibiotic-resistant bacterial infections in patients with chronic inflammatory intestinal conditions.
-
 News
NewsScientists evolve microbial cultures that can sense pH changes
Scientists have successfully evolved microbial cultures that possess the ability to sense pH changes, enabling rapid responses to environmental fluctuations.
-
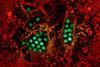 News
NewsImmune response to dengue can predict risk of severe reinfections
Researchers have found that natural killer T (NKT) cells influence whether the immune response generates protective antibodies that neutralise dengue virus or harmful ones that could exacerbate the disease in future infections.
-
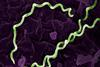 News
NewsResearchers home in on vaccine target in an ancient scourge
Researchers and doctors have collected one of the most extensive genomic surveys of the syphilis bacterium to date and correlated the genetic data with clinical information about the patients who provided the samples.
-
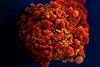 News
NewsTwo-dose schedule could make HIV vaccines more effective
Researchers have found that the first dose primes the immune system, helping it to generate a strong response to the second dose, a week later.
-
 News
NewsGenetic tracing at the Huanan Seafood market supports COVID animal origins
A study provides a list of the wildlife species present at the market from which SARS-CoV-2 most likely arose in late 2019, based on a new analysis of metatranscriptomic data released by the Chinese Center for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC).
-
 News
NewsBreastfeeding is crucial to shaping infant’s microbes, lowering risk of asthma
A study shows that breastfeeding beyond three months supports the gradual maturation of the microbiome in the infant’s digestive system and nasal cavity, the upper part of the respiratory tract.
-
 News
NewsCall for urgent, high-level action to address global scourge of antimicrobial resistance
The World Health Organization (WHO) and partners will call on world leaders to address critical global health challenges throughout the high-level week of the 79th session of the United Nations General Assembly (UNGA79).
-
 News
NewsCells ‘repress’ genomic remnants of ancient viruses
Researchers have identified key cellular control sites that regulate gene expression and prevent the activation of ‘cryptic’ genomic regions, including ancient viral sequences.
-
 News
NewsResearchers push ambitious 1–10–100 unifying goals on antimicrobial resistance ahead of crucial UN meeting
Researchers have shared their goals of using a One Health-approach to save 10 million lives and aim for 100 per cent sustainable access to effective antimicrobials in a new policy paper ahead of a UN high-level meeting in New York later this month.
