Among fungi, including mushrooms and molds, there exists a wide range of yeast species that do not produce mycelium but instead grow as single cells through the processes of budding and division.

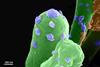
Because yeasts multiply unicellularly, they are well suited to a liquid environment containing nutrients, and a wide variety is obtained from sap, nectar, sludge, and other sources.The gut of insects is also a treasure trove of yeast.
Since the 1970s, yeasts have been detected in the gut of insects belonging to the Chrysopidae family. However, it remains unclear whether yeast is universally present in the entire lacewing family composed of three subfamilies.
Green lacewings
In this study, researchers from the University of Tsukuba collected adult green lacewing insects from the Sugadaira-kogen region of Nagano Prefecture, the University of Tsukuba campus in Ibaraki Prefecture, and the Institute for Nature Study, Tokyo, Japan. They then isolated and cultured yeasts from the insect’s guts to identify and describe their taxonomic affiliations.
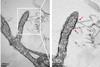
A total of 58 green lacewing insects were identified, which belonged to two subfamilies, six genera, and nine species, and yeast could be isolated from all of them. DNA sequence information revealed that all insects belonged to the genus Metschnikowia and can be divided into three lineages (clades I, II, and III).
Of these, clade I contained one undescribed species. Clade II was a completely new lineage and was divided into two species based on morphology and physiology. Clade II was obtained from two subfamilies of the Chrysopidae family, indicating that yeasts are present in a wider range of green lacewing insects than that known previously.
Based on these results, the isolated yeasts were assigned to three new species of the Metschnikowia genus. Owing to their similarity in shape to a musical instrument Biwa (a Japanese lute), they were named after the famous three Biwa, which appears in Noh plays and the Tale of the Heike. The study was published in Antonie van Leeuwenhoek.





No comments yet