Women’s health is often talked about in terms of major, life-altering events like pregnancy and menopause. A new study from Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory (CSHL) underscores the importance of considering everyday occurrences’ impact on women’s well-being.
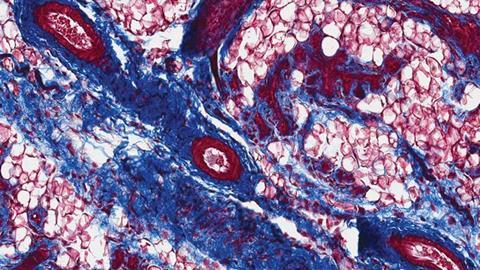
CSHL researchers have made a surprising discovery involving urinary tract infections (UTIs). The scientists found that UTIs in mice can provoke a bodily response that results in structural changes in breast tissue. Remarkably, these changes are reversible once the infections are resolved.
The study was led by CSHL Associate Professor Camila dos Santos, graduate students Samantha Henry and Steven Lewis, and former postdoc Samantha Cyrill. Their findings show how disturbances far across the body can influence breast health.
Abnormal breast cell growth
More than half of all women will experience at least one UTI in their lifetime. So, the potential ramifications here are substantial. “Recurrent and hard-to-treat UTIs could provide opportunities for abnormal breast cell growth,” dos Santos says.
Cyrill notes that the breast changes that the team observed in mice with UTIs “were not directly caused by the infection itself. Rather, they were caused by the body’s responses.” The responses were mainly driven by a molecule called TIMP1. “This molecule mediated increased collagen deposits and milk duct enlargement in breast tissue,” Henry explains. Such changes are also observed during pregnancy.
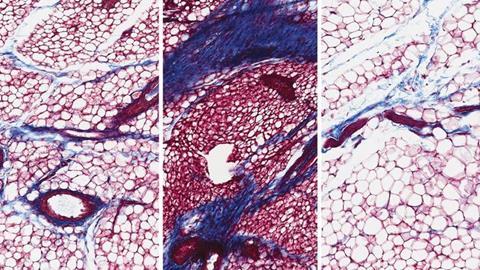
Hormonal changes during pregnancy and menopause are known factors that can influence breast cancer risk. This new research suggests doctors and scientists need to think even more broadly about breast health. “It opened up a new research program in our lab,” dos Santos says. They’re now looking at how other changes women go through in their lifetimes might unexpectedly influence breast tissue.
“More research is needed to determine if the tissue changes we observed contribute to tumor growth and metastasis,” Lewis notes. It’s also not yet clear if UTIs and other infections could be associated with breast cancer risk in humans. Clarifying these relationships would help doctors provide more precise recommendations related to breast cancer risk, screening, and prevention. Moreover, it would empower women to become stronger advocates for their own health.





No comments yet