All Phage Therapy articles – Page 3
-
 News
NewsScientists uncover how certain cholera strains are so successful at evading phage attacks
A new study shows that a virulent lineage of cholera acquired multiple distinct bacterial immune systems that have protected it from diverse types of phages. This defense may have contributed to the massive scale of the Latin American epidemic.
-
 News
NewsPhage expert Graham Hatfull elected as a Fellow of the Royal Society
Graham Hatfull, Eberly Family Professor of Biotechnology and HHMI Professor in the University of Pittsburgh Kenneth P. Dietrich School of Arts and Sciences, has been named a Fellow of the Royal Society.
-
 News
NewsA turning point in medicine: phage therapy moves from promise to practice
From June 10–11, 2025, the international scientific and medical community will gather in Berlin for Targeting Phage Therapy 2025, the leading global event focused on translating phage research into clinical reality.
-
 News
NewsResearchers find CRISPR is capable of even more than we thought
Researchers studying key immune components of some CRISPR systems have announced the newest CARF effector they’ve discovered, which they coined Cat1 - it can deplete a metabolite essential for cellular function.
-
 News
NewsScientist awarded $500,000 Gruber Genetics Prize for pioneering discoveries in bacterial immune systems
The 2025 Gruber Genetics Prize is being awarded to geneticist and molecular biologist Rotem Sorek, Ph.D., of the Weizmann Institute of Science, for his discoveries in the immune system of bacteria.
-
 News
NewsScientists reveal key bacterial immune mechanism
Researchers have uncovered a pivotal mechanism by which bacteria defend themselves against viral infection. Cyclic dinucleotides (CDNs), synthesized during activation of the cyclic oligonucleotide-based anti-phage signaling system (CBASS) immune mechanism, trigger the filamentous assembly of phospholipase effectors, which execute the downstream immune response.
-
 News
NewsUltimate self-sacrifice: Bacteria activate unusual defense to evade viral attack
Scientists discover that the restriction modification system in some bacteria can kill the cell as a last resort if viruses try to thwart it. They trigger their own death using components of the very same systems that the phages were trying to inhibit.
-
 News
NewsBacteria use ancient war trick to outsmart viruses – and it could help us fight superbugs
Scientists have discovered a new type of immune defense in E. coli bacteria that turns viral infection machinery against the virus itself. They’ve named it Kongming after the Chinese military strategist who famously used enemy weapons to defeat his foes.
-
 News
NewsBacteria’s mysterious viruses can fan flames of antibiotic damage, according to new model
Researchers built a model that allows them to diminish phage communities from a mouse gut microbiome — and then bring them back — without affecting the bacteria. A test run found evidence that phages may increase gut bacteria’s sensitivity to antibiotics.
-
 News
NewsOpen benchmarking of CycloneSeq™ for complete bacterial genomes
Benchmark data and analysis of new CycloneSEQ using novel nanopore sequencing technology demonstrates the ability to sequence complete bacterial genomes.
-
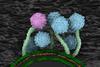 News
NewsThe very first structural images of a tuberculosis-fighting virus
Scientists have used advanced imaging techniques to provide a detailed look at how a tiny virus, known as a phage, invades Mycobacteria. The research could pave the way toward phage-based treatments for antibiotic-resistant mycobacteria.
-
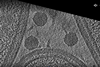 News
NewsResearchers release phage images with unprecedented detail
Researchers have produced the most detailed image to date of a bacteriophage, that has allowed them to see for the first time the structural makeup of the part of the phage that directly attaches to its target Mycobacterium cell.
-
 News
NewsPhage therapy at a crossroads: global experts gather for ground-breaking 2025 Congress
Global multidisciplinary experts and innovators convene for the 8th World Congress on Targeting Phage Therapy 2025 on June 10-11. This leading event is dedicated to the advancement of bacteriophage science and applications in multiple bioscience areas.
-
 News
NewsThe first case of phage therapy for biliary tract infection caused by superbugs
A new study reports the first clinical application case of personalized phage therapy for biliary tract infection.
-
 News
NewsVirus infects cells with a protective cloaking mechanism
The discovery of a jumbo phage’s stealth compartment could be leveraged to engineer new therapies to treat antibacterial-resistant infections.
-
 News
NewsDiscovery of bacteria’s defence against viruses becomes piece of the puzzle against resistance
A new study shows that the emergence of resistance can be understood in the mechanism of how bacteria build up defences against being infected by viruses.
-
 News
NewsNew study sheds light on how bacteria ‘vaccinate’ themselves with genetic material from dormant viruses
Scientists have gained understanding on how bacteria defend themselves from phages, through gaining “memories” from predecessor dormant phages. The study will inform new phage therapies for bacterial infections that confer resistance to antibiotics.
-
 News
NewsA review of Clostridioides difficile infection and treatments
<i>Clostridioides difficile</i> is a serious nosocomial infection that could cause from mild diarrhea to fatal colitis. Here presents a general overview that describes the current and emerging treatment practices for the prevention of <i>Clostridioides difficile</i> infection and its recourrences.
-
 Careers
CareersMy autistic academic maze - and my advice to neurodiverse PhD students
In Neurodiversity Celebration Week, PhD student Joshua Yates reveals the challenges of pursuing a career in microbiology with autism and dyslexia - and his advice to others.
-
 News
NewsMontana State scientist receives $2.8 million grant to advance Lyme disease research
Funding from the National Institutes of Health will allow a Montana State University research team to deepen explorations into a disease that is posing an increasing threat in the U.S. Lyme disease is a bacterial infection transmitted by ticks.
