All Proteomics articles
-
 News
NewsResearchers map correlations between gene variants and proteomes
Scientists have discovered a way to predict the effects of numerous mutations in yeast - a valuable tool for better understanding molecular mechanisms. Key to this discovery was a detailed analysis of the proteome – the collection of all proteins inside a cell.
-
 News
NewsScientists unlock frogs’ antibacterial secrets to combat superbugs
Researchers exploited natural peptides derived from frogs and improved their structural designs as antibiotic candidates, which are effective against complex mock bacterial communities of drug-resistant pathogens in preclinical tests, sparing beneficial microbiota and human cells.
-
 News
NewsMovie reveals DNA unzipping mechanism with implications for viral and cancer treatments
A detailed unwinding mechanism of the double-stranded DNA has been uncovered for the first time using cutting-edge technology, revealing how cells begin the crucial process of copying their genetic material.
-
 News
NewsNewly identified bacterial protein helps design cancer drug delivery system
Researchers have identified a previously unknown bacterial protein, the unique structure of which acts as an actin homolog that can be used to design protein nanoparticles for the targeted delivery of anticancer drugs to tumors.
-
 News
NewsNew immune mechanism revealed in the cellular trash
The enzyme, proteasomes known for its protein degradation and recycling system, has found to serve another useful purpose that provides promising alternatives for strengthening immune defenses against deadly diseases.
-
 News
NewsProtein shuttling mechanism helps bacteria pump out antibiotics
By a joint-university effort, the mechanism of a bacterial efflux pump complex to remove molecules, including antibiotics, has been determined and the extent of bacterial toxin resistance by the complex has also been evaluated with a cutting-edge device.
-
 News
NewsWe know what you ate: Detailed protein maps assess intestinal health
A new method has been designed to map the near-exact molecular details of the human and bacterial protein regulations within the host-gut microbiome interactions. These proteins could be used for medical and dietary intervention to maintain intestinal health.
-
 News
NewsPersistent proteins may influence metabolomics results
Scientists have identified more than 1,000 previously undetected proteins in common metabolite samples, which persist despite extraction methods designed to weed them out.
-
 News
NewsScientists have a new tool in the race to improve the diagnosis and prognosis of sepsis
Scientists identify unique molecular signatures of sepsis and use AI to improve diagnosis and identify patients most likely to develop severe symptoms and suffer poor outcomes.
-
 News
NewsProtein fragments ID two new “extremophile” microbes—and may help find alien life
Scientists used proteotyping to identify two potentially new types of extremophile bacteria. These results suggest proteotyping could be a more complete solution for identifying extremophile microorganisms from small biological samples.
-
 News
NewsResearchers develop a new toolkit in fruit flies to study Zika virus
To study how Zika virus proteins hijack and disrupt host developmental pathways during infection and disease progression, scientists have generated a toolkit of transgenic flies expressing all ten Zika virus proteins.
-
 News
NewsNew approach to tackling bacterial infections identified
Researchers unveil how the self-killing activity of bacteria can be harnessed in the fight against antibiotic resistance.
-
 News
NewsBlood analysis in patients finds characteristics of Long Covid
Analysis of blood samples from patients with Long Covid – a debilitating condition with unknown causes – has revealed serum protein changes as the likely culprit.
-
 News
NewsUnzipping mRNA rallies plant cells to fight infection
Scientists studying a plant called Arabidopsis thaliana have discovered short snippets of folded RNA that are unzipped in the presence of a pathogen to allow plant cells to make defense proteins to fight infection.
-
 News
NewsScientists uncover COVID’s weakness - the need for human cells
New UC Riverside research has revealed COVID’s Achilles heel — its dependence on key human proteins for its replication — which can be used to prevent the virus from making people sick.
-
 News
NewsEnergy depleting mechanism immunizes bacteria against phages
Researchers have described a new family of proteins that deplete cells of their energy, thereby protecting the cells from invaders. The previously unknown immune mechanism is used by many living creatures, from bacteria to bees.
-
 News
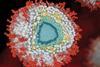
NewsResearchers reveal how the herpes virus HCMV deceives its host cells
Researchers have created a detailed map of the spatial interactions between viral and host cell proteins within HCMV particles, revealing that certain host cell proteins are recruited by viral proteins and play a role in viral replication.
-
 News
NewsNanopore technology achieves breakthrough in protein variant detection
Scientists have developed a breakthrough method to detect structural variations on proteins based on nanopore technologies.
-
 News
NewsResearchers craft ‘origami DNA’ to control virus assembly
Researchers have used DNA ‘origami’ templates to control the way viruses are assembled. The global team behind the research, published in Nature Nanotechnology, developed a way to direct the assembly of virus capsids – the protein shell of viruses - at physiological conditions in a precise and programmable manner. ...
-
 News
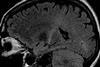
NewsRemnants of ancient virus may fuel ALS in people
Researchers have identified a surprising new player in ALS or motor neurone disease - an ancient, virus-like protein best known for its essential role in enabling placental development.
