All Streptomyces articles
-
 News
NewsScientists create microneedle system to deliver living biofertiliser directly into plants, boosting growth with less waste
A dissolving patch delivers beneficial microbes into leaves and stems, speeding growth in vegetables while using over 15 per cent less biofertiliser than soil application.
-
 News
NewsSpiritual healing sites could be linked to antibiotic-producing microorganisms
A study by AMI member Dr Gerry Quinn highlights the potential of spiritual healing sites as fertile ground for novel antibiotics, particularly from Streptomyces bacteria, known for producing the majority of current antibiotics.
-
 News
NewsEngineered soil microbiomes may secure future tomato yields
New findings suggest that manipulating rhizosphere microbiomes could be a sustainable strategy to enhance crop performance in fluctuating environments, supporting the development of resilient agricultural systems.
-
 Long Reads
Long ReadsCould spiritual healing sites be fertile ground for new antibiotics?
Common motifs between Streptomyces and sites of spiritual healing may help with the discovery of new sites for bioprospecting. Although there may be a temptation to dismiss the spiritual nature of the healing sites, it is important that researchers begin to understand these in the appropriate cultural and spiritual context.
-
 News
NewsNew automated method increases the efficiency of bioactive natural product discovery
In light of the technological advancement in machine learning and bioinformatics tools, researchers developed a fully-automated and integrated platform that enables them to easily identify bioactive natural products in Streptomyces.
-
 News
NewsBacterial ‘jumping genes’ can target and control chromosome ends
Researchers have discovered a new mechanism that transposons, or “jumping genes” use to survive and propagate in bacteria with linear DNA, with applications in biotechnology and drug development.
-
 News
NewsMeet the Global Ambassadors: Our Q&A with Petr Heděnec
The Microbiologist chats with our new Global Ambassador for Malaysia, Petr Heděnec, who is an Assistant Professor/University Lecturer at the Institute of Tropical Biodiversity and Sustainable Development at Universiti Malaysia Terengganu.
-
 News
NewsBacteria produce molecules that help viruses infect competing bacteria
In a new study, researchers have discovered a new way that bacteria can kill their competitors in complex microbial communities, revealing novel approaches to leverage viruses to kill harmful bacteria.
-
 News
NewsBoosting plant health: the role of gene exchange with bacteria
Scientists have discovered 75 genes that were transferred between small, fast-growing plants (Arabidopsis thaliana) and its bacterial companions, influencing key processes like carbohydrate metabolism and hormone synthesis.
-
 News
NewsFunctional predictability of universal gene circuits in diverse microbial hosts
By developing a quantitative framework to explore the universality and reliability of biological parts in non-model organisms, the team characterized universal genetic parts in four microbial hosts that can be used to build biological circuits in living cells.
-
 News
NewsNew class of antimicrobials discovered in soil bacteria
Scientists have mined Streptomyces for antibiotics for nearly a century, but the newly identified umbrella toxin escaped notice.
-
 Opinion
OpinionAntimicrobial chemotherapy - which direction now?
The answer to antimicrobial resistance might not be the continual discovery of new antibiotics - but judicious use of the antibiotics and insights into antibiotic producing organisms we have already discovered.
-
 News
NewsScientists uncover how gadolinium and sulfamethoxazole impact antibiotic and heavy metal resistance genes in activated sludge systems
Researchers investigated the co-occurrence of Gd and SMX in wastewater pollution by applying metagenomics to analyze the mechanisms of changes in ARGs, MRGs, MGEs, and genera in an activated sludge system.
-
 News
NewsSoil bacteria prevail despite drought conditions
Recent research has uncovered the resilience of certain soil microorganisms in the face of increasing drought conditions. While many bacteria become inactive during dry spells, specific groups persist and even thrive.
-
 News
NewsStreptomycetes reveal their arsenal of signalling compounds
Streptomyces bacteria produce a group of signalling molecules that trigger a variety of processes, a new study shows.
-
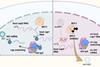 News
NewsNew bacterial product found to inhibit flu virus replication
Researchers have identified a derivative of a bacterial natural product that inhibits the body’s own methyltransferase MTr1, thereby limiting the replication of influenza viruses.
