All USA & Canada articles – Page 68
-
 News
NewsFirst mouse strain that is susceptible to severe COVID-19 without genetic modification is IDed
Mice with a genetically pure background are susceptible to severe SARS-CoV-2 infection, providing an essential tool to develop vaccines and therapeutics for future coronavirus variants and potential pandemics
-
 News
NewsResearchers find rotavirus vaccine is safe for use in NICU babies
Transmission of rotavirus vaccine strains in a neonatal intensive care unit (NICU) is rare and without clinical consequences, suggesting that giving the rotavirus vaccine to eligible infants during their hospitalization provides immune benefits that outweigh any risks.
-
 News
NewsResearch yields new model for replication of BKPyV virus, a major cause of kidney transplant failure
There are no effective antivirals against BK polyomavirus in transplanted kidneys. A better understanding of its replication will offer new ways to protect those kidneys.
-
 News
NewsMutation could facilitate H5N1 bird flu virus infection and potential transmission in humans
A recent study reveals that a single mutation in the H5N1 bird flu virus that has recently infected dairy cows in the U.S. could enhance the virus’ ability to attach to human cells, potentially increasing the risk of passing from person to person.
-
 News
NewsEnterococcus helps E. coli ‘armor up’ in dog, poultry co-infections
A new study finds that two subtypes of pathogenic E. coli produce 5 to 16 times more protective capsular “slime” when Enterococcus faecalis is present.
-
 News
NewsBacterial ‘biopesticide’ against malaria mosquitoes successful in early field tests
An experimental bacteria-derived biopesticide is highly effective in killing malaria-carrying mosquitoes, including those that have developed resistance to chemical pesticides, according to initial field tests.
-
 News
NewsDo soil microbes affect flowers’ ability to attract bees?
New research reveals that certain soil microbes can help plants grow bigger flowers, therefore attracting more bees.
-
 News
NewsHow a middle schooler found a new compound in goose feces
Middle schoolers through a partnership with a local univeristy, collected and analyzed environmental samples to find new antibiotic candidates. One unique sample, goose feces collected at a local park, had a bacterium that showed antibiotic activity.
-
 News
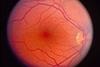
NewsCovid-19 virus can damage the retina - even without severe respiratory disease
An experimental study in mice shows that SARS-CoV-2 infection can damage the retinas, with long-term implications for vision.
-
 News
NewsFungal structures could be deployed in aerospace industry
Manufacturing a material that mimics mushrooms and other fungal structures could provide opportunities in any number of areas, ranging from aerospace engineering to clothing production.
-
 News
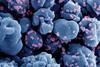
NewsStudy untangles how COVID-19 wreaks widespread damage in the body
A new study sheds light on the pathways that drive organ damage and death in severe COVID-19 and helps explain why survivors of the disease can experience long-term complications.
-
 News
NewsPeat-bog fungi produce substances that kill tuberculosis-causing bacteria
An analysis of fungi collected from peat bogs has identified several species that produce substances toxic to the bacterium that causes the human disease tuberculosis.
-
 News
NewsPregnancy enhances natural immunity to block severe flu
Scientists discover a natural flu defense mechanism that activates in the nasal cavity during pregnancy.
-
 News
NewsHow did human brains get so big? The answer could be in our gut
Microbes supporting the production of more metabolic energy could be key to the evolution of large brains, according to a study that shows gut microbes from different animal species shape variations in their biology.
-
 News
NewsA new approach to predicting malaria drug resistance
Researchers analyzed the genomes of hundreds of malaria parasites to determine which genetic variants are most likely to confer drug resistance.
-
 News
NewsNanorobot hand made of DNA grabs viruses for diagnostics and blocks cell entry
A tiny, four-fingered ‘hand’ folded from a single piece of DNA can pick up the virus that causes COVID-19 for highly sensitive rapid detection and can even block viral particles from entering cells to infect them.
-
 News
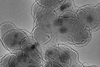
NewsNewly designed nanomaterial shows promise as antimicrobial agent
Newly developed nanocrystals show potential as antimicrobial agents that are stable, effective and easy to produce.
-
 News
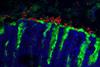
NewsMouse gut fungus reveals secrets of symbiosis and allergy
A fungus discovered in the mouse stomach may hold a key to fungal evolution within the gastrointestinal tract, according to new research. The finding suggests that preclinical studies until now have overlooked a major influencer of mouse physiology.
-
 News
NewsCervical cancer deaths in young women plummet after introduction of HPV vaccine
Cervical cancer deaths have plunged dramatically among women under age 25, and researchers believe this is likely due to HPV vaccination.
-
 News
NewsZoonotic transmission of Covid has led to infections in more than 30 mammalian species
Zoonotic transmission of severe acute respiratory coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) has been found to result in infections in more than 30 mammalian species, according to a study published in Zoonoses journal.
