All The Microbiologist articles in Web Issue – Page 228
-
 Features
FeaturesGenomic microbiology as applied to animal forensics
From the origins of anthrax to advancements in the field, dive into the microbial forensics of livestock, wildlife and human cases.
-
 Features
FeaturesForensic microbiology from an entomological perspective
Bridging multiple disciplines within the forensic sciences helps us better understand how human remains decompose.
-
 Features
FeaturesForensics through biofilm microbiology
In the fashion of the legendary phoenix, microbial life springs from decaying matter such as the carcass of an animal.
-
 News
NewsClimate change portends wider malaria risk as mosquitoes expand range in Africa
Scientists have found that the mosquitoes responsible for transmitting malaria in Africa are spreading deeper into southern Africa and to higher elevations than previously recorded.
-
 News
NewsVillainous pairing makes superbugs more deadly and drug-resistant
Some of the world’s most deadly and drug-resistant pathogens work collaboratively to become more powerful and infectious, a new study has found.
-
 News
NewsMicrobiota from mum regulates lung immunity in newborns
Researchers have discovered that a type of white blood cells, the γδ T cells, influences the transfer of maternal microbiota during birth and nursing, and impacts the lung immune response in newborns.
-
 Careers
CareersPhD candidate? Why and how to develop a career plan…
Tips on how to effectively plan for a career after your PhD.
-
 News
NewsMicrobes that co-operate contribute more carbon emissions
Communities of microbes that work together release more carbon dioxide than competitive communities, contributing more to climate change, a new study reveals.
-
 News
NewsBright orange lichens use their pigments as a ‘sunscreen’ while avoiding toxic effects
Fungi in orange lichens can avoid the toxic effects of bright pigments, allowing them to handle high UV loads.
-
 News
NewsCellular evidence reveals why men are at higher risk from COVID-19
Researchers from Osaka University provide cellular evidence for the observed differences between the response to COVID-19 infection in male and female patients.
-
 News
NewsFlashing bacteria unveil electric signalling's role in antimicrobial resistance
Like the neurons firing in human brains, bacteria use electricity to communicate and respond to environmental cues. Now, researchers have discovered a way to control this electrical signalling in bacteria, to better understand resistance to antibiotics.
-
 News
NewsDecades of conflict in Iraq fuel ‘catastrophic’ rise in antimicrobial resistance
Decades of wars and conflict in Iraq have led to a “catastrophic” rise in antimicrobial resistance in the country, with serious implications for the entire region and the world, international experts have warned.
-
 News
NewsStudy reveals how drug resistant bacteria secrete toxins
Research suggests that reducing virulence in drug resistant infections rather than trying to kill bacteria outright may offer an answer to antimicrobial resistance.
-
 News
NewsQuestion mark over claims that trees talk to each other via underground fungi
A University of Alberta expert challenges the idea that forest trees can “talk” to each other, share resources with their seedlings — and even protect them — through a connective underground web of delicate fungal filaments.
-
 News
NewsExtracts from two wild plants inhibit COVID-19 virus, study finds
Two common wild plants contain extracts that inhibit the ability of the virus that causes COVID-19 to infect living cells, the first major screening of botanical extracts to search for potency against the virus has revealed.
-
 News
NewsResearch team unlocks the secrets to Strep A virulence
Researchers have unlocked one of the secrets as to why some forms of Strep A are associated with severe invasive infection.
-
 News
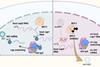
NewsNew bacterial product found to inhibit flu virus replication
Researchers have identified a derivative of a bacterial natural product that inhibits the body’s own methyltransferase MTr1, thereby limiting the replication of influenza viruses.
-
 News
NewsSpotlight on how hepatitis E is able to infect cells
A recently developed cell culture model has finally made it possible for researchers to investigate how hepatitis E is able to infect cells.
-
 News
News PhoQ gene supports the survival of beneficial rhizobacterium in acidic soil
Scientists have identified a gene in a plant-growth promoting rhizobacterium that can be manipulated to allow the bacterium to thrive in acid soils.
-
 News
NewsDose of antibiotic during labour can cut sepsis risk in developing countries
New findings suggest that a single dose of azithromycin given to women planning a vaginal delivery significantly reduces the risk of maternal death or sepsis.
